VGG网络
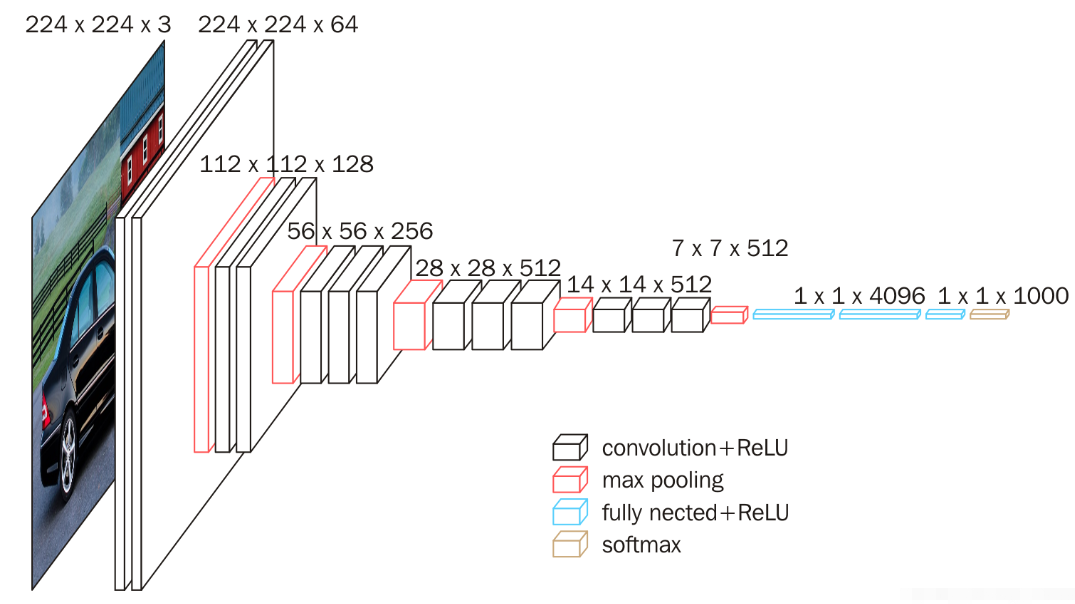
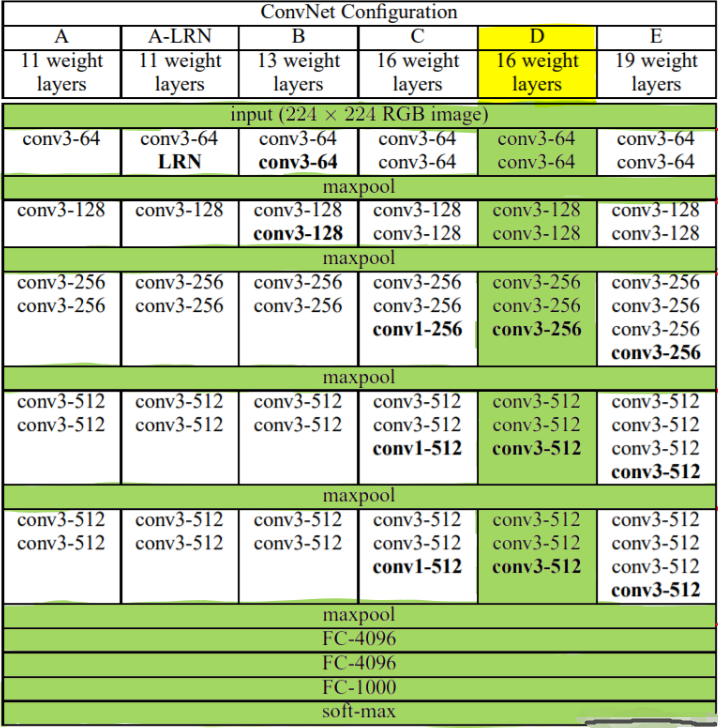
5.7.1 VGG块
import time
import torch
from torch import nn, optim
import pytorch_deep as pyd
device = torch.device('cuda' if torch.cuda.is_available() else 'cpu')
def vgg_block(num_convs, in_channels, out_channels):
blk = []
for i in range(num_convs):
if i == 0:
blk.append(nn.Conv2d(in_channels, out_channels,kernel_size=3, padding=1))
else:
blk.append(nn.Conv2d(out_channels, out_channels,kernel_size=3, padding=1))
blk.append(nn.ReLU())
blk.append(nn.MaxPool2d(kernel_size=2, stride=2)) # 这⾥会使宽⾼减半
return nn.Sequential(*blk)
实现VGG_11网络
def vgg_11(conv_arch, fc_features, fc_hidden_units=4096):
net = nn.Sequential()
# 卷积层部分
for i, (num_convs, in_channels, out_channels) in enumerate(conv_arch):
# 每经过⼀个vgg_block都会使宽⾼减半
net.add_module("vgg_block_" + str(i+1),vgg_block(num_convs, in_channels, out_channels))
# 全连接层部分
net.add_module("fc", nn.Sequential(
pyd.FlattenLayer(),
nn.Linear(fc_features,fc_hidden_units),
nn.ReLU(),
nn.Dropout(0.5),
nn.Linear(fc_hidden_units,fc_hidden_units),
nn.ReLU(),
nn.Dropout(0.5),
nn.Linear(fc_hidden_units, 10)
))
return net
ratio = 8
small_conv_arch = [(1, 1, 64//ratio), (1, 64//ratio, 128//ratio),(2, 128//ratio, 256//ratio),(2, 256//ratio, 512//ratio), (2, 512//ratio,512//ratio)]
fc_features = 512 * 7 * 7 # c *
fc_hidden_units = 4096 # 任意
net = vgg_11(small_conv_arch, fc_features // ratio, fc_hidden_units //ratio)
print(net)
Sequential(
(vgg_block_1): Sequential(
(0): Conv2d(1, 8, kernel_size=(3, 3), stride=(1, 1), padding=(1, 1))
(1): ReLU()
(2): MaxPool2d(kernel_size=2, stride=2, padding=0, dilation=1, ceil_mode=False)
)
(vgg_block_2): Sequential(
(0): Conv2d(8, 16, kernel_size=(3, 3), stride=(1, 1), padding=(1, 1))
(1): ReLU()
(2): MaxPool2d(kernel_size=2, stride=2, padding=0, dilation=1, ceil_mode=False)
)
(vgg_block_3): Sequential(
(0): Conv2d(16, 32, kernel_size=(3, 3), stride=(1, 1), padding=(1, 1))
(1): ReLU()
(2): Conv2d(32, 32, kernel_size=(3, 3), stride=(1, 1), padding=(1, 1))
(3): ReLU()
(4): MaxPool2d(kernel_size=2, stride=2, padding=0, dilation=1, ceil_mode=False)
)
(vgg_block_4): Sequential(
(0): Conv2d(32, 64, kernel_size=(3, 3), stride=(1, 1), padding=(1, 1))
(1): ReLU()
(2): Conv2d(64, 64, kernel_size=(3, 3), stride=(1, 1), padding=(1, 1))
(3): ReLU()
(4): MaxPool2d(kernel_size=2, stride=2, padding=0, dilation=1, ceil_mode=False)
)
(vgg_block_5): Sequential(
(0): Conv2d(64, 64, kernel_size=(3, 3), stride=(1, 1), padding=(1, 1))
(1): ReLU()
(2): Conv2d(64, 64, kernel_size=(3, 3), stride=(1, 1), padding=(1, 1))
(3): ReLU()
(4): MaxPool2d(kernel_size=2, stride=2, padding=0, dilation=1, ceil_mode=False)
)
(fc): Sequential(
(0): FlattenLayer()
(1): Linear(in_features=3136, out_features=512, bias=True)
(2): ReLU()
(3): Dropout(p=0.5)
(4): Linear(in_features=512, out_features=512, bias=True)
(5): ReLU()
(6): Dropout(p=0.5)
(7): Linear(in_features=512, out_features=10, bias=True)
)
)
训练数据
batch_size = 32
# 如出现“out of memory”的报错信息,可减⼩batch_size或resize
train_iter, test_iter = pyd.load_data_fashion_mnist(batch_size,resize=224)
lr, num_epochs = 0.001, 5
optimizer = torch.optim.Adam(net.parameters(), lr=lr)
pyd.train_ch5(net, train_iter, test_iter, batch_size, optimizer,device, num_epochs)
training on cuda
epoch 1, loss 0.5166, train acc 0.810, test acc 0.872,time 57.6 sec
epoch 2, loss 0.1557, train acc 0.887, test acc 0.902,time 57.9 sec
epoch 3, loss 0.0916, train acc 0.900, test acc 0.907,time 57.7 sec
epoch 4, loss 0.0609, train acc 0.912, test acc 0.915,time 57.6 sec
epoch 5, loss 0.0449, train acc 0.919, test acc 0.914,time 57.4 sec

