前言
最近在实习,任务并不是很重,就利用闲暇时间使用Python3在PAT网站上刷题,并致力于使用Python3的特性和函数式编程的理念,其中大部分题目都有着类似的输入输出格式,例如一行读入若干个数字,字符串,每行输出多少个字符串等等,所以产生了很多重复的代码。
Python代码
于是我就利用VS Code的代码片段功能编写了一个用于处理这些输入输出的代码框架,并加入了测试功能(写函数前先写测试时正确的事情)。代码如下
"""Simple Console Program With Data Input And Output."""
import sys
import io
def read_int():
"""Read a seris of numbers."""
return list(map(int, sys.stdin.readline().split()))
def test_read_int():
"""Test the read_int function"""
test_file = io.StringIO("1 2 3
")
sys.stdin = test_file
assert read_int() == [1, 2, 3], "read_int error"
def read_float():
"""Read a seris of float numbers."""
return list(map(float, sys.stdin.readline().split()))
def test_read_float():
"""Test the read_float function"""
test_file = io.StringIO("1 2 3
")
sys.stdin = test_file
assert read_float() == [1.0, 2.0, 3.0], "read_float error"
def read_word():
"""Read a seris of string."""
return list(map(str, sys.stdin.readline().split()))
def test_read_word():
"""Test the read_word function"""
test_file = io.StringIO("1 2 3
")
sys.stdin = test_file
assert read_word() == ["1", "2", "3"], "read_word error"
def combine_with(seq, sep=' ', num=None):
"""Combine list enum with a character and return the string object"""
res = sep.join(list(map(str, seq)))
if num is not None:
res = str(seq[0])
for element in range(1, len(seq)):
res += sep +
str(seq[element]) if element % num != 0 else '
' +
str(seq[element])
return res
def test_combile_with():
"""Test the combile_with function."""
assert combine_with([1, 2, 3, 4, 5], '*', 2) == """1*2 3*4 5""", "combine_with error."
def main():
"""The main function."""
pass
if __name__ == '__main__':
sys.exit(int(main() or 0))
VS Code代码片段
添加到VS Code的默认代码片段的操作大致如下:
- 文件->首选项->用户代码片段,选择Python
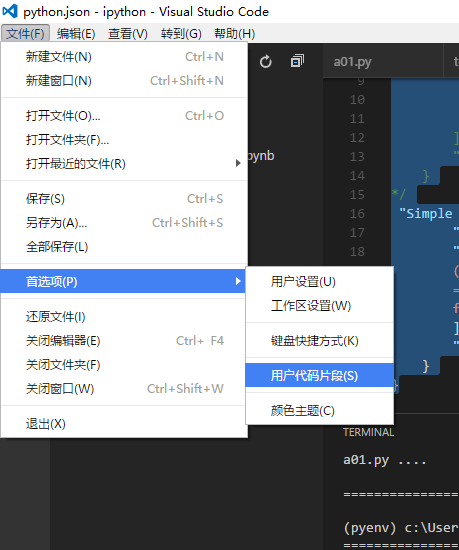
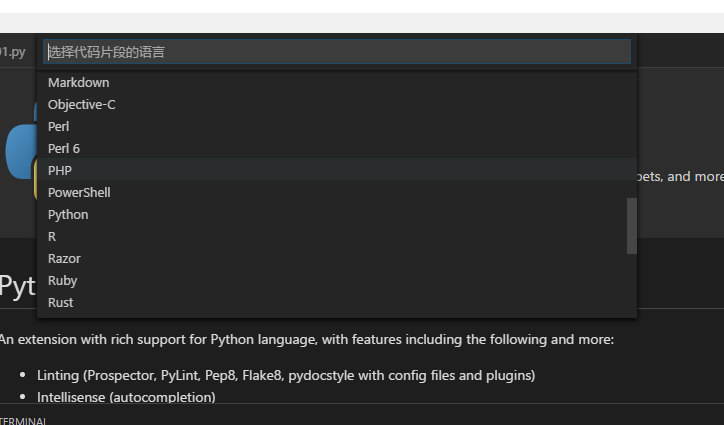
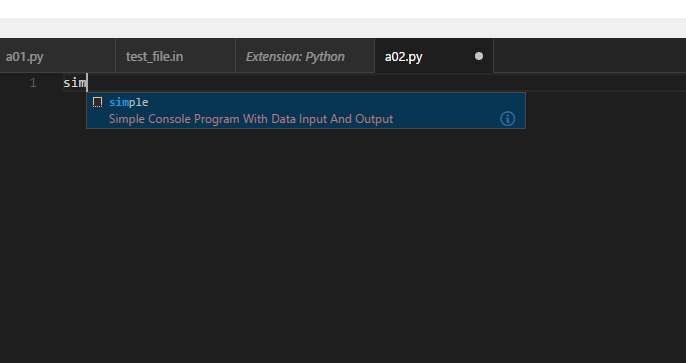
- 编辑"python.json"文件如以下内容
{ /* // Place your snippets for Python here. Each snippet is defined under a snippet name and has a prefix, body and // description. The prefix is what is used to trigger the snippet and the body will be expanded and inserted. Possible variables are: // $1, $2 for tab stops, ${id} and ${id:label} and ${1:label} for variables. Variables with the same id are connected. // Example: "Print to console": { "prefix": "log", "body": [ "console.log('$1');", "$2" ], "description": "Log output to console" } */ "Simple Console Program With Data Input And Output": { "prefix": "simple", "body": [""""Simple Console Program With Data Input And Output.""" import sys def read_int(): """Read a seris of numbers.""" return list(map(int, sys.stdin.readline().split())) def read_float(): """Read a seris of float numbers.""" return list(map(float, sys.stdin.readline().split())) def read_word(): """Read a seris of string.""" return list(map(str, sys.stdin.readline().split())) def combine_with(seq, sep=' ', num=None): """Combine list enum with a character and return the string object""" res = sep.join(list(map(str, seq))) if num is not None: res = str(seq[0]) for element in range(1, len(seq)): res += sep + str(seq[element]) if element % num != 0 else '\n' + str(seq[element]) return res def main(): """The main function.""" pass if __name__ == '__main__': sys.exit(int(main() or 0)) " ], "description": "Simple Console Program With Data Input And Output" } }
总结
虽然Python不是特别适合解答算法题目这种性能要求很高的场景,但是在一些模拟题目如各种排队型和字符串处理的条件下,使用Python可以极大地提高解体效率,另外还可以使用cimport使用C语言的数据结构和Python的语法特性,效率不弱于原生C代码。