Spring学习笔记(一)IoC(XML部分)
学习Spring看的是上学堂马士兵老师的Spring2.5视频教程,里面用的Spring版本是2.5.6。前两天看完IoC部分的视频,在这里总结下笔记,留给以后用到Spring时回忆知识点。
Spring Ioc教程里面分为两个部分:Spring IoC模拟和Spring IoC使用
Spring IoC模拟
需求:需要一个增加用户的需求,增加用户的逻辑可能会在MySQL、SqlServer、Oracle中。
设计(具体设计思想不阐述):实体类User(Model)、UserDAO(功能接口)、UserDAOImpl(UserDAO实现类)、Service(提供方法服务)
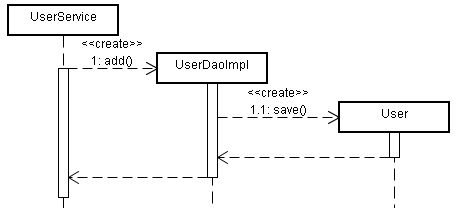
图1 增加用户业务时序图
在图1中。UserService增加用户的服务add()需要实现UserDAO接口的UserDAOImpl的save()方法,即在UserService中哟一个实例化的UserDAOImpl对象,继而,实例化UserService对象的实例化需要依赖于UserDAOImpl对象的注入。
编写Beans.XML文件
Spring的配置文件写在Beans.XML中。
<beans> <bean id="u" class="com.bjsxt.dao.impl.UserDAOImpl" /> <bean id="userService" class="com.bjsxt.service.UserService" > <property name="userDAO" bean="u"/> </bean> </beans>
里面每一个bean代表一个实例化的对象,id为对象的名字,class代表对应的需要实例化的那个对象。property是当前类中的属性。bean="u"即这userDAO对象是id="u"的那个对象。
编写BeanFactory接口和ClassPathXmlApplicationContext类
在Spring中,Bean的读取是通过ClassPathXmlApplicationContext读取的。我们也来模拟一个。
private Map<String , Object> beans = new HashMap<String, Object>();
//IOC Inverse of Control DI Dependency Injection
public ClassPathXmlApplicationContext() throws Exception {
SAXBuilder sb=new SAXBuilder();
//这一部分是beans.xml文件的读取
Document doc=sb.build(this.getClass().getClassLoader().getResourceAsStream("beans.xml")); //构造文档对象
Element root=doc.getRootElement(); //获取根元素HD
List list=root.getChildren("bean");//取名字为disk的所有元素
for(int i=0;i<list.size();i++){
Element element=(Element)list.get(i);
String id=element.getAttributeValue("id");
String clazz=element.getAttributeValue("class");
Object o = Class.forName(clazz).newInstance();
System.out.println(id);
System.out.println(clazz);
beans.put(id, o);
for(Element propertyElement : (List<Element>)element.getChildren("property")) {
String name = propertyElement.getAttributeValue("name"); //userDAO
String bean = propertyElement.getAttributeValue("bean"); //u
Object beanObject = beans.get(bean);//UserDAOImpl instance
String methodName = "set" + name.substring(0, 1).toUpperCase() + name.substring(1);
System.out.println("method name = " + methodName);
Method m = o.getClass().getMethod(methodName, beanObject.getClass().getInterfaces()[0]);
m.invoke(o, beanObject);
}
}
}
上面代码中Map是模拟的Spring的管理池,每一个bean标签都实例化一个对象放入Map池中。IoC(Inversion of Control)控制反转,即原来的类,成员变量是我们进行管理,现在交付给Spring统一管理。
Spring IoC使用
环境搭建:
- 需要spring.jar和commons-logging.jar
- 在项目中增加beans.xml。
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans
http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans-2.5.xsd">
</beans>
bean的获取(得事先在beans.xml中配置相应的bean,参见IoC模拟部分的beans.xml代码)
ApplicationContext ctx = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("beans.xml");
UserService service = (UserService)ctx.getBean("userService");
setter注入和constructor注入
- 在模拟IoC的时候如果一个类中有一个成员变量是对象。那在实例化这个类的时候需要现实里话这个对象成员变量,然后将这个对象注入到这个类中,然后实例化,在模拟IoC部分使,如下面代码,属于setter注入(Setter Injection)
<bean id="userService" class="com.bjsxt.service.UserService"> <!-- <property name="userDAO" ref="u" /> 另一种写法 --> <constructor-arg> <ref bean="u"/> </constructor-arg> </bean>
- 在constructor Injection中,由于累的构造函数可能会有若干个args(参数)。故有两种区分的方式
- 有参数类型区分
- 索引区分
bean的Scope:常用的有singleton(单例)、prototype
- singleton是每一次调用相同的<bean>时都用第一次实例化的<bean>的对象
- prototype则是每一次都new一个新的对象
- prototype的方式跟struts2中的Action一样,struts1中使用的是singleton方式
集合注入
- 在bean中有map、list等集合属性,为这些map、list中的属性注入值。这里参见Spring文档的示例即可,比较简单
自动装配(AutoWire)
- 在bean中不知能需要注入的是哪一个bean。Spring会根据autowire设定的属性确定自动装配容器池中的那个bean
- 注意1,在IoC方式中,autowire的使用很少,在annotation时才会用到。
- 注意2,在autowire="byType"时,bean.xml中有多个相同类型的bean会抛异常
AutoWire之前:
<bean id="u" class="xx">
<property name="UserDaoImpl">
<ref bean="xxxx"></ref>
</property>
</bean>
AutoWire之后:
<bean id="u" class="xx" autowire="byName"> </bean>
这里之列出了一个bean标签。需要额外的bean标签才能完成自动装配。
生命周期
- lazy-init/default-lazy-init:
- 延时启动,在内存不足的时候,或开启有大量的beans时需要经常启动server时才会用到
- init-method,destory-method
- 一般不会用到,常用的是Spring内部的连接池。
- 注意,这两个方法只有在scope=singleton时才有用。scope=prototy时,虽然不会报错,但是不起作用
到这里,Spring IoC(XML)部分的知识点已经说完,这一部分不是很难,总体的逻辑就是,如何配置xml,是的Spring能够管理我们的对象。