简单记录一下CodeQL的一些基础语法
详细请阅读
https://codeql.github.com/docs/ql-language-reference/
QL基础
QL语言
QL是⼀种声明性的,⾯向对象的查询语⾔,经过优化可实现对分层数据结构(尤其是表示软件⼯件的数据
库)的⾼效分析。
数据库是有组织的数据集合。最常⽤的数据库模型是将数据存储在表中的关系模型,⽽SQL(结构化查询
语⾔)是关系数据库最常⽤的查询语⾔。
⾯向对象是QL的重要特征。⾯向对象的好处是众所周知的–它提⾼了模块性,实现了信息隐藏,并允许代
码重⽤。QL在不损害其逻辑基础的情况下提供了所有这些好处。这是通过定义⼀个简单的对象模型实现
的,其中将类建模为谓词,将继承建模为隐含。可⽤于所有受⽀持语⾔的库⼴泛使⽤了类和继承。
QL基本数据类型
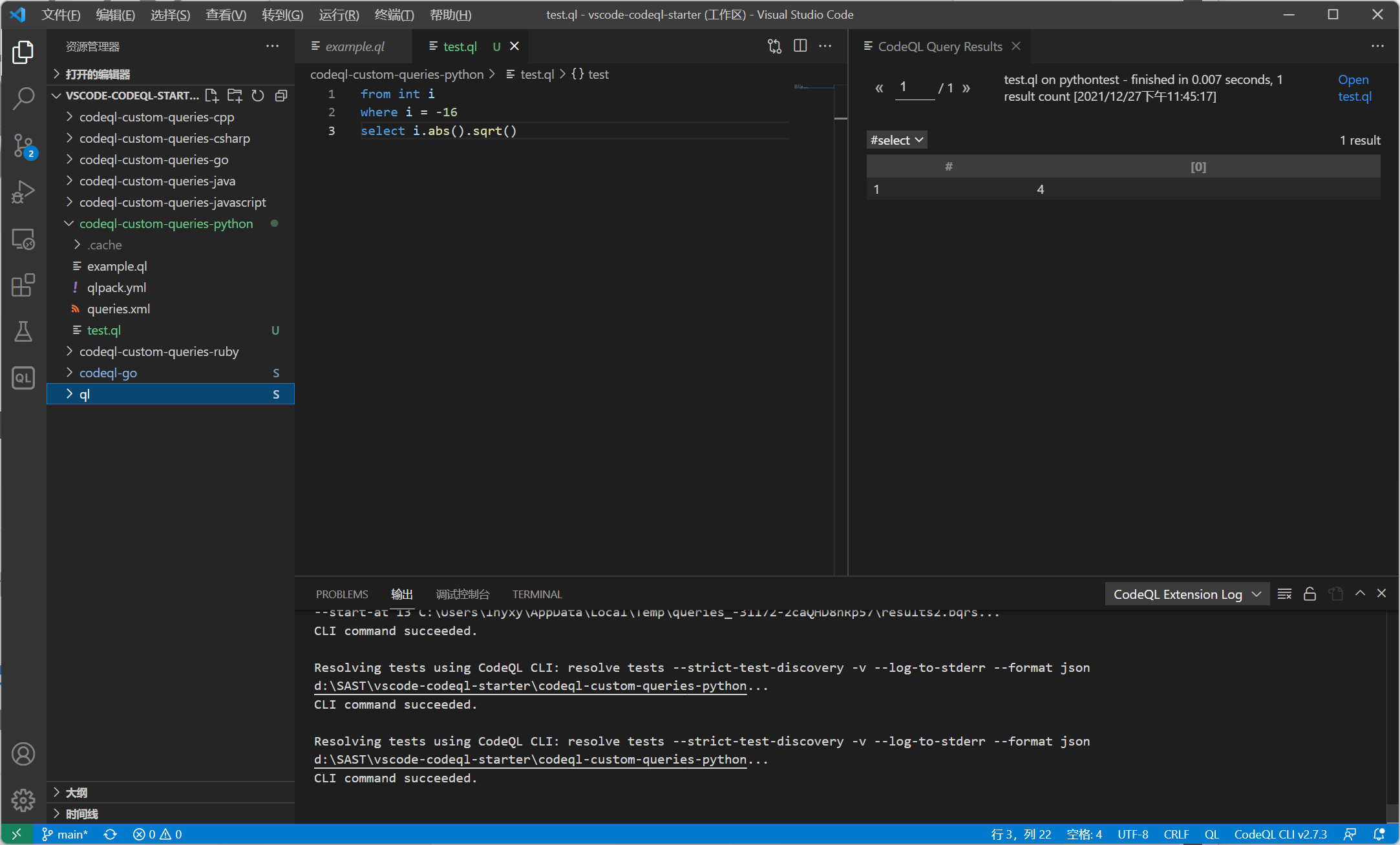
int类型
from int i
where i = -16
select i.abs().sqrt()
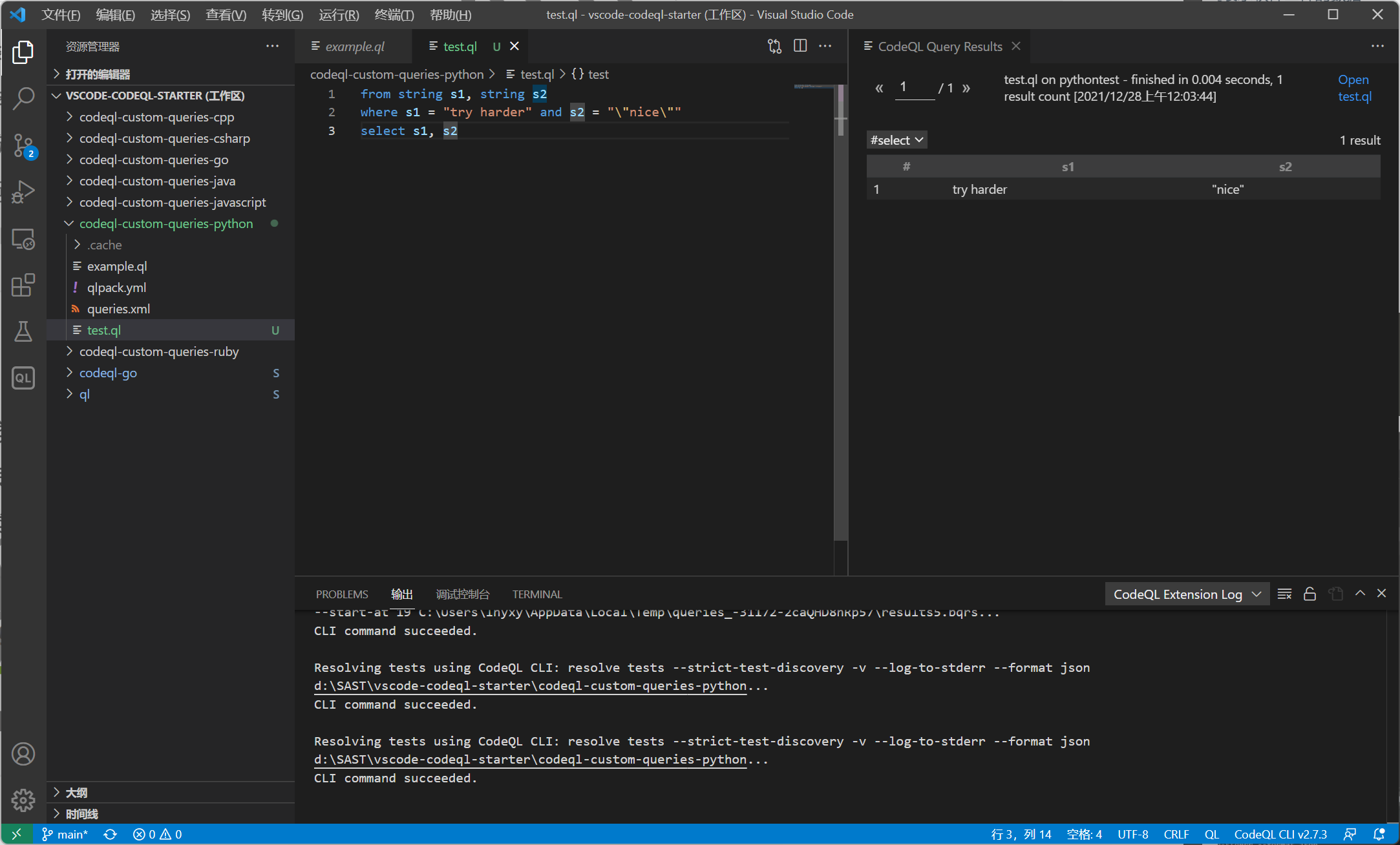
字符串类型
from string s1, string s2
where s1 = "try harder" and s2 = "\"nice\""
select s1, s2
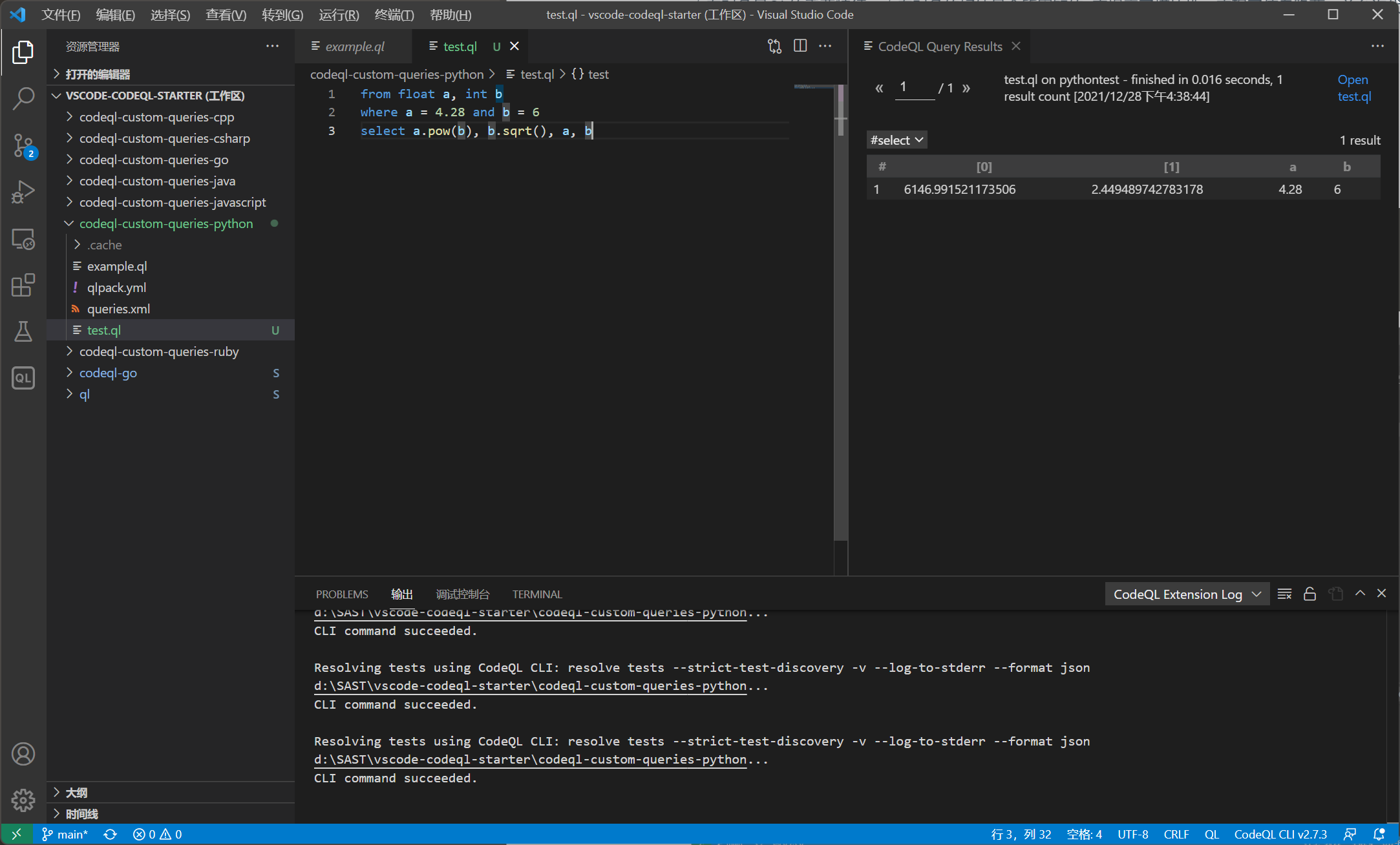
整数和浮点数
from float a, int b
where a = 4.28 and b = 6
select a.pow(b), b.sqrt(), a, b
布尔型
布尔型变量⽤来存放布尔值,即false(假)或者 true(真)。
from boolean b
where b = true
select b.booleanNot(), b.booleanAnd(b)

变量Variable
所有变量声明均由变量的类型和名称组成。名称可以是任何以⼤写或⼩写字⺟开头的标识符。
QL中的变量与代数或逻辑中的变量的使⽤⽅式相似。它们表示⼀组值,这些值通常受公式限制。
变量声明出现在不同的上下⽂中,例如在select⼦句,量化公式内,作为谓词的参数等
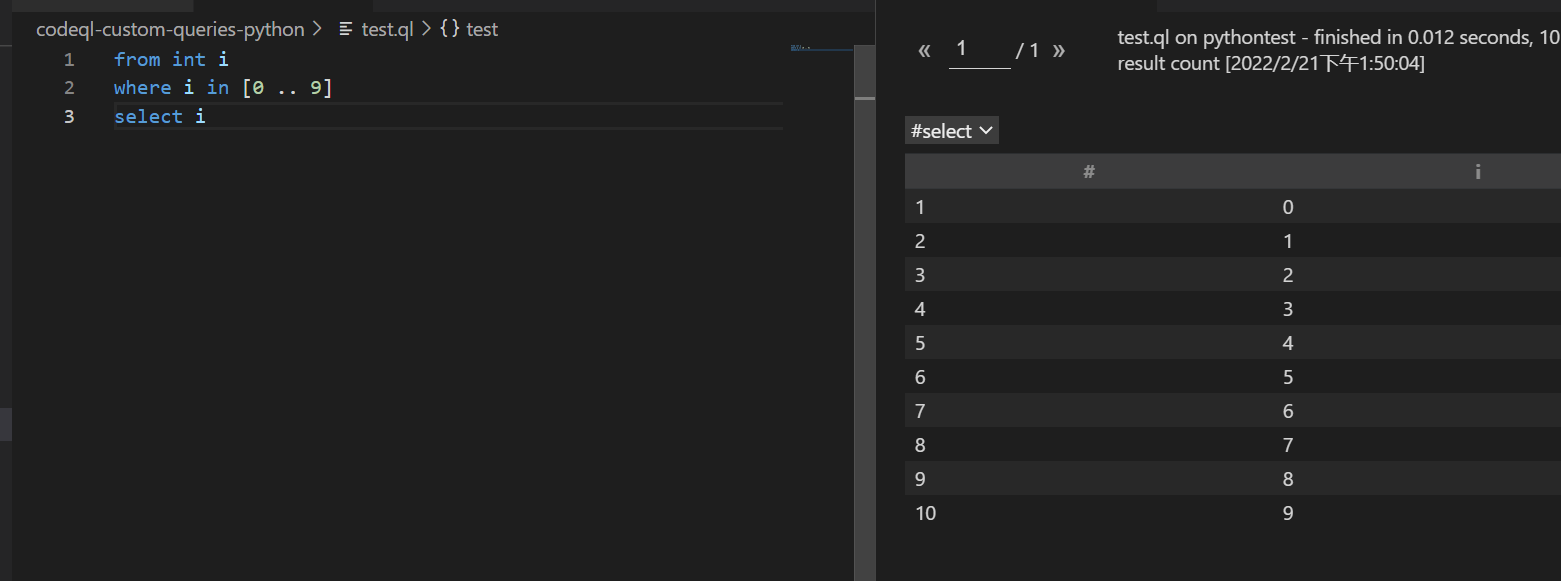
from int i
where i in [0 .. 9]
select i
仅根据其类型,变量 i 可以包含所有整数。但是,它受公式 i in [0 .. 9] 约束。因此,select⼦句的
结果是介于 0 到 9 之间的数字。
自由变量和约束变量
QL中有些变量是free variable,值直接影响使用他们表达式的值,或者使用他们的公式是否成立
有些变量bound variable仅限于特定的值集
"hello".indexOf("l")
min(float f | f in [-3 .. 3])
(i + 7) * 3
x.sqrt()
如上四个表达式
第⼀个表达式没有任何变量。它找到 "l" 字符串中出现位置的(从零开始的)索引 "hello" ,因此它的
结果为 2 和 3 。
第二个表达式有变量f,但是不影响表达式的值为-3。所以f为bound variable
第三,四个表达式值取决于变量的值,所以为free variable
同样,如果⼀个公式包含⾃由变量,则该公式可以保留还是不保留,取决于分配给这些变量的值。
比如(i + 7) * 3 instanceof int
i为自由变量,如果i为整数公式成立,为小数则不成立。
表达式Expressions
表达式的计算结果为⼀组值并具有⼀个类型。
引用变量Variable references
变量引⽤是已声明变量的名称。这种类型的表达式与其所引⽤的变量具有相同的类型。
常量Literal
- 布尔文字
truefalse - 整数文字
0-45 - 浮点文字
1.1314 - 字符串文字
hello
QL中没有“⽇期⽂字”。相反,要指定⼀个date,您应该使⽤ toDate() 谓词将字符串转换为它表示的⽇期。例如, "2016-04-03".toDate() ⽇期是2016年4⽉3⽇,是2000年新年后⼀秒的时间点。 "2000-01-01 00:00:01".toDate()
括号表达式Parenthesis expressions
带括号的表达式是⽤括号 ( 和括起来的表达式 ) 。此表达式的类型和值与原始表达式完全相同。括号可⽤于将表达式分组在⼀起以消除歧义并提⾼可读性。
范围表达式Ranges
它由两个表达式分隔, .. 并⽤⽅括号( [ 和 ] )括起来。例如,是有效的范围表达式。它的值是和之间(包括和本身)之间的任何整数 。 [3 .. 7] 表示3和7内所有的整数在有效范围内,开始和结束表达式是整数,浮点数或⽇期。
常量范围表达式Set literal expressions
可以设置⼀个常量范围表达式,例如: [2, 3, 5, 7, 11, 13, 17, 19, 23, 29] 它表示30以内的质数
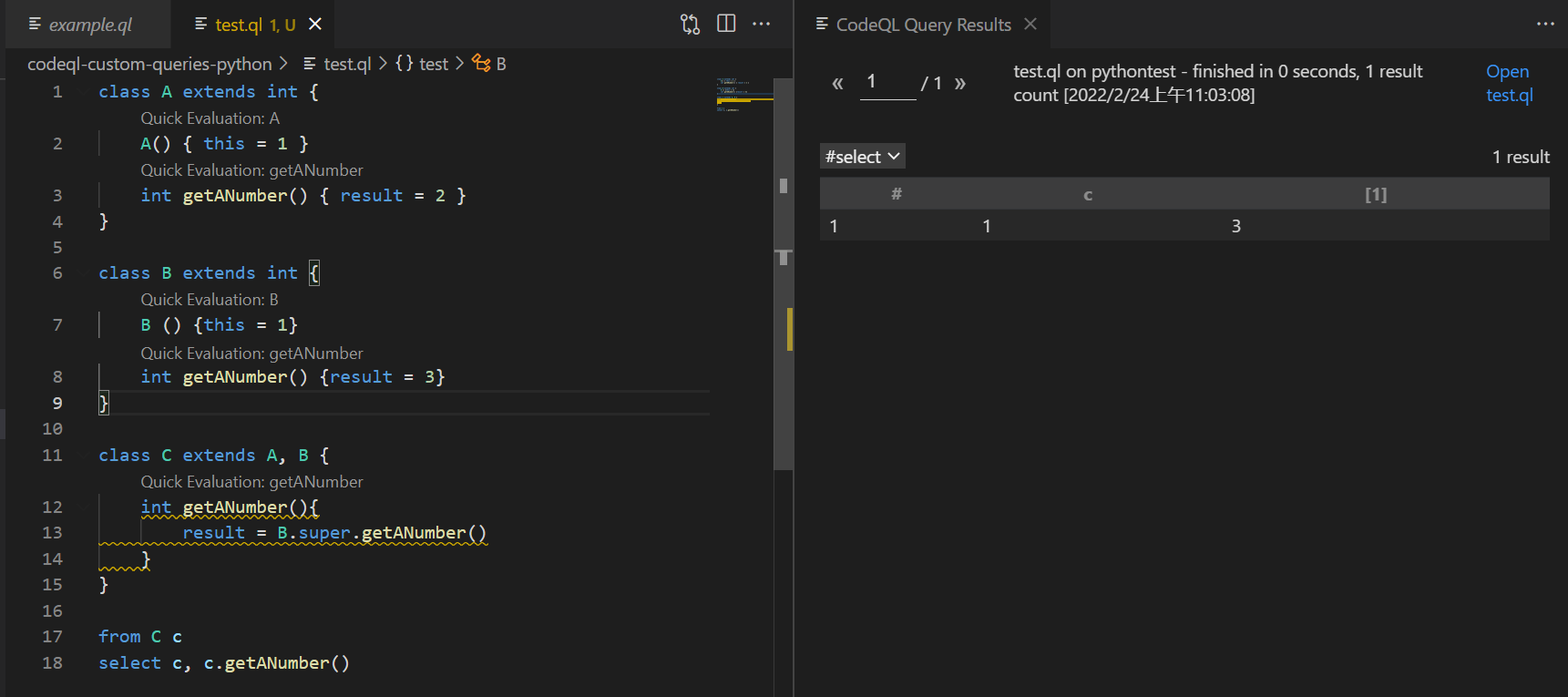
超级表达式Super expressions
当您要使用超类型的谓词定义时,可以在谓词调⽤中使用它们。
class A extends int {
A() { this = 1 }
int getANumber() { result = 2 }
}
class B extends int {
B () {this = 1}
int getANumber() {result = 3}
}
class C extends A, B {
int getANumber(){
result = B.super.getANumber()
}
}
from C c
select c, c.getANumber()
在下面的示例中,该类 C 继承了谓词的两个定义 getANumber() - A ⼀个来⾃和⼀个来自 B 。而不是覆盖两个定义,它使用中的定义 B
聚合Aggregations
<aggregate>(<variable declarations> | <formula> | <expression>)
QL中的汇总
- count
- min,max
- avg
- sum
- concat
- rank
- unique
查询Query
Select子句
from /*...variable declarations...*/
where /*...logical formula...*/
select /*...expressions...*/
from和where部分可选
还有as关键字 order by关键字
from int x, int y
where x = 3 and y in [0 .. 3]
select x, y, x*y as test, "result:" + test

查询谓词
查询谓词是带有注释的非成员谓词query。它返回谓词求值的所有元祖
query int getResult(int x, int y){
x = [1..2] and y = 3 and result = x * y
}

编写查询谓词⽽不是select⼦句的好处是,您也可以在代码的其他部分调⽤谓词。

递归Recursion
例子,输出从0到100的整数
int getANumber(){
result = 0 or result <= 100 and result = getANumber() + 1
}
select getANumber()
相互递归
int getAnEven() {
result = 0 or result <= 100 and result = getAnOdd() +1
}
int getAnOdd() {
result = getAnEven() + 1
}
select getAnEven()

查询从0到100 的偶数
公式
逻辑连接词
- not
- if...then...else
- and
- or
- implies
A implies B和(not A) or B等价
类Class
定义一个类
- 关键字class
- 类的名称,一个以字母开头的标识符
- 要扩展的类型
- 类的主体,用大括号括起来
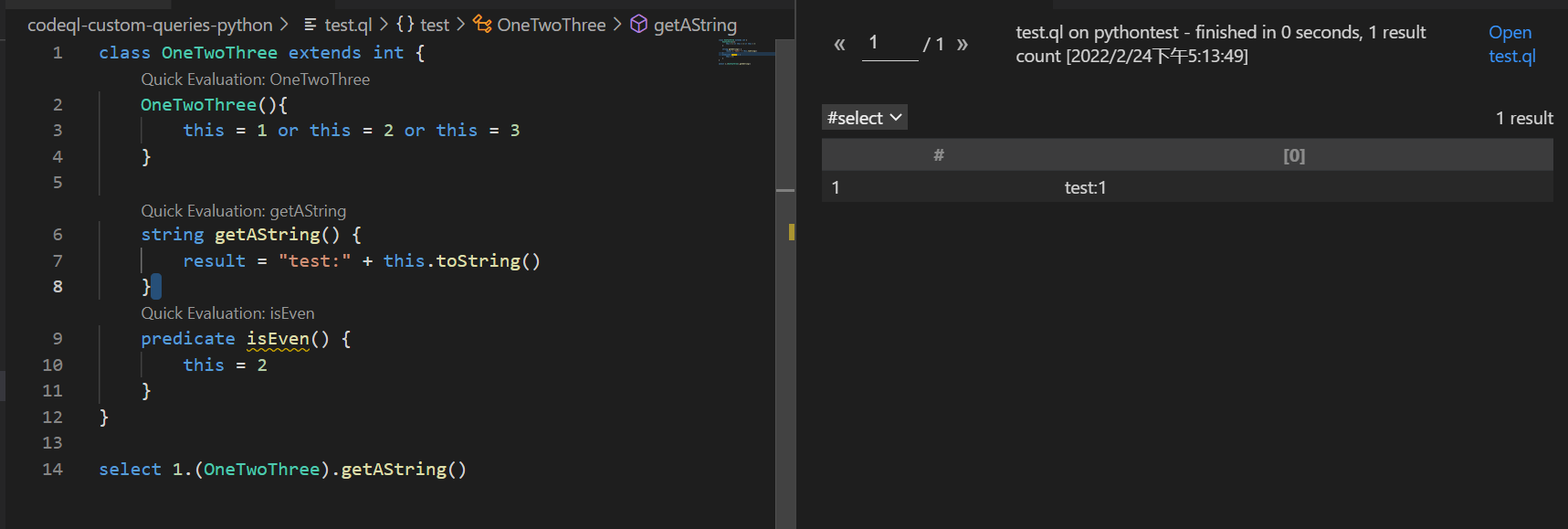
class OneTwoThree extends int {
OneTwoThree(){
this = 1 or this = 2 or this = 3
}
string getAString() {
result = "test:" + this.toString()
}
predicate isEven() {
this = 2
}
}
select 1.(OneTwoThree).getAString()
字段Field
这些是在类主体中声明的变量。⼀个类在其主体内可以具有任意数量的字段声明(即变量声明)。您可以在类内部的谓词声明中使⽤这些变量。就像变量⼀样 this ,字段必须限制在特征谓词中。
class SmallInt extends int {
SmallInt() { this = [1 .. 10] }
}
class DivisibleInt extends SmallInt {
SmallInt divisor;
DivisibleInt(){ this % divisor = 0 }
SmallInt getADivisor() { result = divisor }
}
from DivisibleInt i
select i, i.getADivisor()
在此示例中,声明引⼊了⼀个字段,将其约束在特征谓词中,然后在成员谓词的声明中使⽤它 。这类似于在部分中通过在select语句中声明变量来引⼊变量 。 SmallInt divisor divisor getADivisor from
重写成员谓词
如果类从超类型继承成员谓词,则可以覆盖继承的定义。为此,您可以定义⼀个成员谓词,该成员谓词的名称和别名与继承的谓词相同,并添加 override 注解。
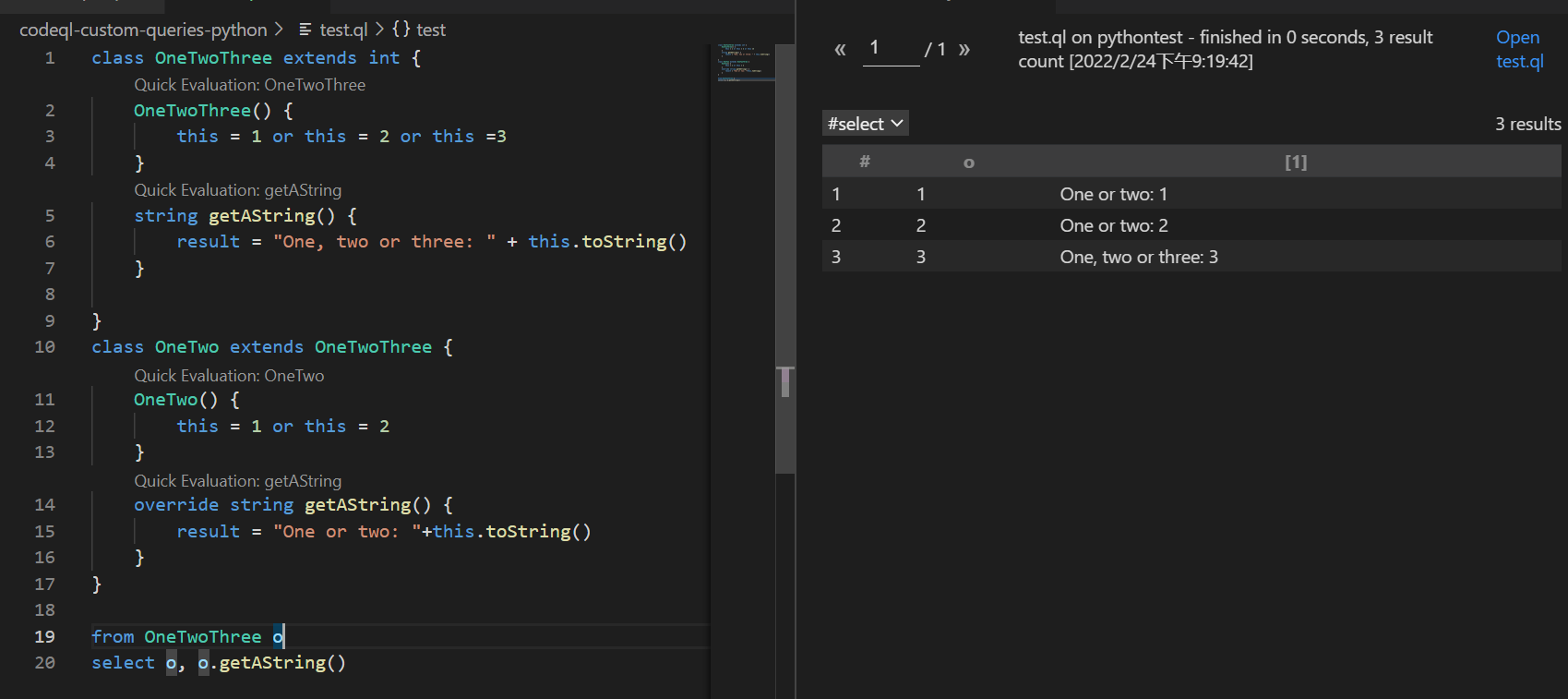
class OneTwoThree extends int {
OneTwoThree() {
this = 1 or this = 2 or this =3
}
string getAString() {
result = "One, two or three: " + this.toString()
}
}
class OneTwo extends OneTwoThree {
OneTwo() {
this = 1 or this = 2
}
override string getAString() {
result = "One or two: "+this.toString()
}
}
from OneTwoThree o
select o, o.getAString()
多重继承
一个类扩展多种类型
class Two extends OneTwo, TwoThree {}
模块modules
文件模块file module
每个查询⽂件(扩展名 .ql )和库⽂件(扩展名 .qll )都隐式定义了⼀个模块。模块的名称与⽂件相同,但⽂件名中的所有空格均由下划线( _ )代替。⽂件的内容构成模块的主体。
库模块Library module
有.qll文件定义。除select子句外,它可以包含下面模块主体列出的任何元素
查询模块Query module
由.ql文件定义
- 查询模块无法导入
- 一个查询模块在其namespace中必须有一个查询。通常是select子句,也可以是查询谓词
谓词Predicates
定义谓词条件:
- 关键字predicate或者结果类型
- 谓词的名称
- 谓词的参数
- 谓词体本身
谓词种类
非成员谓词,成员谓词,特征谓词
int getSuccessor(int i){// 1. Non-member predicate
result = i + 1 and
i in [1 .. 9]
}
class FavoriteNumbers extends int {// 2. Characteristic predicate
FavoriteNumbers() {
this = 1 or this = 4 or this = 9
}
string getName() {// 3. Member predicate for the class `FavoriteNumbers`
this = 1 and result = "one"
or
this = 4 and result = "four"
or
this = 9 and result = "nine"
}
}
from int i
where i = 9
select getSuccessor(i)

int getSuccessor(int i){
result = i + 1 and
i in [1 .. 9]
}
class FavoriteNumbers extends int {
FavoriteNumbers() {
this = 1 or this = 4 or this = 9
}
string getName() {
this = 1 and result = "one"
or
this = 4 and result = "four"
or
this = 9 and result = "nine"
}
}
from FavoriteNumbers f
select f, f.getName()
