Specifications 基本原则
A specification is a named, reusable, combinable and testable class to filter the Domain Objects based on the business rules.
一个规范是一个已命名的、可重用的、可组合的和可测试的类,用于根据业务规则过滤领域对象。
ABP Framework provides necessary infrastructure to easily create specification classes and use them inside your application code. Let's implement the in-active issue filter as a specification class:
ABP框架提供了必要的基础设施来轻松创建规范类并在你的应用程序代码中使用它们。让我们把处于活动状态的问题过滤器实现为一个规范类:
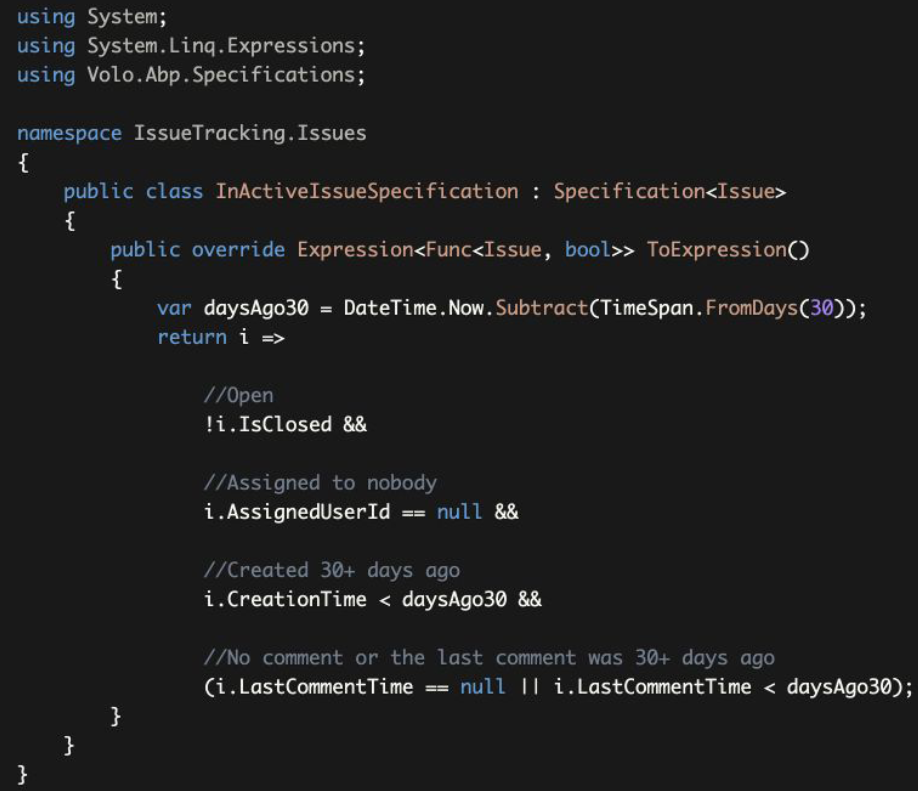
Specification<T> base class simplifies to create a specification class by defining an expression. Just moved the expression here, from the repository.
Specification<T>基类简化了通过定义一个表达式来创建一个规范类。只是把表达式从存储库中移到了这里。
Now, we can re-use the InActiveIssueSpecification in the Issue entity and EfCoreIssueRepository classes.
现在,我们可以在Issue实体和EfCoreIssueRepository类中重新使用InActiveIssueSpecification。
Using within the Entity 在实体内部使用
Specification class provides an IsSatisfiedBy method that returns true if the given object (entity) satisfies the specification. We can re-write the Issue.IsInActive method as shown below:
Specification类提供了一个IsSatisfiedBy方法,如果给定的对象(实体)满足该规范,则返回true。我们可以重新编写Issue.IsInActive方法,如下所示:
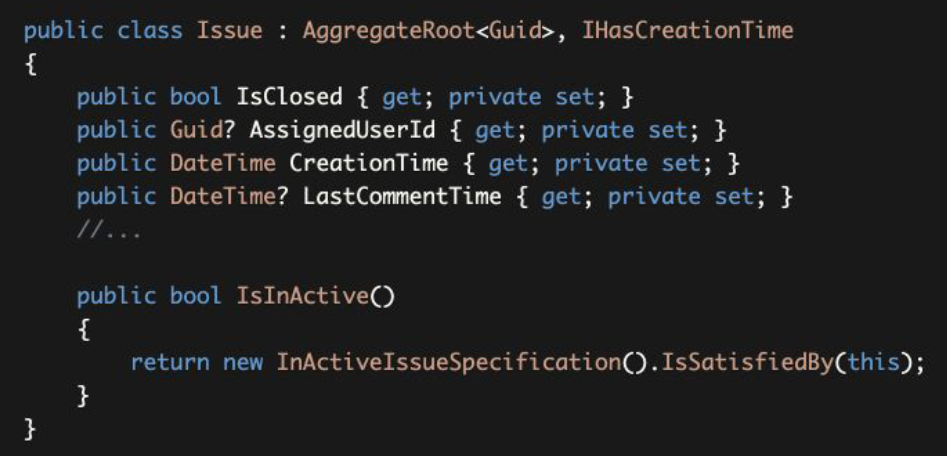
Just created a new instance of the InActiveIssueSpecification and used its IsSatisfiedBy method to re-use the expression defined by the specification.
仅创建了一个InActiveIssueSpecification的新实例,并使用其IsSatisfiedBy方法来重新使用该规范所定义的表达式。
Using with the Repositories 与存储库一起使用
First, starting from the repository interface:
首先,从存储库接口开始:
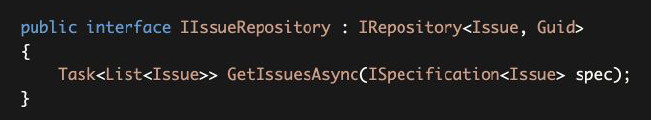
Renamed GetInActiveIssuesAsync to simple GetIssuesAsync by taking a specification object. Since the specification (the filter) has been moved out of the repository, we no longer need to create different methods to get issues with different conditions (like GetAssignedIssues(...), GetLockedIssues(...), etc.)
通过接受一个规范对象,将 GetInActiveIssuesAsync 重命名为简单的 GetIssuesAsync。由于规范(过滤器)已被移出存储库,我们不再需要创建不同的方法来获取不同条件的问题(像GetAssignedIssues(...), GetLockedIssues(...)等)。
Updated implementation of the repository can be like that:
更新后的存储库的实现可以是这样的:
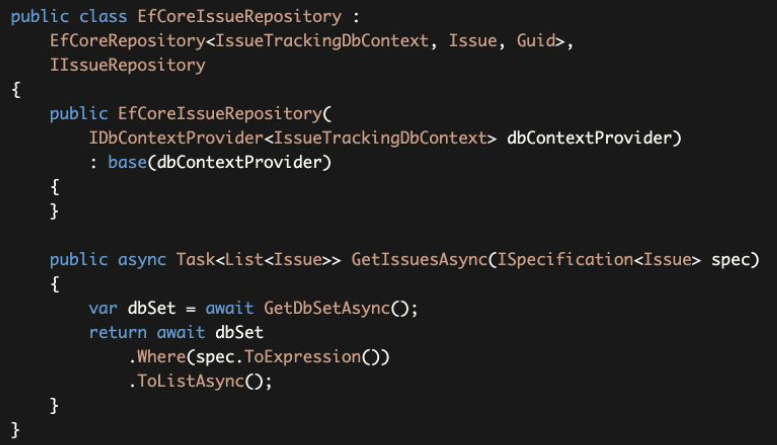
Since ToExpression() method returns an expression, it can be directly passed to the Where method to filter the entities.
由于ToExpression()方法返回一个表达式,它可以直接传递给Where方法来过滤实体。
Finally, we can pass any Specification instance to the GetIssuesAsync method:
最后,我们可以将任何规范实例传递给GetIssuesAsync方法:
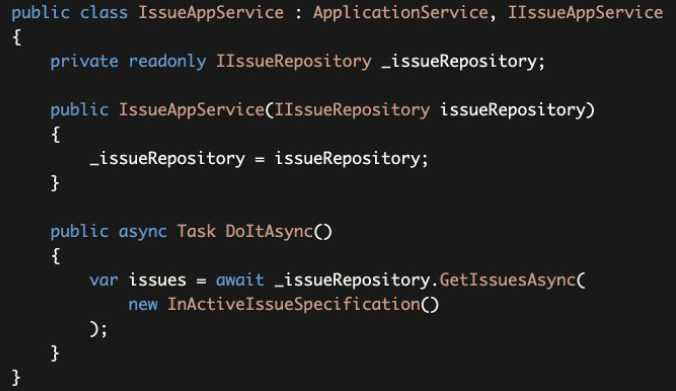
With Default Repositories 使用默认存储库
Actually, you don't have to create custom repositories to be able to use specifications. The standard IRepository already extends the IQueryable, so you can use the standard LINQ extension methods over it:
实际上,你不需要创建自定义的资源库就能使用规范。标准的IRepository已经扩展了IQueryable,所以你可以在标准的LINQ扩展方法中使用它。
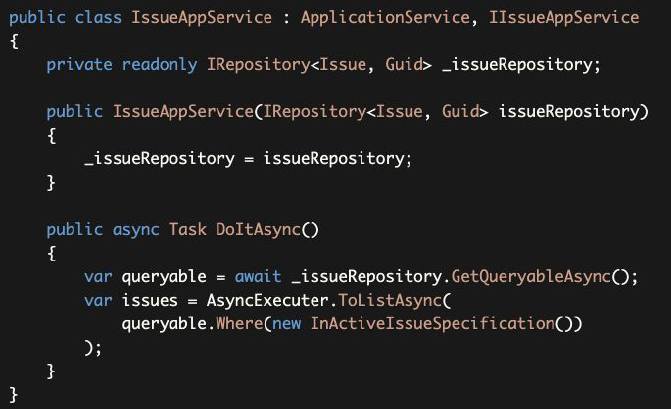
AsyncExecuter is a utility provided by the ABP Framework to use asynchronous LINQ extension methods (like ToListAsync here) without depending on the EF Core NuGet package. See the Repositories document for more information.
AsyncExecuter是ABP框架提供的一个工具,用于使用异步LINQ扩展方法(比如这里的ToListAsync),而不依赖于EF Core NuGet包。更多信息请参见Repositories文档。
Combining the Specifications 规范原则
One powerful side of the Specifications is they are combinable. Assume that we have another specification that returns true only if the Issue is in a Milestone:
规范的一个强大方面是它们是可以组合的。假设我们有另一个的规范要求Issue处于Milestone时返回true:
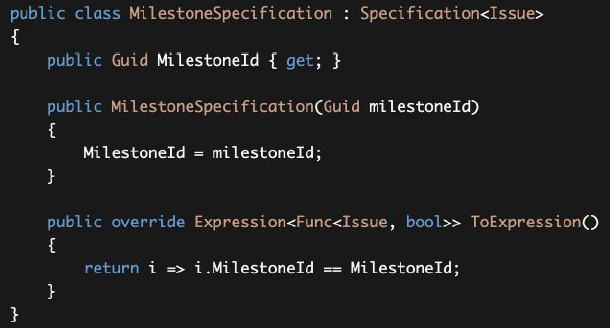
This Specification is parametric as a difference from the InActiveIssueSpecification. We can combine both specifications to get a list of inactive issues in a specific milestone:
这个规范是参数化的,与InActiveIssueSpecification不同。我们可以结合这两个规范来获得一个特定里程碑中的非活动问题的列表:
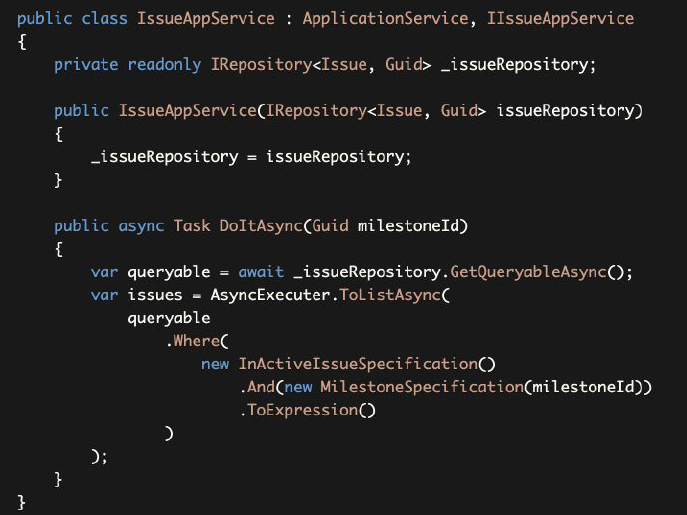
The example above uses the And extension method to combine the specifications. There are more combining methods are available, like Or(...) and AndNot(...).
上面的例子使用了And扩展方法来组合规范。还有更多的组合方法可用,如Or(...)和AndNot(...)。
See the Specifications document for more details about the specification infrastructure provided by the ABP Framework.
关于ABP框架所提供的规范基础设施的更多细节,请参见规范文档。