词频统计程序
词频统计程序开发思路。
1.首先创建一个结构体用于存放单词和数目。
2.从文件中以空格为分节符读出一段字符串。
3.对读出的字符串进行处理。
4.将处理后的字符串存放到结构体数组中。
5.对结构体数组进行排序。
代码地址:https://git.coding.net/Vector121/homework.git
首先创建一个结构体,包含单词的和数目。
struct words
{
int num;
char word[40];
};
判断单词是否重复出现过。
int issame(struct words *p, char b[], int n)
{
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
{
if ((strcmp(p[i].word, b)) == 0)
{
return i; //有重复,并返回重复单词的坐标
}
}
return 0; //没有重复
}
字符串处理。
char dispose(char temp[])
{
int j = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < (strlen(temp)); i++)
{
//将大写字符转成小写字母
if (temp[i] >= 65 && temp[i] <= 90)
{
temp[i] = temp[i] + 32;
}
//去除非字母字符
if (temp[i] >= 97 && temp[i] <= 122)
{
temp[j++] = temp[i];
}
}
temp[j] = '�';
return 1;
}
排序。
void sort(struct words str[],int n)
{
for (int i = 1; i < n; i++)
{
for (int j = 0; j < n - 1; j++)
{
if (str[j].num < str[j + 1].num)
{
struct words temp = str[j];
str[j] = str[j + 1];
str[j + 1] = temp;
}
}
}
}
主函数。
int main()
{
int no = 1;
struct words *str = (struct words*)malloc(NUM * sizeof(struct words));
memset(str, 0, NUM);
char filename[200];
scanf("%s", filename);
FILE *fp;
if ((fp = fopen(filename, "r")) == NULL)
{
printf("文件打开失败
");
system("pause");
exit(0);
}
char temp[40]; //临时存放单词
unsigned int n = 0; //标记数组当前的长度
while (feof(fp) == 0)
{
fscanf(fp, "%s", temp); //输入文件名
//字符串过滤
dispose(temp);
if (temp != NULL)
{
int i = 0; //标记返回值
//判断是否有重复
if ((i = issame(str, temp, n)) != 0)
{
//有重复
str[i].num += 1;
}
else
{
//没有重复
sprintf(str[n].word, temp);
str[n].num = 1;
if ((n%NUM) == 0)
{
//no += 1;
str = (struct words*)realloc(str, NUM * ++no * sizeof(struct words));
memset(str, 0, NUM);
}
n++;
}
}
}
fclose(fp);
sort(str, n);
printf("total %d words
", n);
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++)
{
printf("%-20s%-10d
", str[i].word, str[i].num);
n--;
}
system("pause");
}
难点:对于小文件可以直接定义一个字符串数组,但是对于大文件来说,就没有办法预先定义数组的长度,只能采用动态定义的方法。
盲点:由于长时间没有写代码,导致对fscanf()函数有些生疏,进行查阅学习后才熟悉怎么使用。
突破:动态分配内存之前只是听说过理论,但是一直没有实现过,通过这次开发自己实现了这个理论。
总结:上面代码只能实现功能一和功能二,并且在效率上还有有待提高。
功能一:
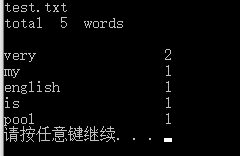
功能二:
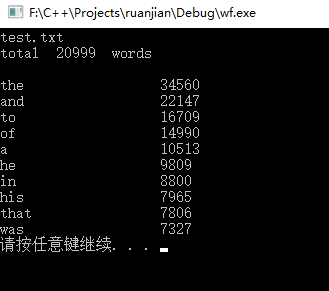
目前只能完成功能一和功能二。
PSP2.1
| PSP2.1 | 预计时间 | 实际时间 | 时间差 | 原因 |
| 计划 | 5分钟 | 5分钟 | 0 | |
| · 估计这个时间需要多少时间 | 5分钟 | 5分钟 | 0 | |
| 开发 | 140分钟 | 444分钟 | 304分钟 | |
| · 设计开发思路 | 10分钟 | 20分钟 | 10分钟 | 长时间没有写代码,所以对自己的能力估计不足。 |
| · 具体编码 | 100分钟 | 350分钟 | 250分钟 | 长时间没有写代码,导致一些知识点生疏,对细节把握不好,例如fscanf()函数的使用,对动态内存分配掌握不扎实。 |
| · 代码复审 | 20分钟 | 43分钟 | 23分钟 | |
| · 测试 | 10分钟 | 31分钟 | 21分钟 | |
| 报告 | 35分钟 | 55分钟 | 20分钟 | |
| · 计算工作量 | 5分钟 | 3分钟 | -2分钟 | |
| · 编写博客 | 30分钟 | 52分钟 | 22分钟 |