隐藏属性
一个设置,一个获取,定义方法间接去取变量, 否则可能语法上是通的,但逻辑上有问题。
class Dog:
def set_age(self,new_age):
if new_age>0 and new_age<=100:
self.age = new_age
else:
self.age = 0
def get_age(self):
return self.age
dog = Dog()
dog.set_age(-10)
age = dog.get_age()
print(age)
私有方法
class Dog:
#私有方法
def __send_msg(self):
print("------正在发送短信------")
#公有方法
def send_msg(self,new_money):
if new_money>10000:
self.__send_msg()
else:
print("余额不足,请先充值,再发送短信")
dog = Dog()
dog.send_msg(100)
class Dog:
pass
dog1 = Dog()
dog2 = dog1
del dog1 #数据只有1份,名字可以好几个,指向同一个对象
del dog2 #看引用计数是否为0 sys.getrefcount() 测量引用个数比实际大1继承
父类 基类
子类 派生类 可以拥有父类的功能,也可以拥有父类的父类的功能
class Dog(Animal):
重写
一般不会修改父类,直接修改子类的功能
class Xiaotq(Dog):
def bark(self):
print("---狂叫---")
#第一种调用被重写的父类的方法
#Dog.bark(self)
#第二种
super().bark
调用被重写的功能
见上
私有方法私有属性在继承中的表现
class A:
def __init__(self):
self.num1 = 100
self.__num2 = 200
def test1(self):
print("----test1----")
def __test2(self):
print("----test2----")
def test3(self):
self.__test2()
print(self.__num2)
class B(A):
pass
b = B()
b.test1()
#b.__test2() #私有方法不会被继承
print(b.num1)
print(b.num2)
b.test3 #调用父类的公有方法,执行调用私有属性和方法,让用多继承
调用,C3算法,有搜索路径,先找c,再找b....
class Base(object):
def test(self):
print("----Base")
class A(Base):
def test(self):
print("----a")
class B(Base):
def test(self):
print("----b")
class C(A,B):
def test(self):
print("----c")
c = C()新式类和经典类
python3 默认都是新式类,不必添加object
多态
定义的时候不确定它具有哪些功能,等到调用方法时才确定调用父类还是子类的方法
面试
1. python是面向过程还是面向对象呢?
既支持面向过程也支持面向对象
2. python语言面向对象的三个要素是什么?
封装、继承、多态
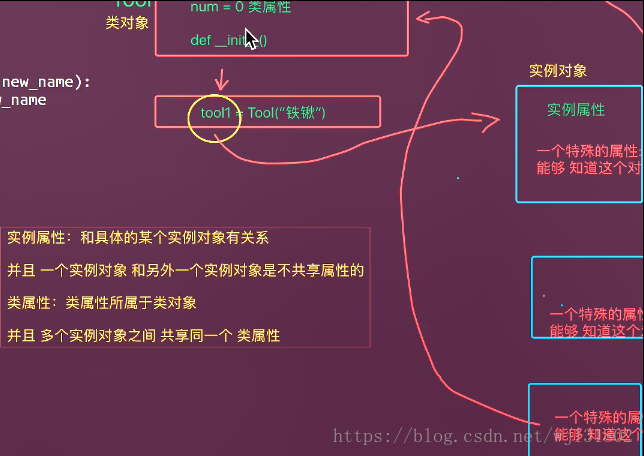
类属性、实例属性
class Tool(object):
#类属性
num = 0
#方法
def __init__(self,new_name):
self.name = new_name
Tool.num+=1
tool1 = Tool("铁锹")
tool2 = Tool("工兵铲")
tool3 = Tool("水桶")
print(Tool.num)实例方法、类方法和静态方法
#类属性
num = 0
#实例方法
def __init__(self):
#实例属性
self.name = "laowang"
#类方法
@classmethod
def add_num(cls):
cls.num = 100
#静态方法
@staticmethod
def print_menu():
print("-------------")
print(" 穿越火线v11.1")
print(" 1. 开始游戏")
print(" 2. 结束游戏")
print("-------------")
game = Game()
Game.add_num()#可以通过类的名字调用类方法
print(Game.num)#还可以通过这个类创建出来的对象 去调用这个类方法
Game.print_menu()#通过类 去调用静态方法
game.print_menu()#通过实例对象 去调用静态方法设计4s店类
class CarStore(object):
def order(self, car_type):
return select_car_by_type(car_type)
def select_car_by_type(car_type): #用函数解耦
if car_type=="索纳塔":
return Suonata()
elif car_type=="名图":
return Mingtu()
class Car(object):
def move(self):
print("车在移动...")
def music(self):
print("车在播放音乐...")
def stop(self):
print("车在停止...")
class Suonata(Car):
pass
class Mingtu(Car):
pass
car_store = CarStore()
car = car_store.order("索纳塔")
car.move()
car.music()
car.stop()
开发文档
select_car_by_type(car_type)
功能: 返回一个汽车对象的引用
参数:需要得到汽车的类型class CarStore(object):
def __init__(self):
self.factory = Factory()
def order(self, car_type):
return self.factory.select_car_by_type(car_type)
class Factory(object):
def select_car_by_type(car_type): #用函数解耦
if car_type=="索纳塔":
return Suonata()
elif car_type=="名图":
return Mingtu()
class Car(object):
def move(self):
print("车在移动...")
def music(self):
print("车在播放音乐...")
def stop(self):
print("车在停止...")
class Suonata(Car):
pass
class Mingtu(Car):
pass
car_store = CarStore()
car = car_store.order("索纳塔")
car.move()
car.music()
car.stop()
设计模式
为了解决哪一类问题,设计的套路
工厂方法模式
父类定义接口,把基本的流程规定好,子类具体来实现功能
class Store(object):
def select_car(self):
pass
def order(self, car_type):
return self.select_car(car_type)
class BMWCarStore(object):
def select_car(self, car_type):
return BMWFactory().select_car_by_type(car_type)
bmw_store = BMWCarStore()
bmw = bmw_store.order("720li")
class Factory(object):
def select_car_by_type(car_type):
if car_type=="索纳塔":
return Suonata()
elif car_type=="名图":
return Mingtu()
class Car(object):
def move(self):
print("车在移动...")
def music(self):
print("车在播放音乐...")
def stop(self):
print("车在停止...")
class Suonata(Car):
pass
class Mingtu(Car):
pass
car_store = CarStore()
car = car_store.order("索纳塔")
car.move()
car.music()
car.stop()
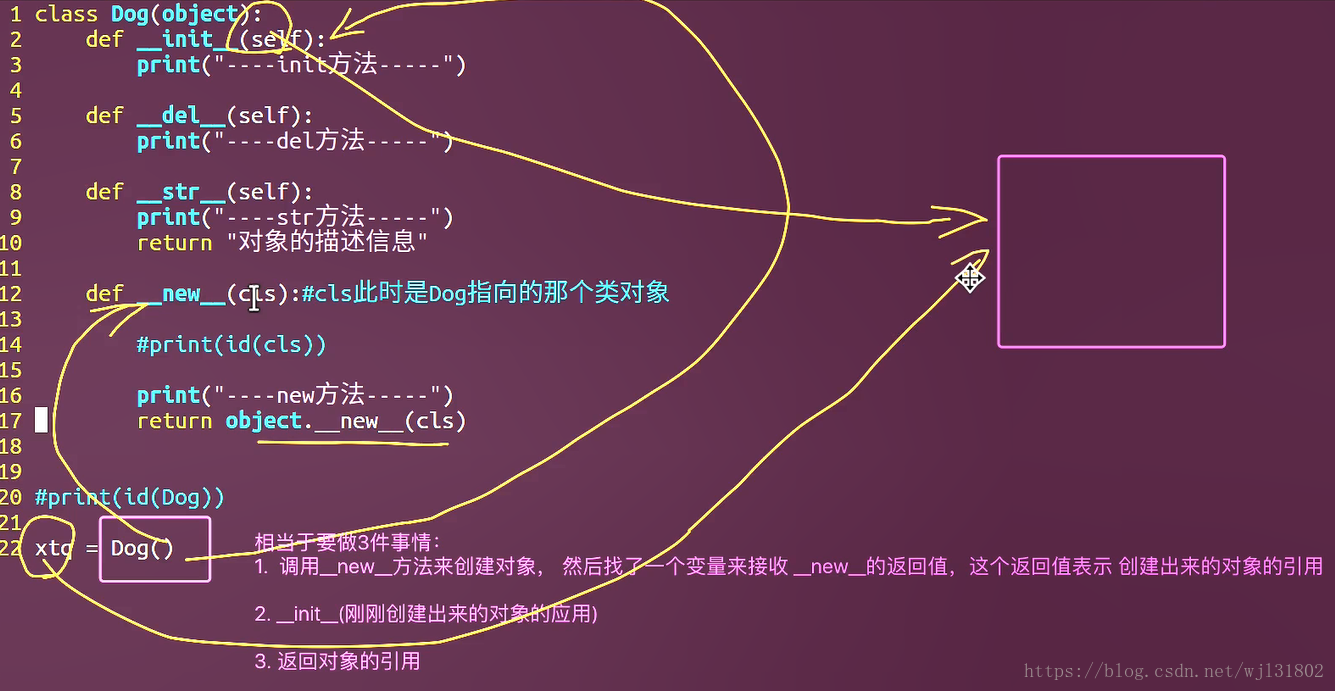
__new__方法
class Dog(object):
def __init__(self):
print("-----init方法-------")
def __del__(self):
print("-----del方法-------")
def __str__(self):
print("-----str方法-------")
def __new__(cls):#cls此时是Dog指向的那个类对象
print(id(cls))
print("-----new方法-------")
#object.__new__(cls)
print(id(Dog))
xtq = Dog()__new__至少要有一个参数cls,代表要实例化的类,此参数在实例化时由python解释器自动提供
__new__必须要有返回值,返回实例化出来的实例,可以return父类__new__出来的实例或者直接object的
__init__有一个参数self,就是这个__new__返回的实例,__init__在__new__的基础上可以完成一些其他初始化的工作,__init__不需要返回值
如果将类比作制造商,__new__方法就是前期的原材料购买环节,__init__就是在原材料的基础上,加工,初始化商品环节
创建单例对象
class Dog(object):
__instance = None
def __new__(cls):
if cls.__instance == None:
cls.__instance = object.__new__(cls)
return cls.__instance
else:
#return 上一次创建对象的引用
return cls.__instance
a = Dog()
print(id(a))
b = Dog()
print(id(b))