1、文件引入是一种单例模式
2、自定义类方法(有代价,告知所有人,以后实例化时,不要再 类(),使用 类.instance() ),无法支持多线程 50分
class Foo(object):
_instance = None
def __init__(self,name):
self.name = name
@classmethod
def instance(cls,*args,**kwargs):
if hasattr(cls,'_instance'):
obj = cls(*args,**kwargs)
setattr(cls,'_instance,obj)
return cls._instance
obj1 = Foo.instance('alex')
obj2 = Foo.instance('alex')
print(id(obj1),id(obj2))
3、自定义类方法(支持多线程)70分

1 import time 2 import threading 3 class Singleton(object): 4 _instance_lock = threading.Lock() 5 6 def __init__(self): 7 time.sleep(1) 8 9 @classmethod 10 def instance(cls, *args, **kwargs): 11 if not hasattr(Singleton, "_instance"): 12 with Singleton._instance_lock: 13 if not hasattr(Singleton, "_instance"): 14 Singleton._instance = Singleton(*args, **kwargs) 15 return Singleton._instance 16 17 18 def task(arg): 19 obj = Singleton.instance() 20 print(obj) 21 for i in range(10): 22 t = threading.Thread(target=task,args=[i,]) 23 t.start() 24 time.sleep(20) 25 obj = Singleton.instance() 26 print(obj)
4、基于__new__方法实现单例模式 80分(对于用户更友好,和普通实例化一样)

# class Singleton(object): # def __init__(self): # print('init',self) # # # def __new__(cls, *args, **kwargs): # o = object.__new__(cls, *args, **kwargs) # print('new',o) # return o # # obj = Singleton() # # print('xxx',obj) #先执行__new__方法,创建对象,再执行__init__方法,再赋值给obj,他们三个打印的对象是一样的。

import time import threading class Singleton(object): _instance_lock = threading.Lock() def __init__(self): pass def __new__(cls, *args, **kwargs): if not hasattr(Singleton, "_instance"): with Singleton._instance_lock: if not hasattr(Singleton, "_instance"): Singleton._instance = object.__new__(cls, *args, **kwargs) return Singleton._instance obj1 = Singleton() obj2 = Singleton() print(obj1,obj2)
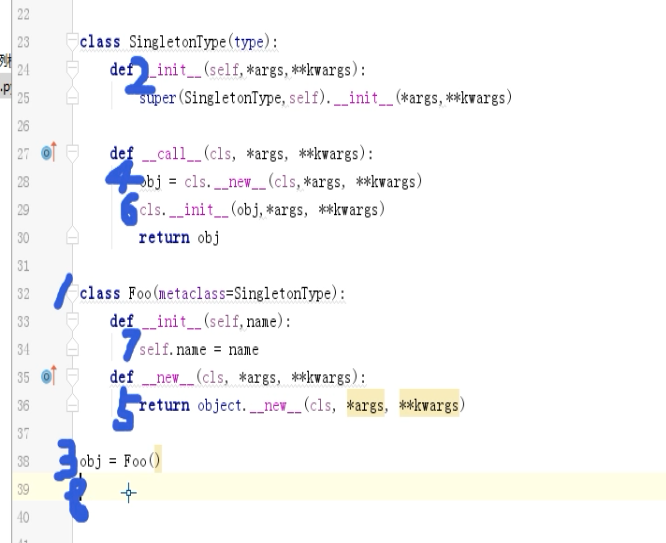
5、基于metaclass方式实现

""" 1.对象是类创建,创建对象时候类的__init__方法自动执行,对象()执行类的 __call__ 方法 2.类是type创建,创建类时候type的__init__方法自动执行,类() 执行type的 __call__方法(类的__new__方法,类的__init__方法) # 第0步: 执行type的 __init__ 方法【类是type的对象】 class Foo: def __init__(self): pass def __call__(self, *args, **kwargs): pass # 第1步: 执行type的 __call__ 方法 # 1.1 调用 Foo类(是type的对象)的 __new__方法,用于创建对象。 # 1.2 调用 Foo类(是type的对象)的 __init__方法,用于对对象初始化。 obj = Foo() # 第2步:执行Foo的 __call__ 方法 obj() """ """ class SingletonType(type): def __init__(self,*args,**kwargs): super(SingletonType,self).__init__(*args,**kwargs) def __call__(cls, *args, **kwargs): obj = cls.__new__(cls,*args, **kwargs) cls.__init__(obj,*args, **kwargs) # Foo.__init__(obj) return obj class Foo(metaclass=SingletonType): def __init__(self,name): self.name = name def __new__(cls, *args, **kwargs): return object.__new__(cls, *args, **kwargs) obj = Foo('name') """
执行顺序:

import threading class SingletonType(type): _instance_lock = threading.Lock() def __call__(cls, *args, **kwargs): if not hasattr(cls, "_instance"): with SingletonType._instance_lock: if not hasattr(cls, "_instance"): cls._instance = super(SingletonType,cls).__call__(*args, **kwargs) return cls._instance class Foo(metaclass=SingletonType): def __init__(self,name): self.name = name obj1 = Foo('name') obj2 = Foo('name') print(obj1,obj2)
