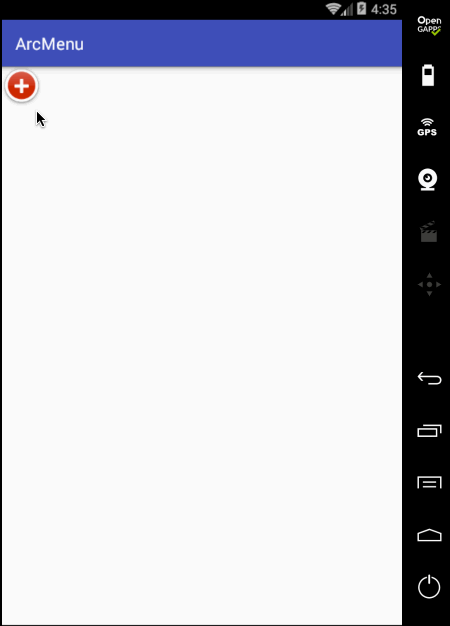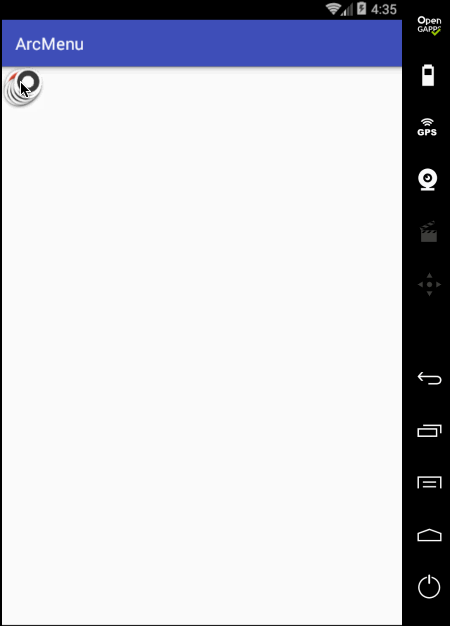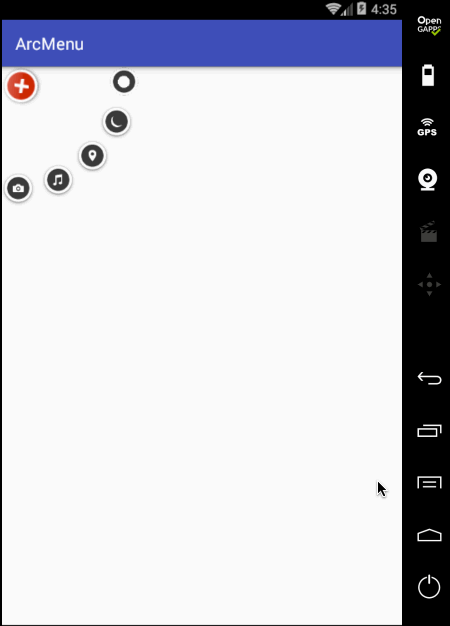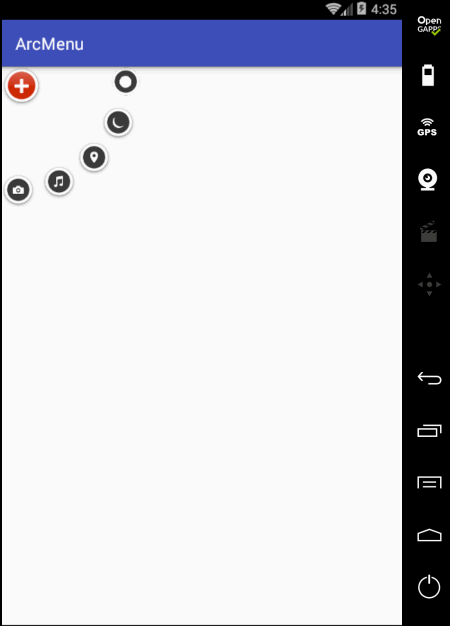
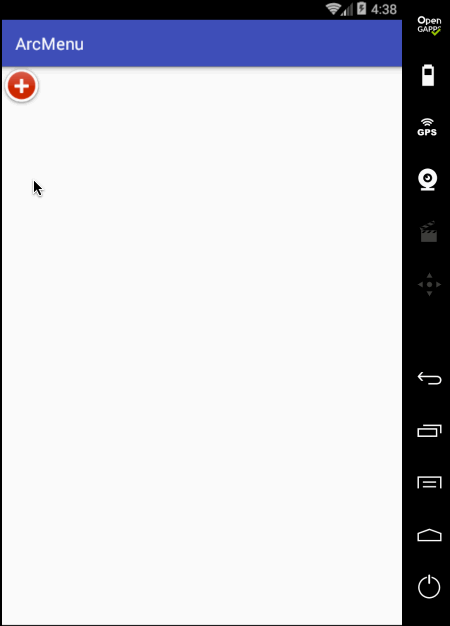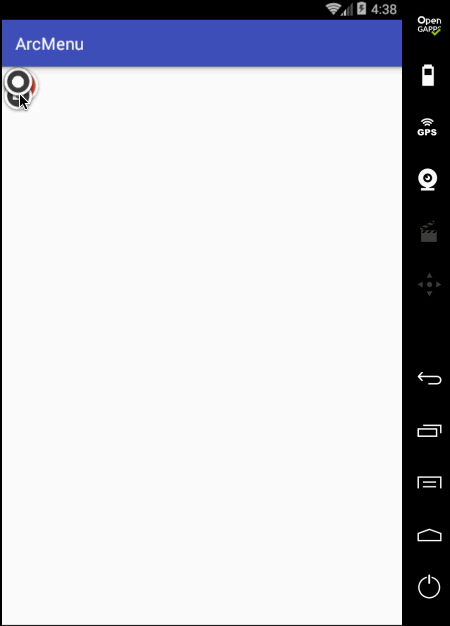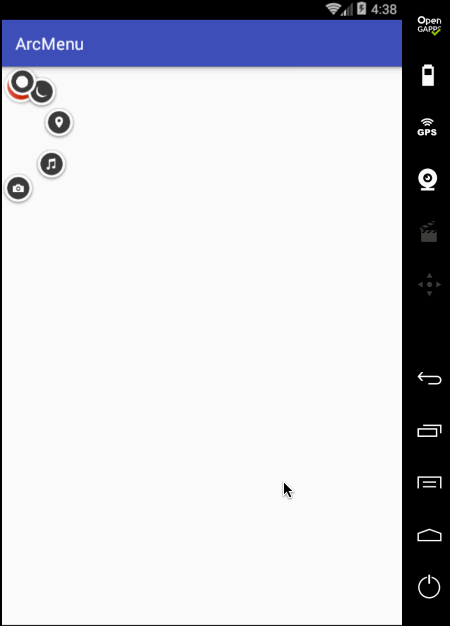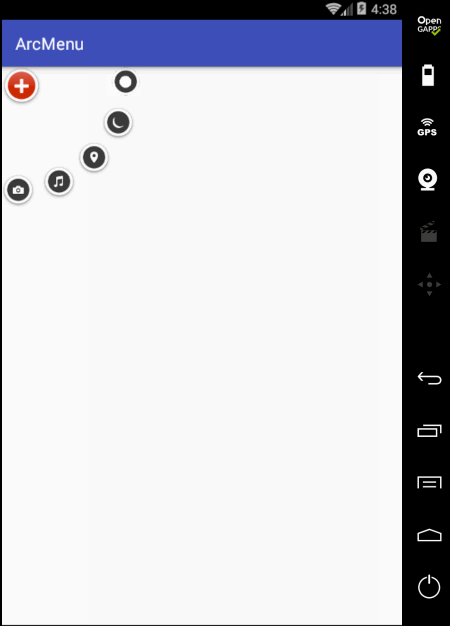
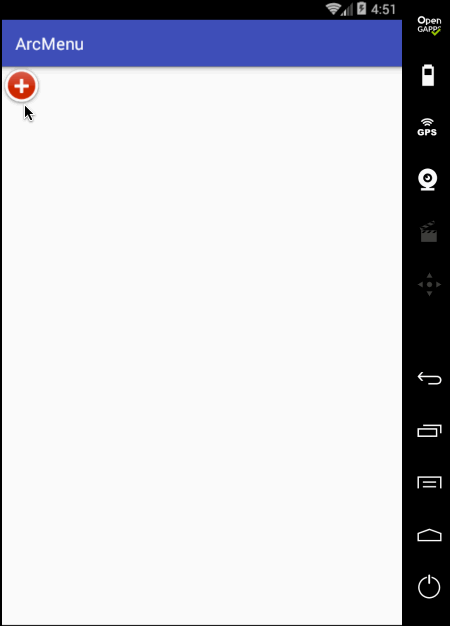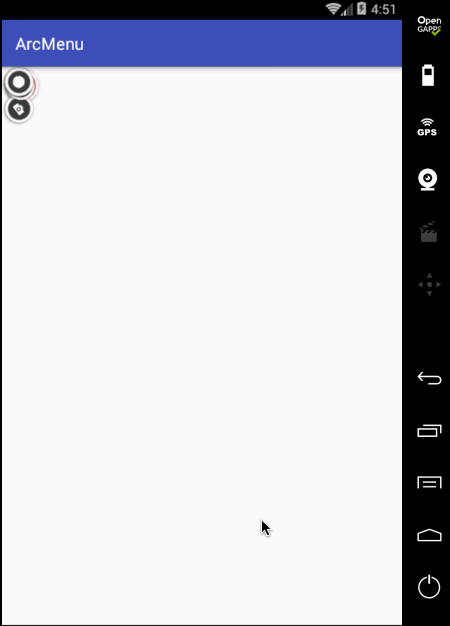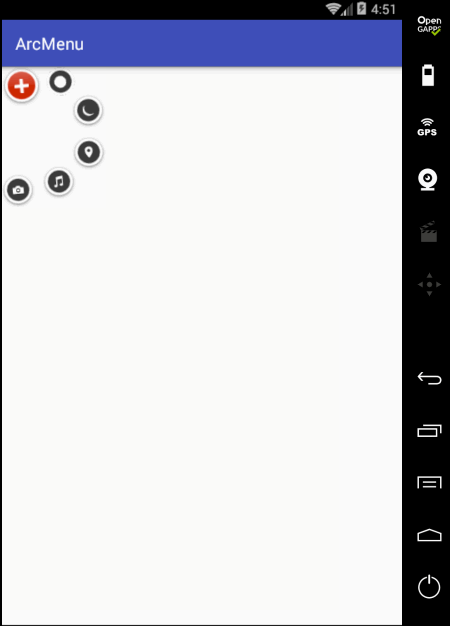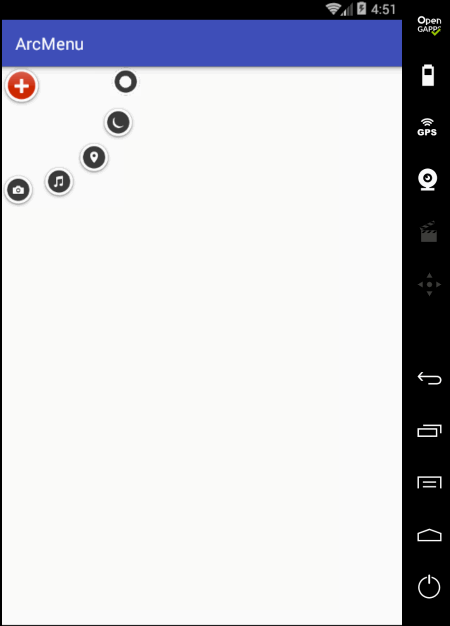
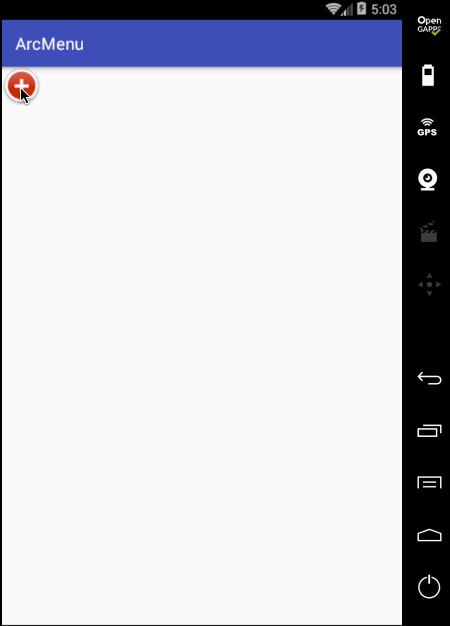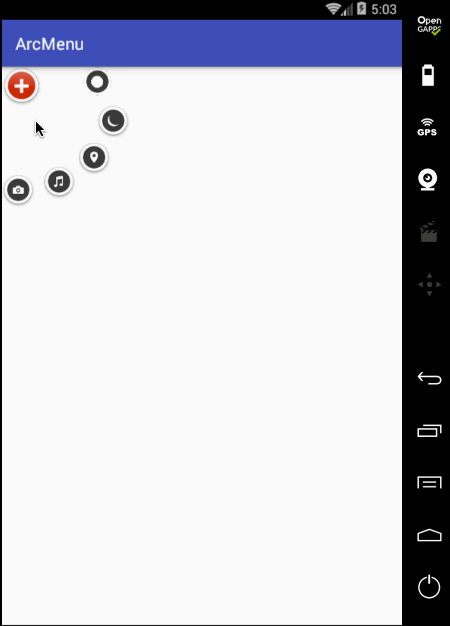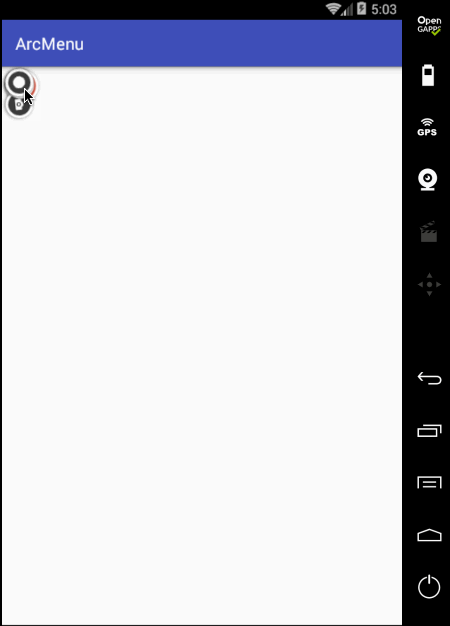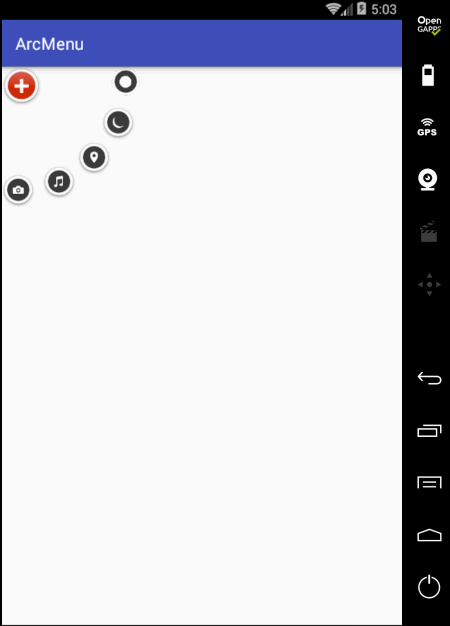
先来看一下最终要实验的效果:
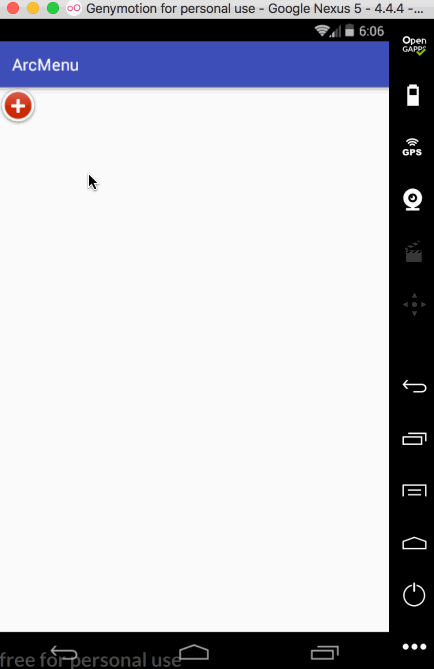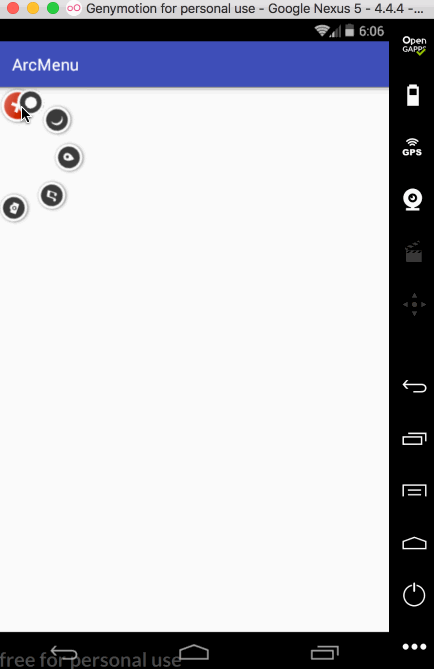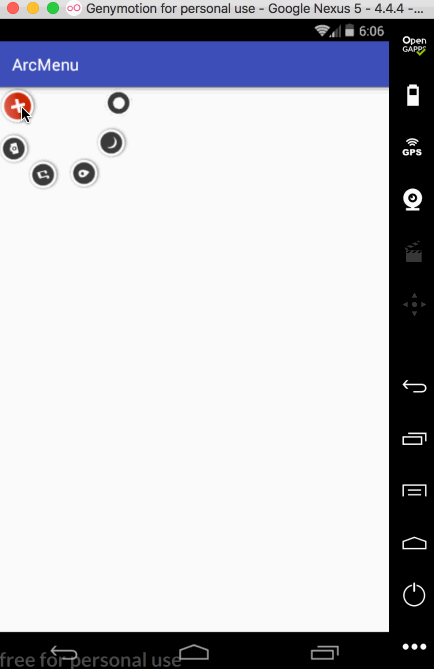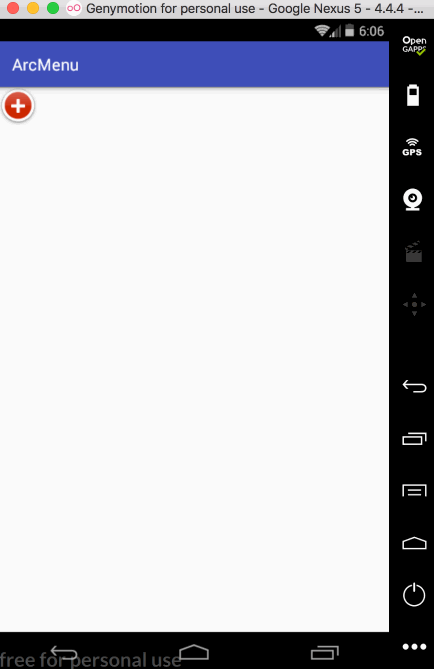
是不是跟国外的一款Path的菜单效果类似,这里的动画采用补间动画去实现,正而操练一下补间动画。
布局和子视图的测量处理:
新建一自定义View继承ViewGroup:
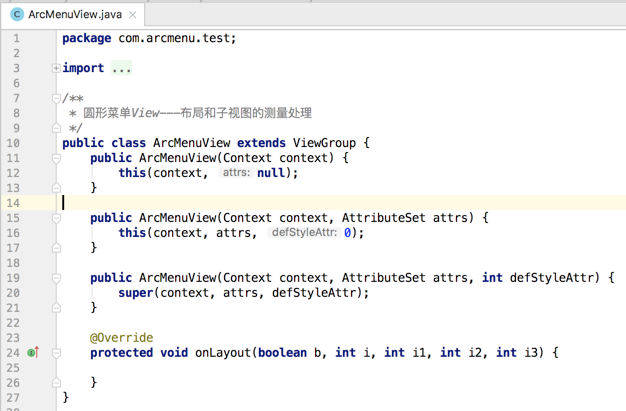
然后在布局中进行声明:
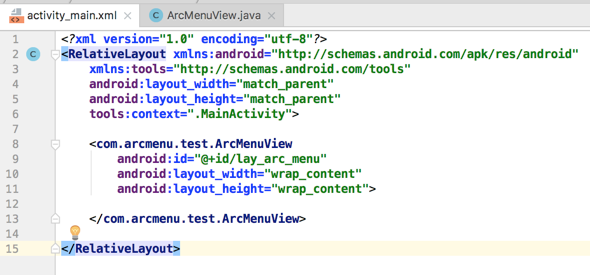
然后在ViewGroup中需要准备子菜单元素,这里直接在布局文件中的ArcMenuView里面进行声明,首先是菜单的“+”号,由两张图片构成:
composer_button.png:
composer_icn_plus.png:

然后再准备展开的5个菜单项,可以由ImageView组成,定义在布局文件中如下:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?> <RelativeLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android" xmlns:tools="http://schemas.android.com/tools" android:layout_width="match_parent" android:layout_height="match_parent" tools:context=".MainActivity"> <com.arcmenu.test.ArcMenuView android:id="@+id/lay_arc_menu" android:layout_width="wrap_content" android:layout_height="wrap_content"> <!-- "+"按钮 --> <RelativeLayout android:id="@+id/lay_plus" android:layout_width="wrap_content" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:gravity="center"> <ImageView android:layout_width="wrap_content" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:layout_centerInParent="true" android:src="@drawable/composer_button" /> <ImageView android:layout_width="wrap_content" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:layout_centerInParent="true" android:src="@drawable/composer_icn_plus" /> </RelativeLayout> <!-- 相机按钮 --> <ImageView android:layout_width="wrap_content" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:src="@drawable/composer_camera" /> <!-- 音乐按钮 --> <ImageView android:layout_width="wrap_content" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:src="@drawable/composer_music" /> <!-- 定位按钮 --> <ImageView android:layout_width="wrap_content" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:src="@drawable/composer_place" /> <!-- 月亮按鈕 --> <ImageView android:layout_width="wrap_content" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:src="@drawable/composer_sleep" /> <!-- 太阳按钮 --> <ImageView android:layout_width="wrap_content" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:src="@drawable/composer_sun" /> </com.arcmenu.test.ArcMenuView> </RelativeLayout>
其资源图如下:





此时运行肯定看不到任何效果:

因为咱们还得处理子视图的测试及位置摆放处理,毕境不像系统写好的四大布局,所以接下来对子视图进行测量:
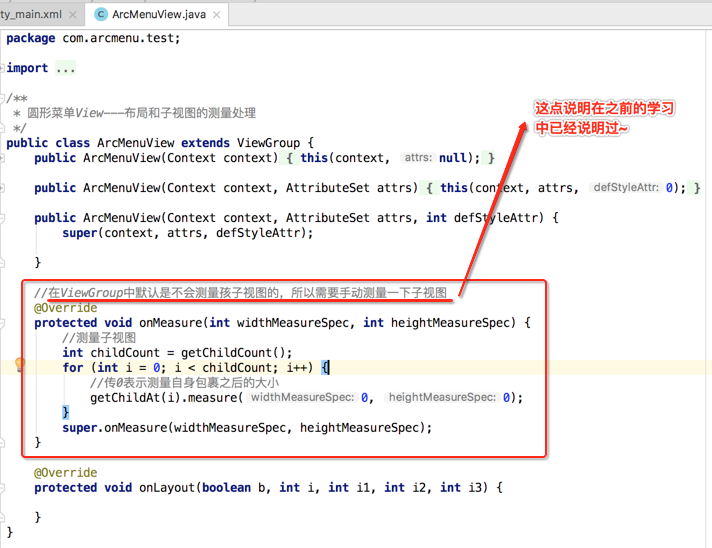
子视图布局处理的细节分析:
当测量好之后,要想让子视图显示成咱们想要的样子,接下来就得对子视图如何布局进行处理了,在实现之前首先得对其进行分析一下:
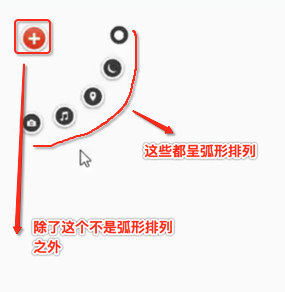
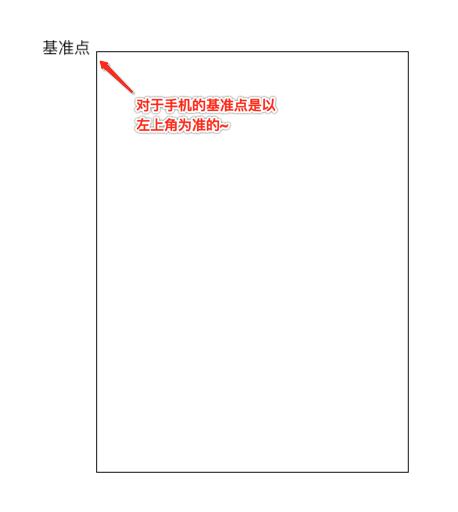
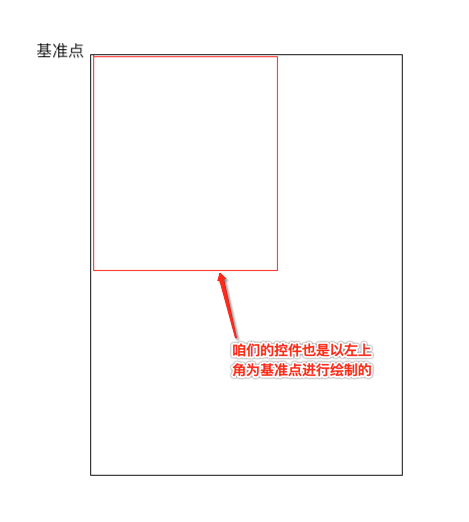
对于第一个“+”号应该就是在默认左上角的位置,而对于其它的元素则应该以弧形的样式进行摆放,那这个弧形具体的摆放规则是怎么样的呢?
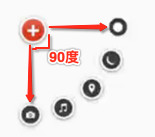
也就是这五个元素均等分了90度,现在的问题就是怎么来算这些点的摆放位置的左上右下,还是以草图进行分析:
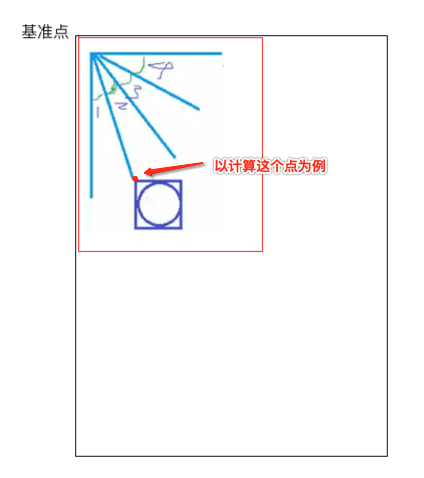
∠1 = ∠2 = ∠3 = ∠4 = π / 2 / 4。
然后咱们可以定一个半径的长度,也就是目前已知的条件有:
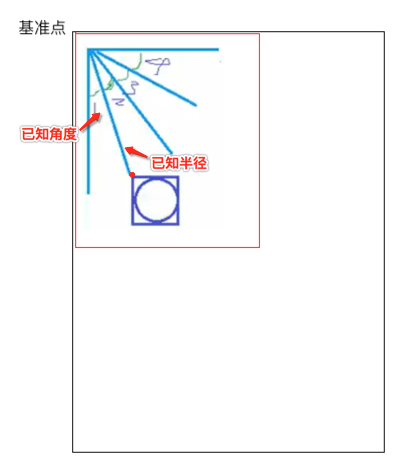
要求x、y:
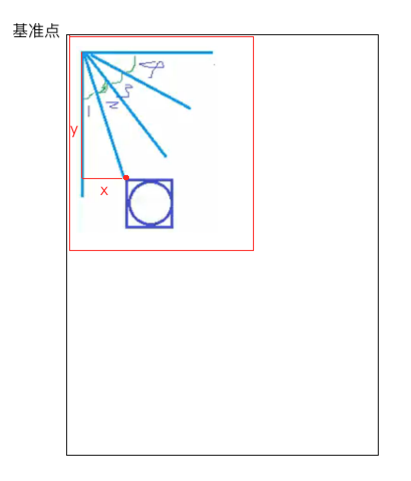
根据三角函数就可轻松求解,如下:
x = radius * Math.sin(π / 2 / 4);
y = radius * Math.cos(π / 2 / 4);
而求得了left和top,那right和bottom就比较简单了,直接加相应控件的宽高既可求得。
那如果再换一个元素其求法又有啥变化呢?

只是角度由原来的1变为了1+2,也就是2倍的角度1,因为每个夹角都是相等的,于是随着元素的变化不断去更改夹角的度数既可,其计算公式是一样的,好,有了实现的思路之后下面来用代码来实现一下子视图弧形的排列。
子视图弧形排列实现:
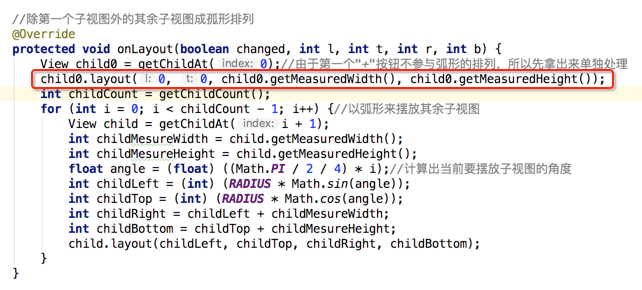
由于第一个"+"号元素不参与弧形的排列,所以先将它拿出来稍后再单独对它进行处理:

/** * 圆形菜单View---布局和子视图的测量处理 */ public class ArcMenuView extends ViewGroup { /* 定义要摆放圆的半径,其子视图的摆放位置需要依据它来计算 */ private static final float RADIUS = 130f; public ArcMenuView(Context context) { this(context, null); } public ArcMenuView(Context context, AttributeSet attrs) { this(context, attrs, 0); } public ArcMenuView(Context context, AttributeSet attrs, int defStyleAttr) { super(context, attrs, defStyleAttr); } //在ViewGroup中默认是不会测量孩子视图的,所以需要手动测量一下子视图 @Override protected void onMeasure(int widthMeasureSpec, int heightMeasureSpec) { //测量子视图 int childCount = getChildCount(); for (int i = 0; i < childCount; i++) { //传0表示测量自身包裹之后的大小 getChildAt(i).measure(0, 0); } super.onMeasure(widthMeasureSpec, heightMeasureSpec); } //除第一个子视图外的其余子视图成孤形排列 @Override protected void onLayout(boolean changed, int l, int t, int r, int b) { View child0 = getChildAt(0);//由于第一个"+"按钮不参与弧形的排列,所以先拿出来单独处理 int childCount = getChildCount(); for (int i = 0; i < childCount - 1; i++) {//以弧形来摆放其余子视图 View child = getChildAt(i + 1); int childMesureWidth = child.getMeasuredWidth(); int childMesureHeight = child.getMeasuredHeight(); float angle = (float) ((Math.PI / 2 / 4) * i);//计算出当前要摆放子视图的角度 int childLeft = (int) (RADIUS * Math.sin(angle)); int childTop = (int) (RADIUS * Math.cos(angle)); int childRight = childLeft + childMesureWidth; int childBottom = childTop + childMesureHeight; child.layout(childLeft, childTop, childRight, childBottom); } } }
编译运行:

接着还差一个“+”号的摆放,这个比较简单,稍加处理一下:
再次编译运行:

第0个和其余的子视图的旋转处理:
接下来增加点击的动画效果,首先处理旋转效果,先处理点击“+”号的旋转,先给“+”View增加点击事件:
/** * 圆形菜单View---第0个和其余子视图的旋转处理 */ public class ArcMenuView extends ViewGroup implements View.OnClickListener { /* 定义要摆放圆的半径,其子视图的摆放位置需要依据它来计算 */ private static final float RADIUS = 130f; public ArcMenuView(Context context) { this(context, null); } public ArcMenuView(Context context, AttributeSet attrs) { this(context, attrs, 0); } public ArcMenuView(Context context, AttributeSet attrs, int defStyleAttr) { super(context, attrs, defStyleAttr); } //在ViewGroup中默认是不会测量孩子视图的,所以需要手动测量一下子视图 @Override protected void onMeasure(int widthMeasureSpec, int heightMeasureSpec) { //测量子视图 int childCount = getChildCount(); for (int i = 0; i < childCount; i++) { //传0表示测量自身包裹之后的大小 getChildAt(i).measure(0, 0); } super.onMeasure(widthMeasureSpec, heightMeasureSpec); } //除第一个子视图外的其余子视图成孤形排列 @Override protected void onLayout(boolean changed, int l, int t, int r, int b) { View child0 = getChildAt(0);//由于第一个"+"按钮不参与弧形的排列,所以先拿出来单独处理 child0.layout(0, 0, child0.getMeasuredWidth(), child0.getMeasuredHeight()); child0.setOnClickListener(this); int childCount = getChildCount(); for (int i = 0; i < childCount - 1; i++) {//以弧形来摆放其余子视图 View child = getChildAt(i + 1); int childMesureWidth = child.getMeasuredWidth(); int childMesureHeight = child.getMeasuredHeight(); float angle = (float) ((Math.PI / 2 / 4) * i);//计算出当前要摆放子视图的角度 int childLeft = (int) (RADIUS * Math.sin(angle)); int childTop = (int) (RADIUS * Math.cos(angle)); int childRight = childLeft + childMesureWidth; int childBottom = childTop + childMesureHeight; child.layout(childLeft, childTop, childRight, childBottom); } } @Override public void onClick(View view) { switch (view.getId()) { case R.id.lay_plus: rotateChild0(view); break; } } private void rotateChild0(View view) { RotateAnimation rotateAnimation = new RotateAnimation(0, 360, RotateAnimation.RELATIVE_TO_SELF, 0.5f, RotateAnimation.RELATIVE_TO_SELF, 0.5f); rotateAnimation.setDuration(2000); rotateAnimation.setFillAfter(true); view.startAnimation(rotateAnimation); } }
编译运行:
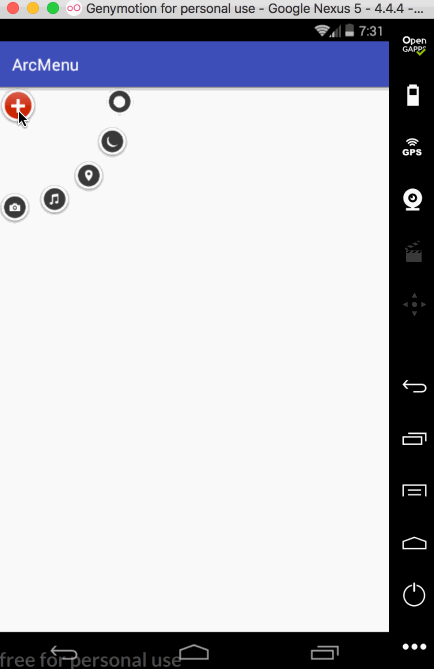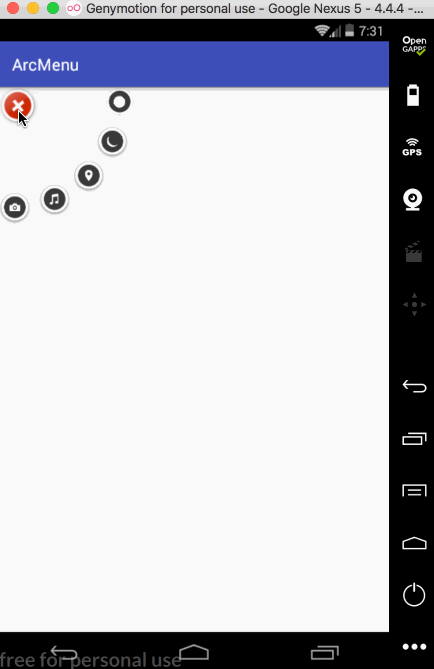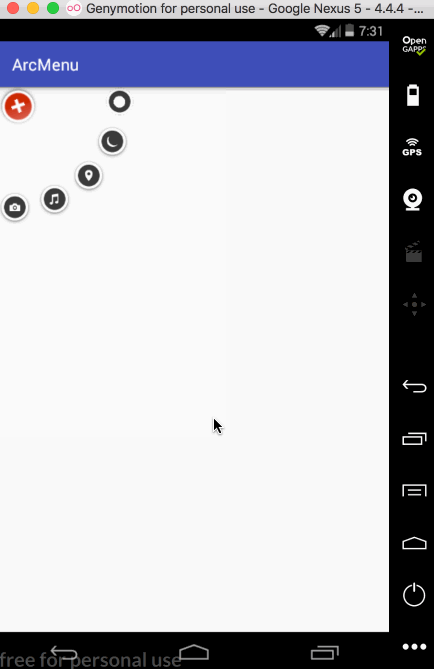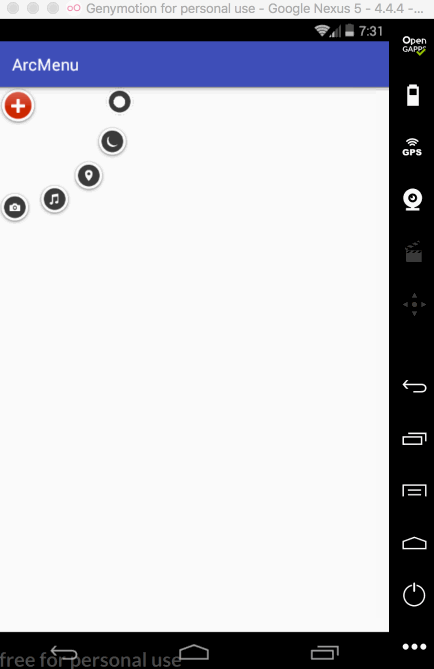
接下来再让其它的子元素也进行相应的旋转,如下:
/** * 圆形菜单View---第0个和其余子视图的旋转处理 */ public class ArcMenuView extends ViewGroup implements View.OnClickListener { /* 定义要摆放圆的半径,其子视图的摆放位置需要依据它来计算 */ private static final float RADIUS = 130f; public ArcMenuView(Context context) { this(context, null); } public ArcMenuView(Context context, AttributeSet attrs) { this(context, attrs, 0); } public ArcMenuView(Context context, AttributeSet attrs, int defStyleAttr) { super(context, attrs, defStyleAttr); } //在ViewGroup中默认是不会测量孩子视图的,所以需要手动测量一下子视图 @Override protected void onMeasure(int widthMeasureSpec, int heightMeasureSpec) { //测量子视图 int childCount = getChildCount(); for (int i = 0; i < childCount; i++) { //传0表示测量自身包裹之后的大小 getChildAt(i).measure(0, 0); } super.onMeasure(widthMeasureSpec, heightMeasureSpec); } //除第一个子视图外的其余子视图成孤形排列 @Override protected void onLayout(boolean changed, int l, int t, int r, int b) { View child0 = getChildAt(0);//由于第一个"+"按钮不参与弧形的排列,所以先拿出来单独处理 child0.layout(0, 0, child0.getMeasuredWidth(), child0.getMeasuredHeight()); child0.setOnClickListener(this); int childCount = getChildCount(); for (int i = 0; i < childCount - 1; i++) {//以弧形来摆放其余子视图 View child = getChildAt(i + 1); int childMesureWidth = child.getMeasuredWidth(); int childMesureHeight = child.getMeasuredHeight(); float angle = (float) ((Math.PI / 2 / 4) * i);//计算出当前要摆放子视图的角度 int childLeft = (int) (RADIUS * Math.sin(angle)); int childTop = (int) (RADIUS * Math.cos(angle)); int childRight = childLeft + childMesureWidth; int childBottom = childTop + childMesureHeight; child.layout(childLeft, childTop, childRight, childBottom); } } @Override public void onClick(View view) { switch (view.getId()) { case R.id.lay_plus: rotateChild0(view); rotateOtherChildren(); break; } } private void rotateChild0(View view) { RotateAnimation rotateAnimation = new RotateAnimation(0, 360, RotateAnimation.RELATIVE_TO_SELF, 0.5f, RotateAnimation.RELATIVE_TO_SELF, 0.5f); rotateAnimation.setDuration(2000); rotateAnimation.setFillAfter(true); view.startAnimation(rotateAnimation); } private void rotateOtherChildren() { int childCount = getChildCount(); for (int i = 0; i < childCount - 1; i++) { View child = getChildAt(i + 1); RotateAnimation rotateAnimation = new RotateAnimation(0, 360, RotateAnimation.RELATIVE_TO_SELF, 0.5f, RotateAnimation.RELATIVE_TO_SELF, 0.5f); rotateAnimation.setDuration(2000); rotateAnimation.setFillAfter(true); child.startAnimation(rotateAnimation); } } }
编译运行:
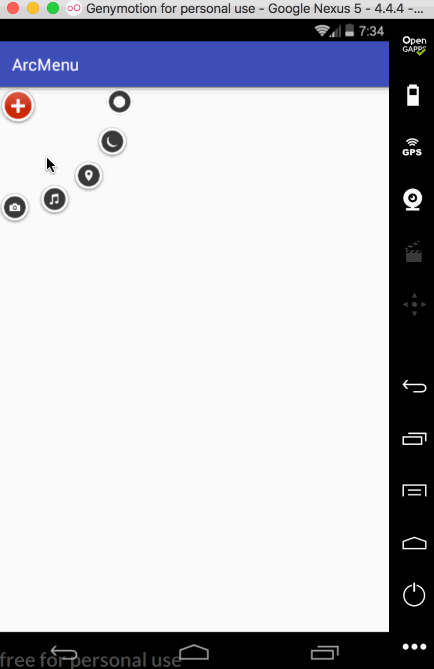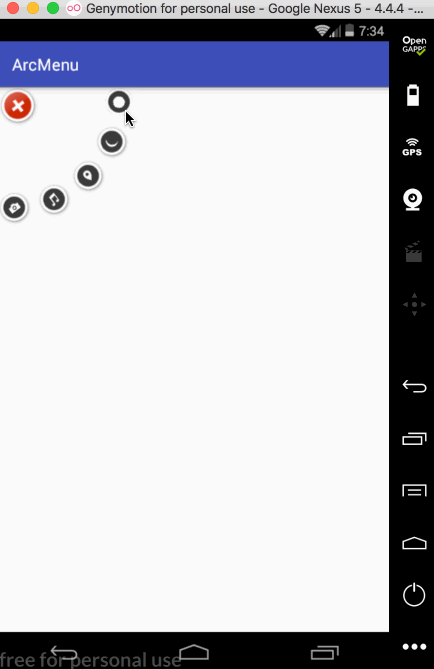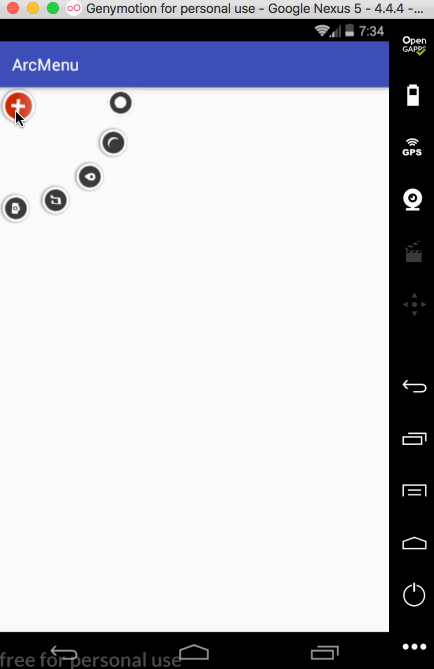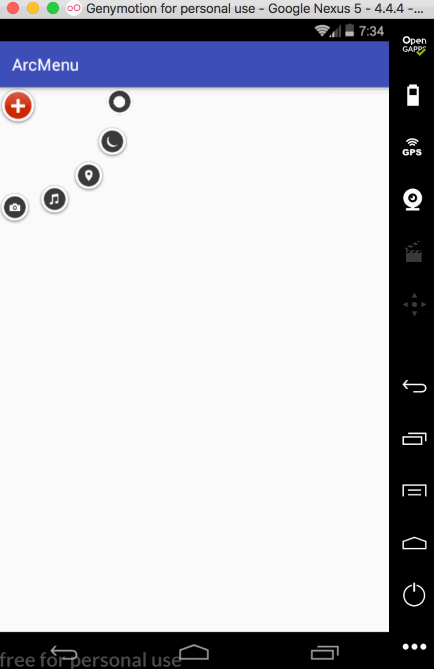
平移处理:
接下来处理点击“+”进行子view的平稳,默认其弧形菜单项应该是隐藏,只显示一个“+”,处理如下:

编译运行:

接下来则需要处理一点击“+”,需要让弧形的元素平移旋转出来,那如何平移呢,以其中的一个元素来分析:
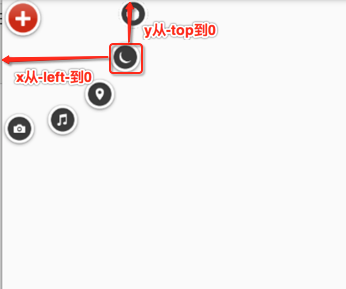
所以具体代码如下:
private void rotateOtherChildren() { int childCount = getChildCount(); for (int i = 0; i < childCount - 1; i++) { View child = getChildAt(i + 1); int childLeft = child.getLeft(); int childTop = child.getTop(); //移动的类型包含:ABSOLUTE、RELATIVE_TO_PARENT、RELATIVE_TO_SELF //参数1,3:x方向移动的类型 //参数2,4:x方向从2到4 //参数5,7:y方向移动的类型 //参数6,8:y方向从6到8 TranslateAnimation translateAnimation = new TranslateAnimation(TranslateAnimation.ABSOLUTE, -childLeft, TranslateAnimation.ABSOLUTE, 0, TranslateAnimation.ABSOLUTE, -childTop, TranslateAnimation.ABSOLUTE, 0); translateAnimation.setDuration(1500); translateAnimation.setFillAfter(true); RotateAnimation rotateAnimation = new RotateAnimation(0, 360, RotateAnimation.RELATIVE_TO_SELF, 0.5f, RotateAnimation.RELATIVE_TO_SELF, 0.5f); rotateAnimation.setDuration(2000); rotateAnimation.setFillAfter(true); child.startAnimation(translateAnimation); } }
先只做平移处理,旋转暂且不加,编译运行:
目前弧形菜单项是同时间平移的,而实际效果是需要一个个有个先后顺序出来,所以这里需要处理一个属性来达到此效果,如下:

再次编译运行:
另外原效果在每个弧形菜单平移完之后都会有一个回调效果,所以此时就需要加入一个插值器来达到这样的效果,如下:

再来看效果:
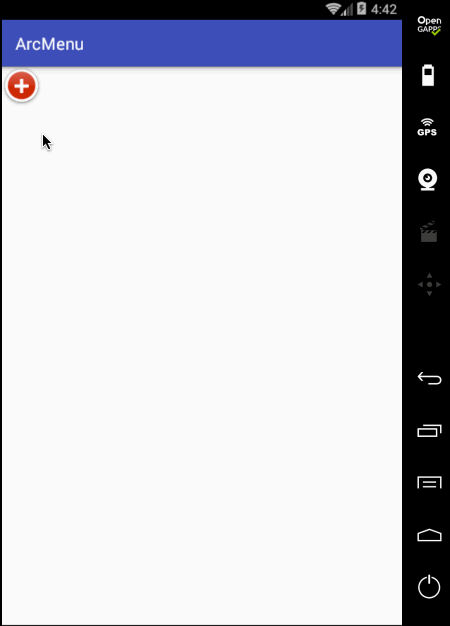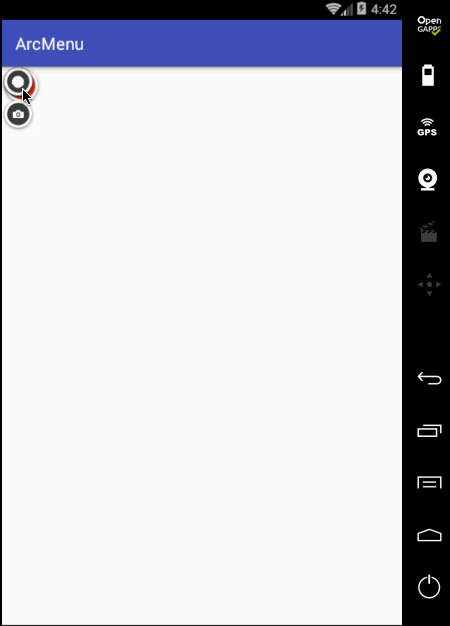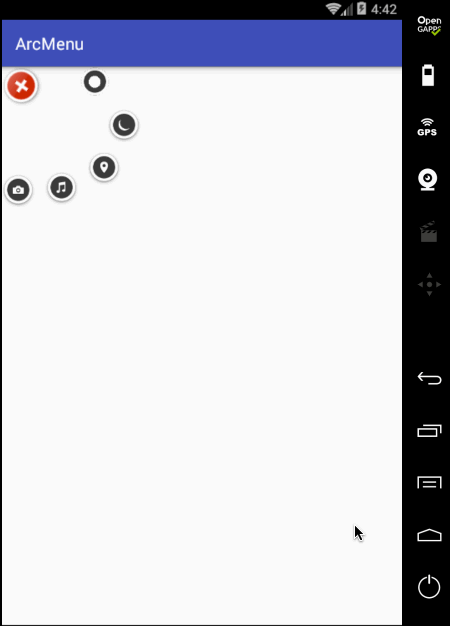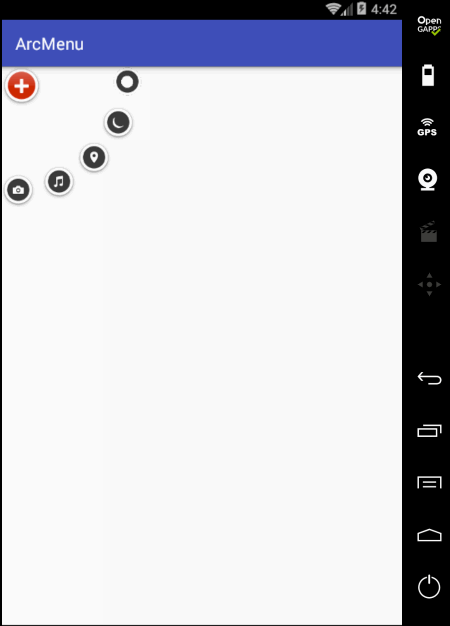
好这个平移效果基本差不多,此时在平移过程中把之前的旋转动画给加进来,具体如下:
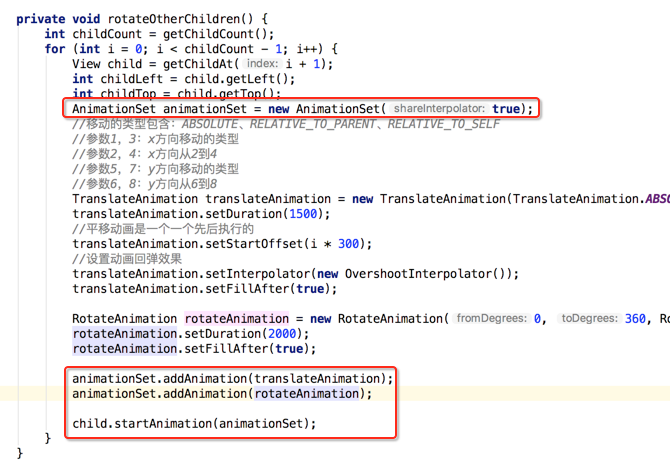

呃~~动画出问题了,这是因为目前是先添加的平移动画之后再添加的旋转动画,这个旋转的中心坐标会被不断改变,调一个顺序既可,如下:
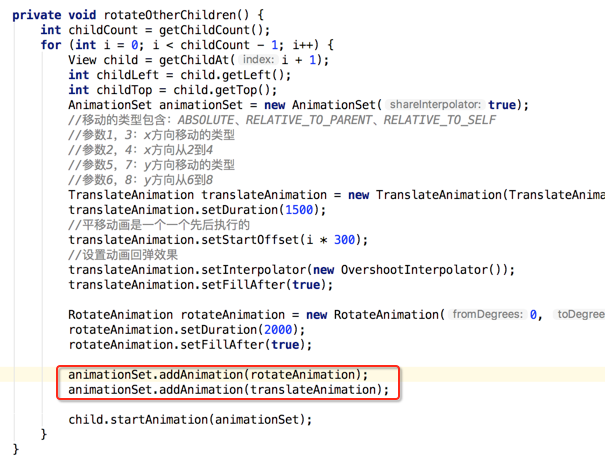
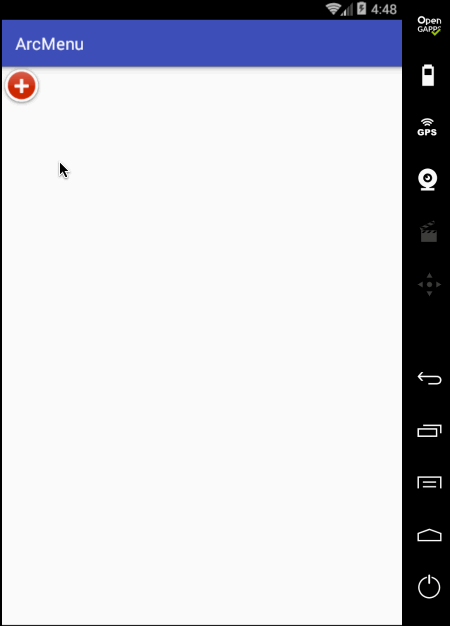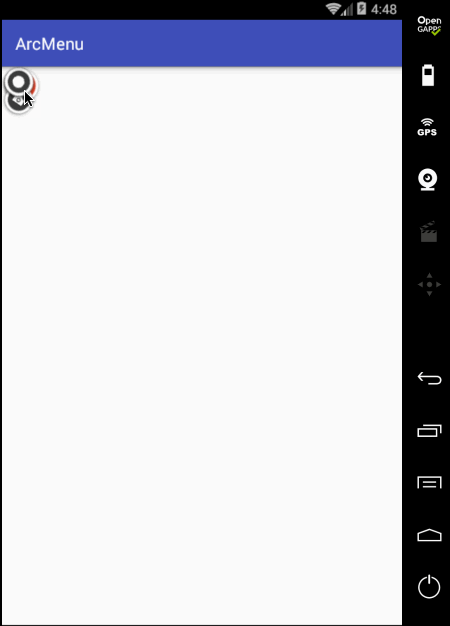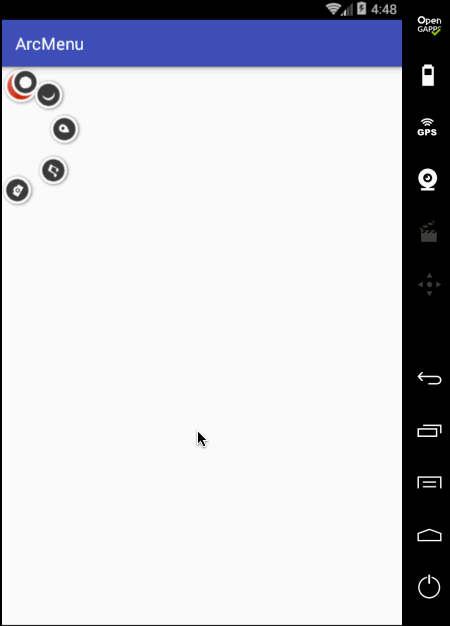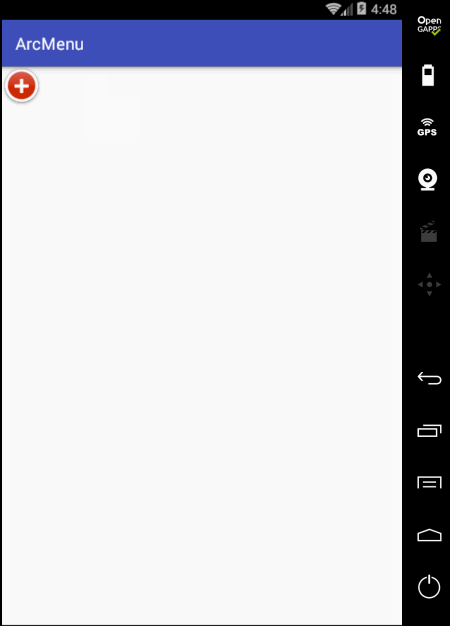
嗯~~动画是对了,不过在动画执行完之后元素又消失了,这是因为默认元素是INVISIBLE状态的,这里简单处理就是在执行动画之前将其置为显示既可,如下:
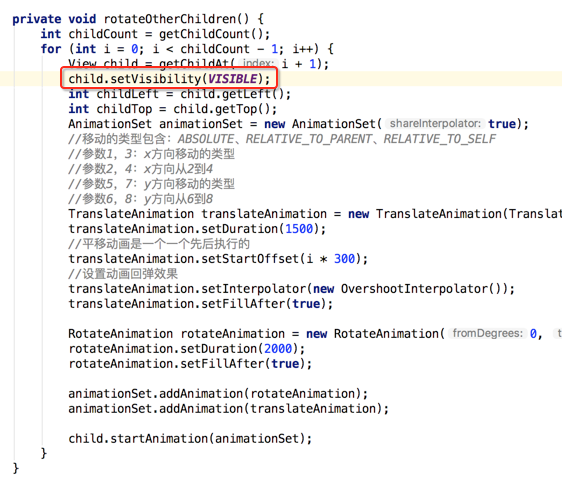
再来看:
另外还有一个旋转的小细节,目前在动画执行过程中的旋转貌似停掉了,也就是旋转的因数少了点,加大旋转角度:

编译运行:
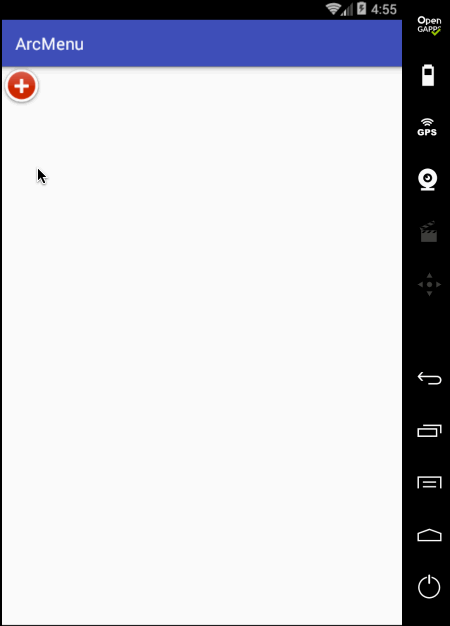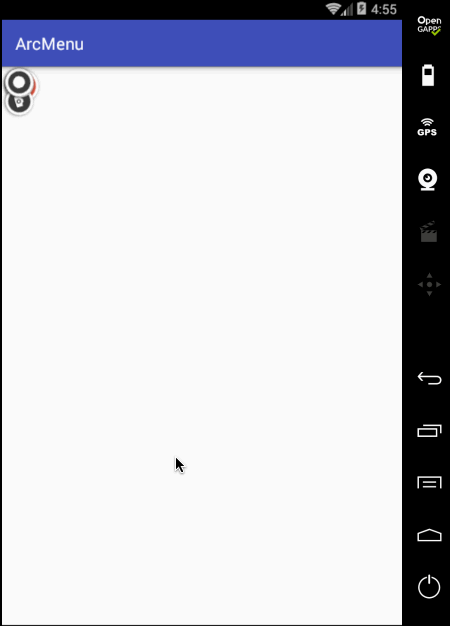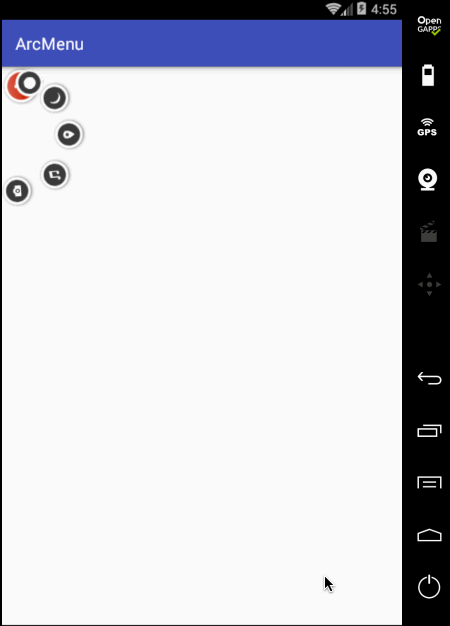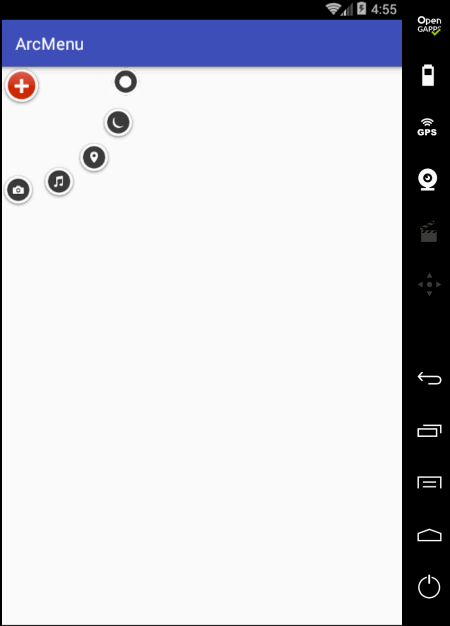
另外在点“+”时应该可以控制圆弧菜单项的打开和关闭,所以这里需要给程序定义状态:
/** * 圆形菜单View---非第0个子视图的平移处理 */ public class ArcMenuView extends ViewGroup implements View.OnClickListener { /* 定义要摆放圆的半径,其子视图的摆放位置需要依据它来计算 */ private static final float RADIUS = 130f; private CurrentStatus currentStatus = CurrentStatus.CLOSE; /* 定义卫星菜单打开和关闭状态 */ public enum CurrentStatus { OPEN, CLOSE } public ArcMenuView(Context context) { this(context, null); } public ArcMenuView(Context context, AttributeSet attrs) { this(context, attrs, 0); } public ArcMenuView(Context context, AttributeSet attrs, int defStyleAttr) { super(context, attrs, defStyleAttr); } //在ViewGroup中默认是不会测量孩子视图的,所以需要手动测量一下子视图 @Override protected void onMeasure(int widthMeasureSpec, int heightMeasureSpec) { //测量子视图 int childCount = getChildCount(); for (int i = 0; i < childCount; i++) { //传0表示测量自身包裹之后的大小 getChildAt(i).measure(0, 0); } super.onMeasure(widthMeasureSpec, heightMeasureSpec); } //除第一个子视图外的其余子视图成孤形排列 @Override protected void onLayout(boolean changed, int l, int t, int r, int b) { View child0 = getChildAt(0);//由于第一个"+"按钮不参与弧形的排列,所以先拿出来单独处理 child0.layout(0, 0, child0.getMeasuredWidth(), child0.getMeasuredHeight()); child0.setOnClickListener(this); int childCount = getChildCount(); for (int i = 0; i < childCount - 1; i++) {//以弧形来摆放其余子视图 View child = getChildAt(i + 1); int childMesureWidth = child.getMeasuredWidth(); int childMesureHeight = child.getMeasuredHeight(); float angle = (float) ((Math.PI / 2 / 4) * i);//计算出当前要摆放子视图的角度 int childLeft = (int) (RADIUS * Math.sin(angle)); int childTop = (int) (RADIUS * Math.cos(angle)); int childRight = childLeft + childMesureWidth; int childBottom = childTop + childMesureHeight; child.layout(childLeft, childTop, childRight, childBottom); child.setVisibility(INVISIBLE); } } @Override public void onClick(View view) { switch (view.getId()) { case R.id.lay_plus: rotateChild0(view); animateOtherChildren(); break; } } private void rotateChild0(View view) { RotateAnimation rotateAnimation = new RotateAnimation(0, 720, RotateAnimation.RELATIVE_TO_SELF, 0.5f, RotateAnimation.RELATIVE_TO_SELF, 0.5f); rotateAnimation.setDuration(2000); rotateAnimation.setFillAfter(true); view.startAnimation(rotateAnimation); } private void animateOtherChildren() { int childCount = getChildCount(); for (int i = 0; i < childCount - 1; i++) { View child = getChildAt(i + 1); child.setVisibility(VISIBLE); int childLeft = child.getLeft(); int childTop = child.getTop(); AnimationSet animationSet = new AnimationSet(true); //移动的类型包含:ABSOLUTE、RELATIVE_TO_PARENT、RELATIVE_TO_SELF //参数1,3:x方向移动的类型 //参数2,4:x方向从2到4 //参数5,7:y方向移动的类型 //参数6,8:y方向从6到8 TranslateAnimation translateAnimation = new TranslateAnimation(TranslateAnimation.ABSOLUTE, -childLeft, TranslateAnimation.ABSOLUTE, 0, TranslateAnimation.ABSOLUTE, -childTop, TranslateAnimation.ABSOLUTE, 0); translateAnimation.setDuration(1500); //平移动画是一个一个先后执行的 translateAnimation.setStartOffset(i * 300); //设置动画回弹效果 translateAnimation.setInterpolator(new OvershootInterpolator()); translateAnimation.setFillAfter(true); RotateAnimation rotateAnimation = new RotateAnimation(0, 720, RotateAnimation.RELATIVE_TO_SELF, 0.5f, RotateAnimation.RELATIVE_TO_SELF, 0.5f); rotateAnimation.setDuration(2000); rotateAnimation.setFillAfter(true); animationSet.addAnimation(rotateAnimation); animationSet.addAnimation(translateAnimation); child.startAnimation(animationSet); } changeCurrentStatus(); } private void changeCurrentStatus() { currentStatus = currentStatus == CurrentStatus.CLOSE ? CurrentStatus.OPEN : CurrentStatus.CLOSE; } }
编译运行:
状态不对,这个平移应该根据打开和关闭需要改变起始坐标和结束坐标,具体如下:
/** * 圆形菜单View---非第0个子视图的平移处理 */ public class ArcMenuView extends ViewGroup implements View.OnClickListener { /* 定义要摆放圆的半径,其子视图的摆放位置需要依据它来计算 */ private static final float RADIUS = 130f; private CurrentStatus currentStatus = CurrentStatus.CLOSE; /* 定义卫星菜单打开和关闭状态 */ public enum CurrentStatus { OPEN, CLOSE } public ArcMenuView(Context context) { this(context, null); } public ArcMenuView(Context context, AttributeSet attrs) { this(context, attrs, 0); } public ArcMenuView(Context context, AttributeSet attrs, int defStyleAttr) { super(context, attrs, defStyleAttr); } //在ViewGroup中默认是不会测量孩子视图的,所以需要手动测量一下子视图 @Override protected void onMeasure(int widthMeasureSpec, int heightMeasureSpec) { //测量子视图 int childCount = getChildCount(); for (int i = 0; i < childCount; i++) { //传0表示测量自身包裹之后的大小 getChildAt(i).measure(0, 0); } super.onMeasure(widthMeasureSpec, heightMeasureSpec); } //除第一个子视图外的其余子视图成孤形排列 @Override protected void onLayout(boolean changed, int l, int t, int r, int b) { View child0 = getChildAt(0);//由于第一个"+"按钮不参与弧形的排列,所以先拿出来单独处理 child0.layout(0, 0, child0.getMeasuredWidth(), child0.getMeasuredHeight()); child0.setOnClickListener(this); int childCount = getChildCount(); for (int i = 0; i < childCount - 1; i++) {//以弧形来摆放其余子视图 View child = getChildAt(i + 1); int childMesureWidth = child.getMeasuredWidth(); int childMesureHeight = child.getMeasuredHeight(); float angle = (float) ((Math.PI / 2 / 4) * i);//计算出当前要摆放子视图的角度 int childLeft = (int) (RADIUS * Math.sin(angle)); int childTop = (int) (RADIUS * Math.cos(angle)); int childRight = childLeft + childMesureWidth; int childBottom = childTop + childMesureHeight; child.layout(childLeft, childTop, childRight, childBottom); child.setVisibility(INVISIBLE); } } @Override public void onClick(View view) { switch (view.getId()) { case R.id.lay_plus: rotateChild0(view); animateOtherChildren(); break; } } private void rotateChild0(View view) { RotateAnimation rotateAnimation = new RotateAnimation(0, 720, RotateAnimation.RELATIVE_TO_SELF, 0.5f, RotateAnimation.RELATIVE_TO_SELF, 0.5f); rotateAnimation.setDuration(2000); rotateAnimation.setFillAfter(true); view.startAnimation(rotateAnimation); } private void animateOtherChildren() { int childCount = getChildCount(); for (int i = 0; i < childCount - 1; i++) { final View child = getChildAt(i + 1); child.setVisibility(VISIBLE); int childLeft = child.getLeft(); int childTop = child.getTop(); AnimationSet animationSet = new AnimationSet(true); //移动的类型包含:ABSOLUTE、RELATIVE_TO_PARENT、RELATIVE_TO_SELF //参数1,3:x方向移动的类型 //参数2,4:x方向从2到4 //参数5,7:y方向移动的类型 //参数6,8:y方向从6到8 TranslateAnimation translateAnimation = null; if (CurrentStatus.CLOSE == currentStatus) { translateAnimation = new TranslateAnimation(TranslateAnimation.ABSOLUTE, -childLeft, TranslateAnimation.ABSOLUTE, 0, TranslateAnimation.ABSOLUTE, -childTop, TranslateAnimation.ABSOLUTE, 0); } else { translateAnimation = new TranslateAnimation(TranslateAnimation.ABSOLUTE, 0, TranslateAnimation.ABSOLUTE, -childLeft, TranslateAnimation.ABSOLUTE, 0, TranslateAnimation.ABSOLUTE, -childTop); } translateAnimation.setDuration(1500); //平移动画是一个一个先后执行的 translateAnimation.setStartOffset(i * 300); //设置动画回弹效果 translateAnimation.setInterpolator(new OvershootInterpolator()); translateAnimation.setFillAfter(true); translateAnimation.setAnimationListener(new Animation.AnimationListener() { @Override public void onAnimationStart(Animation animation) { } @Override public void onAnimationEnd(Animation animation) { if (CurrentStatus.CLOSE == currentStatus) { child.setVisibility(INVISIBLE); } } @Override public void onAnimationRepeat(Animation animation) { } }); RotateAnimation rotateAnimation = new RotateAnimation(0, 720, RotateAnimation.RELATIVE_TO_SELF, 0.5f, RotateAnimation.RELATIVE_TO_SELF, 0.5f); rotateAnimation.setDuration(2000); rotateAnimation.setFillAfter(true); animationSet.addAnimation(rotateAnimation); animationSet.addAnimation(translateAnimation); child.startAnimation(animationSet); } changeCurrentStatus(); } private void changeCurrentStatus() { currentStatus = currentStatus == CurrentStatus.CLOSE ? CurrentStatus.OPEN : CurrentStatus.CLOSE; } }
编译运行:
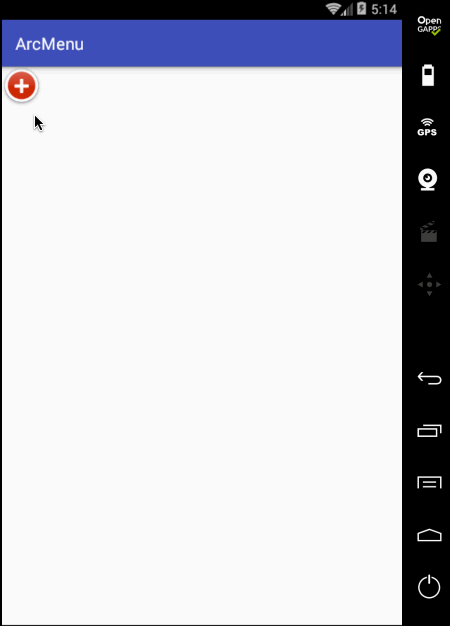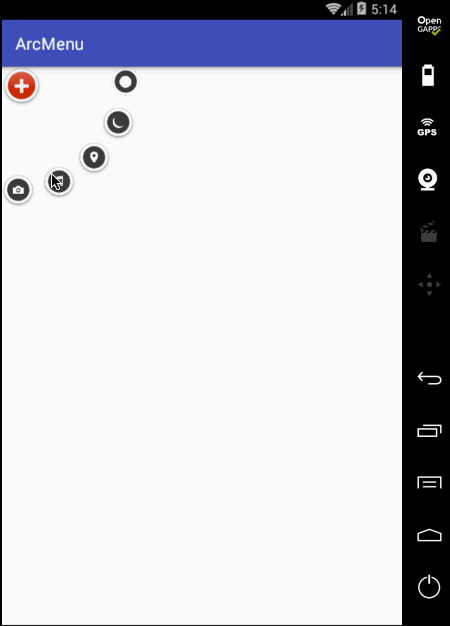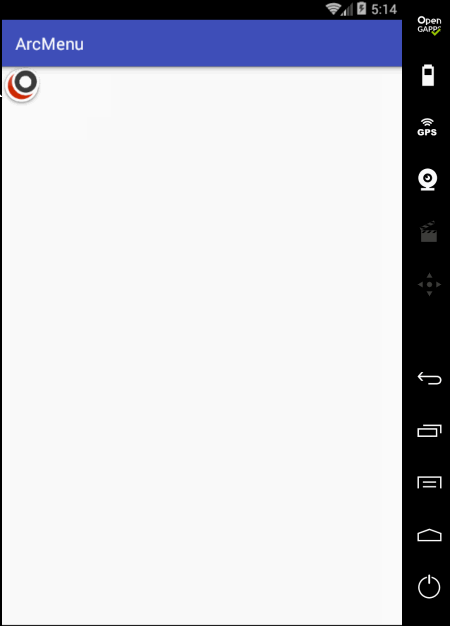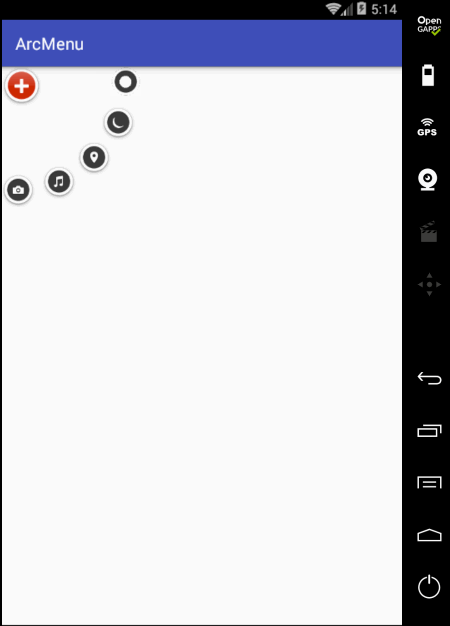
至此整个效果就实现完了,可见如果不用补间动画来实现,而是采用纯View绘制的方式来实现那是何等的麻烦~