一、项目中对于线程池的应用
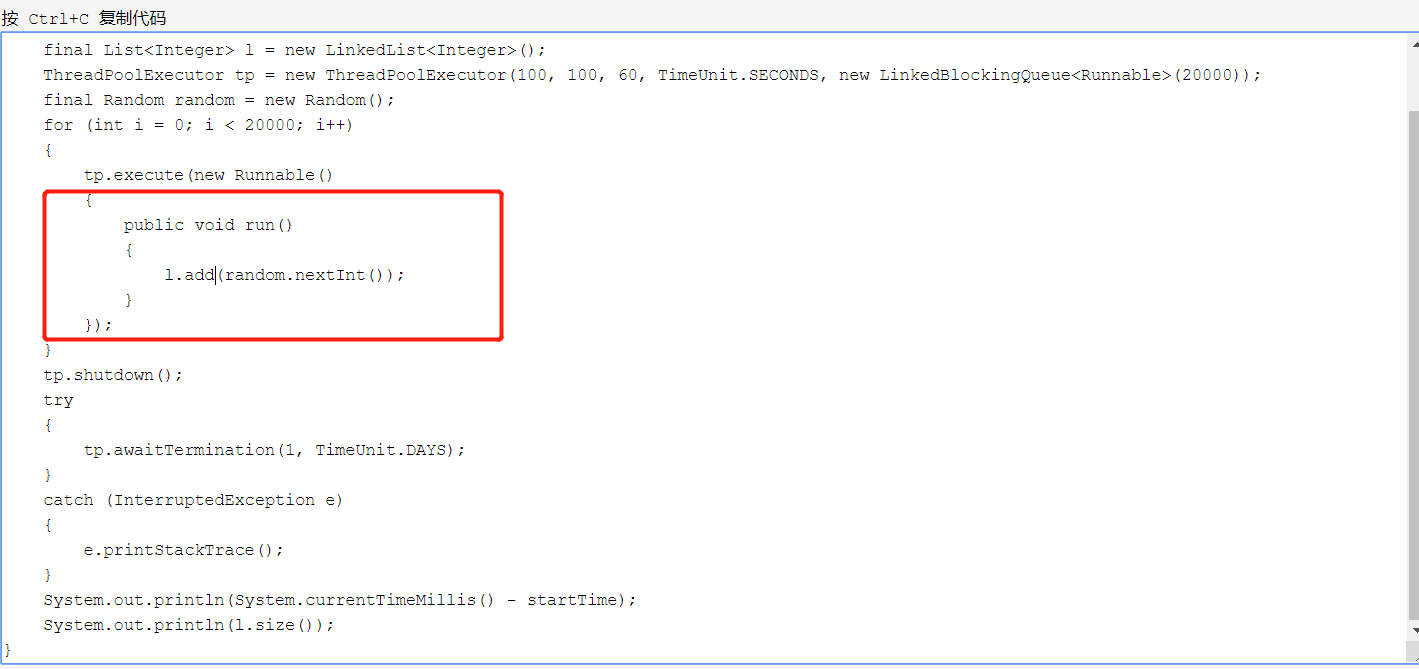
1、通过上一章,我们可以看到,最简单的线程池是如何创建,如何执行的。execute()里的参数是一个继承Thread类或实现了Runnable接口的线程。需要用到线程池的逻辑是放在这个线程的run()方法里的。例如第一个例子中,通过for循环,创建了20000个线程,这20000个线程通过线程池来执行,线程越多,run()方法里需要处理的逻辑越复杂,数据量越大,越能体现线程池的效率。
2、上面可能说的有点乱,但是整体的意思就是说明在哪里用到了线程池及为什么要用线程池。
3、下面通过准备金系统具体的例子来说明对线程池的应用。
二、A系统的佣兵*方法
2.1 前言
A系统的佣兵*任务执行工具,就是针对线程池,开发出来的一套多线程执行工具
2.2 佣兵
1 package com.asd.common.mission.mercenary; 2 4 import com.asd.common.mission.methodHandler.MethodManager; 5 import com.asd.common.mission.mission.Mission; 6 import com.asd.common.mission.missionHandler.MissionHandleListener; 7 import com.asd.common.mission.missionHandler.MissionHandlerAOP; 8 9 /** 10 * 佣兵 11 * @author 69420 12 * 13 */ 14 public class Mercenary implements Runnable{ 15 private MethodManager methodManager; 16 private String methodName; 17 private Mission mission; 18 private MissionHandlerAOP handlerAOP; 19 private MissionHandleListener missionHandleListener; 20 21 /** 22 * @param methodManager 处理工具 23 * @param handlerAOP 切面方法 24 * @param missionHandleListener 监听器 25 * @param methodName 处理方法 26 * @param mission 任务 27 */ 28 public Mercenary(MethodManager methodManager, 29 MissionHandlerAOP handlerAOP, 30 MissionHandleListener missionHandleListener, 31 String methodName,Mission mission) { 32 this.methodManager = methodManager; 33 this.handlerAOP = handlerAOP; 34 this.missionHandleListener = missionHandleListener; 35 this.methodName = methodName; 36 this.mission = mission; 37 } 38 39 public void run() { 40 try { 41 if(handlerAOP!=null){ 42 handlerAOP.handleBefore(mission); 43 } 44 if(missionHandleListener!=null){ 45 missionHandleListener.handleBefore(mission); 46 } 47 execute(); 48 if(handlerAOP!=null){ 49 handlerAOP.handleAfter(mission); 50 } 51 if(missionHandleListener!=null){ 52 missionHandleListener.handleAfter(mission); 53 } 54 } catch (Exception e) { 55 e.printStackTrace(); 56 if(handlerAOP!=null){ 57 handlerAOP.handleException(mission,e); 58 } 59 if(missionHandleListener!=null){ 60 missionHandleListener.handleException(mission,e); 61 } 62 } 63 } 64 65 /** 66 * 执行一个任务 67 * @throws Exception 68 */ 69 public void execute() throws Exception{ 70 methodManager.execute(methodName, mission); 71 } 72 75 }
1、佣兵,意思很浅显,就是用来干活的。
这个佣兵其实就相当于上一章中的如下图标红处的代码。在A系统的多线程工具中,单独抽取取来,封装了一个佣兵类多线程,因为在实际的程序里,业务逻辑一定会特别复杂,只用好的封装,才更有复用性。
2、可以看到,这个多线程类中,任务(方法名)是当作参数传进来的。这就体现了封装的好处,将一切逻辑相关的东西,都封装在了任务里,下面会对任务进行详细说明。
3、这个方法里封装了通过反射执行方法的代码,见标蓝的代码。这里的任务均指的需要通过线程池来执行的方法,下面不再进行说明。
还可以看到,任务执行前后的切面方法与监听,都是在这里调用的,这里不对监听和切面方法做重点说明了。
4、方法经理
package com.asd.common.mission.methodHandler; public class MethodManagerFactory { /** * 获取方法管理工具 * @param handler * @return */ public static MethodManager getMethodManager(Handler handler){ MethodManager mm = new MethodManager(); mm.init(handler); return mm; } }
1 package com.asd.common.mission.methodHandler; 2 3 import com.asd.common.utils.method.MethodUtils; 4 5 import java.lang.reflect.Method; 6 import java.util.HashMap; 7 import java.util.List; 8 import java.util.Map; 9 10 11 public class MethodManager { 12 private Map<String, Method> methodMap = null; 13 private Handler handler; 14 /** 15 * 初始化 16 * @param handler 17 */ 18 public void init(Handler handler){ 19 this.handler = handler; 20 List<Method> methodList = MethodUtils.getMethods(handler); 21 methodMap = new HashMap<String, Method>(); 22 for (Method method : methodList) { 23 if(method.isAnnotationPresent(MethodHandler.class)){ 24 //System.out.println(method.getAnnotation(MethodHandler.class).value()); 25 methodMap.put(method.getAnnotation(MethodHandler.class).value(), 26 method); 27 } 28 } 29 } 30 /** 31 * 执行一个方法 32 * @param channel 订阅号 33 * @param param 参数 34 */ 35 public void execute(String channel, Object... param) throws Exception{ 36 if(methodMap==null){ 37 return; 38 } 39 Method mt = methodMap.get(channel); 40 MethodUtils.executeMethod(handler, mt, param); 41 } 42 }
方法工具类

1 package com.asd.common.utils.method; 2 3 import com.asd.common.utils.object.ClassUtils; 4 5 import java.lang.reflect.Method; 6 import java.util.ArrayList; 7 import java.util.HashMap; 8 import java.util.List; 9 import java.util.Map; 10 import java.util.concurrent.ConcurrentHashMap; 11 12 13 /** 方法工具,通过反射操作方法,均为静态调用 14 * 15 * @author lmaos 16 * 2016年11月14日 上午10:50:12 17 */ 18 public class MethodUtils { 19 /** 方法缓存 初始时申请128长度,保证允许更多的线程同时访问 20 * 21 */ 22 protected static Map<Class, Map<String,Method>> methodCache = new ConcurrentHashMap<Class, Map<String,Method>>(128); 23 private static Object MethodCacheLock = new Object(); 24 25 /** 生成一个方法的key 26 * 27 * @param method 28 * @return 29 */ 30 public static String getMethodKey(Method method){ 31 String key = getMethodKey(method.getName(), method.getParameterTypes()); 32 return key; 33 } 34 35 /** 生成一个方法的key 36 * 37 * @param method 38 * @param params 39 * @return 40 */ 41 public static String getMethodKey(String method,Class... params){ 42 StringBuffer key_buf = new StringBuffer(method); 43 if(params!=null&¶ms.length>0){ 44 for (Class param : params) { 45 key_buf.append(param.hashCode()).append(","); // 通过hashcode确定方法key。 46 // key_buf.append(param.getName()).append(","); // 通过方法名确定方法key。 47 } 48 key_buf.replace(key_buf.length()-1, key_buf.length(), ""); 49 } 50 String key = key_buf.toString(); 51 return key; 52 } 53 /** 添加一个方法的缓存。。 54 * 55 * @param clazz 56 * @param method 57 * @param replace 如果true 则如果存在这个key指向的方法则替换。如果false 则不替换 58 */ 59 public static void addMethodCache(Class clazz,Method method){ 60 61 Map<String,Method> subMethodCache = methodCache.get(clazz); // 获取这个子缓存 62 if(subMethodCache == null){ 63 synchronized (MethodCacheLock) { // 此处同步不会有第二个线程同时操作 64 subMethodCache = methodCache.get(clazz); 65 if(subMethodCache == null){ // 确定缓存不存在 66 subMethodCache = new HashMap<String,Method>(); 67 methodCache.put(clazz, subMethodCache); 68 } 69 } 70 } 71 String key = getMethodKey(method); 72 if(!subMethodCache.containsKey(key)){ 73 subMethodCache.put(key, method); 74 } 75 } 76 77 /** 从缓存获取当前方法 78 * 79 * @param clazz 80 * @param name 81 * @param params 携带参数类型 82 * @return 83 */ 84 protected static Method getMethodByCache(Class clazz, String name, Class... params){ 85 Map<String,Method> subMethodCache = methodCache.get(clazz); // 获取这个子缓存 86 Method method = null; 87 if(subMethodCache!=null){ 88 method = subMethodCache.get(getMethodKey(name, params)); 89 } 90 return method; 91 } 92 93 protected static List<Method> getMethodsByCache(Class clazz){ 94 Map<String,Method> subMethodCache = methodCache.get(clazz); // 获取这个子缓存 95 List<Method> methods = new ArrayList<Method>(); 96 if(subMethodCache!=null){ 97 methods.addAll(subMethodCache.values()); 98 } 99 return methods; 100 } 101 102 103 104 // 加载方法到同步锁,多线程时候线程安全 105 protected final static Object loadMethodsLock = new Object(); 106 /** 加载全部都方法到缓存中。 107 * 108 * @param clazz 109 */ 110 public static void loadAllMethods(Class clazz,boolean replace){ 111 synchronized (loadMethodsLock) { 112 113 /* *********************************************************** * 114 * 如果不存在当前缓存,则首先查询当前类所有继承的类。 115 * 得到所有继承的类后装载所有放假,会从子类一直加载到继承的父类上。 116 * *********************************************************** */ 117 if(!methodCache.containsKey(clazz)){ 118 Map<String,Method> subMethodCache = new HashMap<String, Method>(); 119 List<Class> classs = ClassUtils.getClassAll(clazz, false); 120 for (Class cl : classs) { 121 Method[] methods = cl.getDeclaredMethods(); 122 for (Method method : methods) { 123 method.setAccessible(true); // 设置访问权限,设置为true 则可以对这个方法非法修改与访问 124 String key = getMethodKey(method); 125 if(!subMethodCache.containsKey(key)){ 126 subMethodCache.put(key, method); 127 } 128 // addMethodCache(clazz, method); 129 } 130 } // for-end 131 methodCache.put(clazz, subMethodCache); 132 }else if(replace){ // 替换操作 133 134 Map<String,Method> subMethodCache = new HashMap<String,Method>(); 135 136 List<Class> classs = ClassUtils.getClassAll(clazz, true); 137 for (Class cl : classs) { 138 Method[] methods = cl.getDeclaredMethods(); 139 for (Method method : methods) { 140 String key = method.getName(); 141 method.setAccessible(true); // 设置访问权限,设置为true 则可以对这个字段非法修改与访问 142 subMethodCache.put(key, method); 143 } 144 } // for-end 145 methodCache.put(clazz, subMethodCache); //替换方法缓存 146 } 147 } 148 } 149 150 /** 加载全部都方法到缓存中。 151 * 152 * @param clazz 153 */ 154 public static void loadAllMethods(Class clazz){ 155 loadAllMethods(clazz, false); 156 } 157 158 159 160 161 162 163 164 165 /** 获取方法 166 * 167 * @param clazz 168 * @param name 169 * @return 170 */ 171 public static Method getMethod(Class clazz,String name, Class... params){ 172 173 if(!methodCache.containsKey(clazz)){ 174 loadAllMethods(clazz); 175 } 176 177 Method method = getMethodByCache(clazz, name, params); 178 return method; 179 } 180 181 /** 获取当前对象中这个方法当对象 182 * 183 * @param obj 184 * @param name 185 * @return 186 */ 187 public static Method getMethod(Object obj,String name, Class... params){ 188 Class clazz = obj.getClass(); 189 Method method = getMethod(clazz, name, params); 190 return method; 191 } 192 193 public static List<Method> getMethods(Object obj){ 194 return getMethods(obj.getClass()); 195 } 196 /** 获取全部都方法 197 * 198 * @param clazz 199 * @return 200 */ 201 public static List<Method> getMethods(Class clazz){ 202 if(!methodCache.containsKey(clazz)){ 203 loadAllMethods(clazz); 204 } 205 return getMethodsByCache(clazz); 206 } 207 public static Map<String, Method> getMethodsToMap(Object obj){ 208 return getMethodsToMap(obj.getClass()); 209 } 210 211 /** 获取这些方法集合,map结构 212 * 213 * @param clazz 214 * @return 215 */ 216 public static Map<String, Method> getMethodsToMap(Class clazz){ 217 if(!methodCache.containsKey(clazz)){ 218 loadAllMethods(clazz); 219 } 220 Map<String,Method> subMethodCache = methodCache.get(clazz); // 获取这个子缓存 221 if(subMethodCache==null){ 222 return new HashMap<String,Method>(); 223 } 224 return new HashMap<String,Method>(subMethodCache); 225 } 226 /** 执行这个方法 227 * 228 * @param obj 229 * @param name 方法名称 230 * @param clparam 方法中参数类型集合 231 * @param valparams 参数类型对应的传餐 232 * @return 233 * @throws Exception 234 */ 235 public static Object executeMethod(Object obj, String name,Class[] clparam,Object[] valparams) throws Exception{ 236 Method method = getMethod(obj, name, clparam); 237 return executeMethod(obj, method, valparams); 238 } 239 240 /** 241 * 242 * @param obj 243 * @param method 要执行的方法 244 * @param valparams 方法中参数 245 * @return 246 * @throws Exception 247 */ 248 public static Object executeMethod(Object obj, Method method,Object... valparams) throws Exception{ 249 if(method == null){ 250 System.err.println("传入方法为null"); 251 throw new Exception(); 252 //return null; 253 } 254 if(!method.isAccessible()){ 255 method.setAccessible(true); 256 } 257 return method.invoke(obj, valparams); 258 } 259 /** 查询被这些注解修饰到方法 260 * 261 * @param clazz 262 * @param annotationClasss 263 * @return 264 */ 265 public static List<Method> indexMethodByAnnotation(Class clazz,Class... annotationClasss){ 266 if(annotationClasss == null || annotationClasss .length == 0){ 267 return getMethods(clazz); 268 } 269 /* ****************************************************** * 270 * 结果集合储存查询的被这些注解修饰当方法。 271 * 先查询出所有方法,然后一条一条匹配注解。 272 * ***************************************************** */ 273 List<Method> resultMethods = new ArrayList<Method>(); 274 List<Method> cacheMethods = getMethods(clazz); 275 for (Method method : cacheMethods) { 276 for (Class annotationClass : annotationClasss) { 277 if(method.isAnnotationPresent(annotationClass)){ 278 resultMethods.add(method); 279 break; 280 } 281 } 282 283 } 284 return resultMethods; 285 } 286 287 288 /** 查询方法名称为指定名称结束的 289 * 290 * @param clazz 291 * @param end 292 * @return 293 */ 294 public static List<Method> indexMethodByEndText(Class clazz,String end){ 295 if(end == null || "".equals(end)){ 296 return getMethods(clazz); 297 } 298 /* ****************************************************** * 299 * 结果集合储存查询的方法名为end结束。 300 * ***************************************************** */ 301 List<Method> cacheMethods = getMethods(clazz); 302 List<Method> resultMethods = new ArrayList<Method>(); // 结果 303 for (Method Method : cacheMethods) { 304 if(Method.getName().endsWith(end)){ 305 resultMethods.add(Method); 306 } 307 308 } 309 return resultMethods; 310 } 311 312 /** 查询方法名称包含指定的内容的所有方法 313 * 314 * @param clazz 315 * @param include 包含的内容 316 * @return 317 */ 318 public static List<Method> indexMethodByIncludeText(Class clazz,String include){ 319 if(include == null || "".equals(include)){ 320 return getMethods(clazz); 321 } 322 /* ****************************************************** * 323 * 结果集合储存查询的方法名包含include 324 * ***************************************************** */ 325 List<Method> cacheMethods = getMethods(clazz); 326 List<Method> resultMethods = new ArrayList<Method>(); // 结果 327 for (Method Method : cacheMethods) { 328 if(Method.getName().indexOf(include)!=-1){ 329 resultMethods.add(Method); 330 } 331 332 } 333 return resultMethods; 334 } 335 336 337 }
方法经理是在创建佣兵*对象时实例化的,在佣兵*中标蓝色。
可以看出,在实例化方法经理时,入参是Handler(任务)接口,任务(方法)都会实现该接口,这也是为什么所有的任务都实现这个接口的原因(这里就体现了多态的好处)。我们要执行的每个任务都不可能一样,通过多态,以父类当作入参,保证不同的任务都可以在这里进行可以初始化。
2.3 佣兵*
package com.asd.common.mission.mercenary;
import com.asd.common.mission.methodHandler.Handler;
import com.asd.common.mission.methodHandler.MethodManager;
import com.asd.common.mission.methodHandler.MethodManagerFactory;
import com.asd.common.mission.mission.Mission;
import com.asd.common.mission.mission.MissionPakage;
import com.asd.common.mission.mission.MissionRecord;
import com.asd.common.mission.missionHandler.MissionHandleListener;
import com.asd.common.mission.missionHandler.MissionHandlerAOP;
import com.asd.common.mission.missionHandler.MissionHandlerAOPImpl;
import com.asd.common.utils.random.RandomUtils;
import java.util.concurrent.LinkedBlockingQueue;
import java.util.concurrent.RejectedExecutionHandler;
import java.util.concurrent.ThreadPoolExecutor;
import java.util.concurrent.TimeUnit;
/**
* 佣兵*
* @author 69420
*
*/
public class MercenaryGroup {
/**
* 佣兵*ID
*/
private String groupId;
/**
* 任务执行器
*/
private MethodManager methodManager = null;
/**
* 线程池
*/
private ThreadPoolExecutor pool = null;
/**
* 线程池等待队列
*/
private LinkedBlockingQueue<Runnable> workQueue = null;
/**
* 任务记录
*/
private MissionRecord missionRecord = new MissionRecord();
/**
* 任务处理切面方法
*/
private MissionHandlerAOP handlerAOP = new MissionHandlerAOPImpl(missionRecord);
/**
* 任务处理监听方法
*/
private MissionHandleListener missionHandleListener = null;
/**
* 创建一个有mercenarySize个佣兵的佣兵*
* @param handler 佣兵*处理工具
* @param mercenarySize 佣兵*大小
* @param waitingSize 阻塞队列大小,如果为-1则大小无上限
* @param missionHandleListener 任务监听方法
*/
public MercenaryGroup(Handler handler,
int mercenarySize, int waitingSize,
MissionHandleListener missionHandleListener) {
this.groupId = RandomUtils.getUniqueId();
this.methodManager = MethodManagerFactory.getMethodManager(handler);
if(waitingSize <= 0){
this.workQueue = new LinkedBlockingQueue<Runnable>();
}else{
this.workQueue = new LinkedBlockingQueue<Runnable>(waitingSize);
}
if(missionHandleListener!=null){
this.missionHandleListener = missionHandleListener;
}
this.pool = new ThreadPoolExecutor(mercenarySize, mercenarySize, 0, TimeUnit.SECONDS, workQueue,
new RejectedExecutionHandler() {
public void rejectedExecution(Runnable r, ThreadPoolExecutor executor) {
try {
executor.getQueue().put(r);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
});
}
/**
* 创建一个有mercenarySize个佣兵的佣兵*
* @param groupId 佣兵*ID
* @param handler 佣兵*处理工具
* @param mercenarySize 佣兵*大小
* @param waitingSize 阻塞队列大小,如果为-1则大小无上限
* @param missionHandleListener 任务包切面工具
*/
public MercenaryGroup(String groupId, Handler handler,
int mercenarySize, int waitingSize,
MissionHandleListener missionHandleListener) {
this.groupId = groupId;
this.methodManager = MethodManagerFactory.getMethodManager(handler);
if(waitingSize == -1){
this.workQueue = new LinkedBlockingQueue<Runnable>();
}else{
this.workQueue = new LinkedBlockingQueue<Runnable>(waitingSize);
}
if(missionHandleListener!=null){
this.missionHandleListener = missionHandleListener;
}
this.pool = new ThreadPoolExecutor(mercenarySize, mercenarySize, 5, TimeUnit.SECONDS, workQueue,
new RejectedExecutionHandler() {
public void rejectedExecution(Runnable r, ThreadPoolExecutor executor) {
try {
executor.getQueue().put(r);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
});
}
/**
* 执行一个任务
* @param methodChannel 执行任务的方法名称
* @param mission 任务包
* @throws Exception
*/
public void execute(String methodChannel, Mission mission){
if(mission == null || methodChannel == null){
return;
}
missionRecord.loadMission(mission);
this.pool.execute(new Mercenary(methodManager,
handlerAOP,
missionHandleListener,
methodChannel, mission));
}
/**
* 执行一个任务
* @param methodChannel 执行任务的方法名称
* @param missionPakage 任务包
* @throws Exception
*/
public void execute(String methodChannel, MissionPakage missionPakage){
if(missionPakage == null || methodChannel == null){
return;
}
missionRecord.loadMissionPakage(missionPakage);
while(missionPakage.hasNext()){
this.pool.execute(new Mercenary(methodManager,
handlerAOP,
missionHandleListener,
methodChannel, missionPakage.get()));
}
}
/**
* 获取佣兵*ID
* @return
*/
public String getGroupId() {
return groupId;
}
/**
* 佣兵*大小
* @return
*/
public int groupSize(){
return pool.getMaximumPoolSize();
}
/**
* 任务包是否完成
* @param missionPakageId
* @return
*/
public boolean isComplete(String missionPakageId){
return missionRecord.isComplete(missionPakageId);
}
/**
* 任务包是否完成
* @param missionPakageIds
* @return
*/
public boolean isComplete(String... missionPakageIds){
boolean is = true;
for (int i = 0; i < missionPakageIds.length; i++) {
is = is && missionRecord.isComplete(missionPakageIds[i]);
}
return is;
}
/**
* 等待任务包完成
* @param missionPakageIds
*/
public void waitForComplete(String... missionPakageIds){
if(missionPakageIds!=null){
while(!isComplete(missionPakageIds)){
try {
Thread.sleep(1000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}
/**
* 等待死亡,如果规定时间内无任务进入也无任务完成/发生异常,则认为死亡
* @param timeout
*/
public void waitForDead(long timeout){
missionRecord.setHeartBeat(timeout);
while(!missionRecord.isDead()){
try {
Thread.sleep(1000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
/**
* 销毁拥兵组
*/
public void destory(){
this.methodManager = null;
this.missionRecord = null;
this.handlerAOP = null;
this.missionHandleListener = null;
this.pool.shutdown();
this.pool = null;
}
}
2.4 任务(方法)及任务(方法)参数对象
2.4.1 方法接口
package com.asd.common.mission.methodHandler; public interface Handler { }
2.4.2 方法接口
package com.asd.common.mission.missionHandler; import com.asd.common.mission.methodHandler.Handler; /** * * 任务处理方法接口,只需要实现该接口,自定义方法,用MehtodHandler注释,即可使用 * 所有方法默认参数有且仅有一个参数:Mission * @author 69420 * */ public interface MissionHandler extends Handler { }
2.4.3 方法
在这里编写业务逻辑。
package com.asd.common.mission.missionHandler; import com.asd.common.mission.methodHandler.MethodHandler; import com.asd.common.mission.mission.Mission; public class DemoHandler implements MissionHandler { @MethodHandler("default") public void run(Mission mission){ try { Thread.sleep(1000); } catch (InterruptedException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } System.out.println("我进来了"+mission.getId()); } }
2.4.4 任务对象
任务对象用来封装方法的参数信息
package com.asd.common.mission.mission; import com.asd.common.utils.random.RandomUtils; import com.asd.common.utils.string.StringUtils; import java.util.HashMap; import java.util.Map; /** * 任务对象 * @author 69420 * */ public class Mission extends HashMap<String, Object>{ private static final long serialVersionUID = 2903723764002940136L; /** * 任务ID */ private String id; /** * 任务包ID */ private String pakageId; /** * 订阅号 */ private String channel = null; /** * 任务内容 */ private Object content = null; public Mission() { id = RandomUtils.getUniqueId(); } public Mission(String id) { this.id = id; } /** * 获取任务ID * @return */ public String getId() { return id; } /** * 获取任务包ID * @return */ public String getPakageId() { return pakageId; } /** * 设置任务包ID * @param pakageId */ public void setPakageId(String pakageId) { this.pakageId = pakageId; } /** * 获取任务开始位置 * @return */ public int getStartPosition() { return Integer.parseInt(get(id+"-startPosition").toString()); } /** * 设置任务开始位置 * @param startPosition */ public void setStartPosition(int startPosition) { put(id+"-startPosition", startPosition); } /** * 获取任务大小 * @return */ public int getMissionSize() { return Integer.parseInt(get(id+"-missionSize").toString()); } /** * 设置任务大小 * @param missionSize */ public void setMissionSize(int missionSize) { put(id+"-missionSize", missionSize); } /** * 获取订阅号 * @return */ public String getChannel() { return channel; } /** * 设置订阅号 * @param channel */ public void setChannel(String channel) { this.channel = channel; } public void setMissionParams(Map<String, Object> map){ if(map!=null){ for (String key : map.keySet()) { put(key, map.get(key)); } } } public void setMissionParams(String jsonObj){ setMissionParams(StringUtils.jsonToMap(jsonObj)); } public void setContent(Object content) { this.content = content; } public Object getContent() { return content; } }
2.5 调用
package com.asd.common.mission.demo; import com.asd.common.mission.mercenary.MercenaryGroup; import com.asd.common.mission.mission.Mission; import com.asd.common.mission.mission.MissionPakage; import com.asd.common.mission.missionHandler.DemoHandler; import com.asd.common.mission.missionHandler.DemoListenner; import java.util.ArrayList; import java.util.List; public class Demo { public static void main(String[] args) { demo2(); } /** *@Author: MrZs on 2020/3/31 17:03 *@params: *@return: *@Description: */ public static void demo1(){ // 创建任务执行佣兵* MercenaryGroup mercenaryGroup = new MercenaryGroup(new DemoHandler(), 10, 1, new DemoListenner()); // 组装任务对象 List<Mission> missions = new ArrayList<Mission>(); for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) { Mission mission = new Mission(); missions.add(mission); } // 组装任务包 String missionPakageId = "defaultPakage"; MissionPakage pakage = new MissionPakage(missionPakageId,missions); // 指定佣兵*执行任务包 String chanel = "default"; mercenaryGroup.execute(chanel,pakage); // 等待任务包执行完毕 mercenaryGroup.waitForComplete(missionPakageId); System.out.println("任务执行完毕"); // 佣兵*销毁 mercenaryGroup.destory(); } /** *@Author: MrZs on 2020/3/31 16:56 *@params: *@return: *@Description:这个demo里说明了有多个请求时,是如何调用线程池的 * 首先,创建佣兵*MercenaryGroup实例,来创建了一个线程池的实例。 * 下面通过多线程,模拟多个请求,针对每一个请求(即一个线程),都会通过上面的 * 线程池去执行任务 * */ public static void demo2(){ // 创建任务执行佣兵* final MercenaryGroup mercenaryGroup = new MercenaryGroup(new DemoHandler(), 10, 1, new DemoListenner()); // 指定佣兵*执行任务 final String chanel = "default"; mercenaryGroup.execute(chanel,new Mission()); // 等待任务包执行完毕 Thread th = new Thread(new Runnable() { @Override public void run() { for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) { try { Thread.sleep(3000); } catch (InterruptedException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } mercenaryGroup.execute(chanel,new Mission()); } } }); th.start(); System.out.println("开始等待死亡"); mercenaryGroup.waitForDead(10000); System.out.println("已死亡"); // 佣兵*销毁 mercenaryGroup.destory(); } }
可以看出,demo1通过循环,创建了十个相同任务对象,将这十个任务进行打包,封装到一个任务包中。调用佣兵*时,会对这个任务包进行循环,一个一个的调用线程池。跟上一个章节的线程池例子一样。mission的作用就是封装每个任务的参数。

而demo2,是通过循环创建了十个线程。相当于十次请求(十个线程),这十个线程共用了一个线程池实例。
重点说明:
业务系统向准备金系统土司推送数据,用的是demo1。
准备金系统从业务系统同步数据的方法是用多线程来写的。通过异步同步方法,利用多线程,实现的即异步同步数据:同一时点,多次送数,会有多个线程,(相当于demo2)互不干涉的同时进行数据同步。通过继承Thread类,数据不共享。
在每个线程任务里,又用到了线程池。每五十条数,发送执行一次任务。
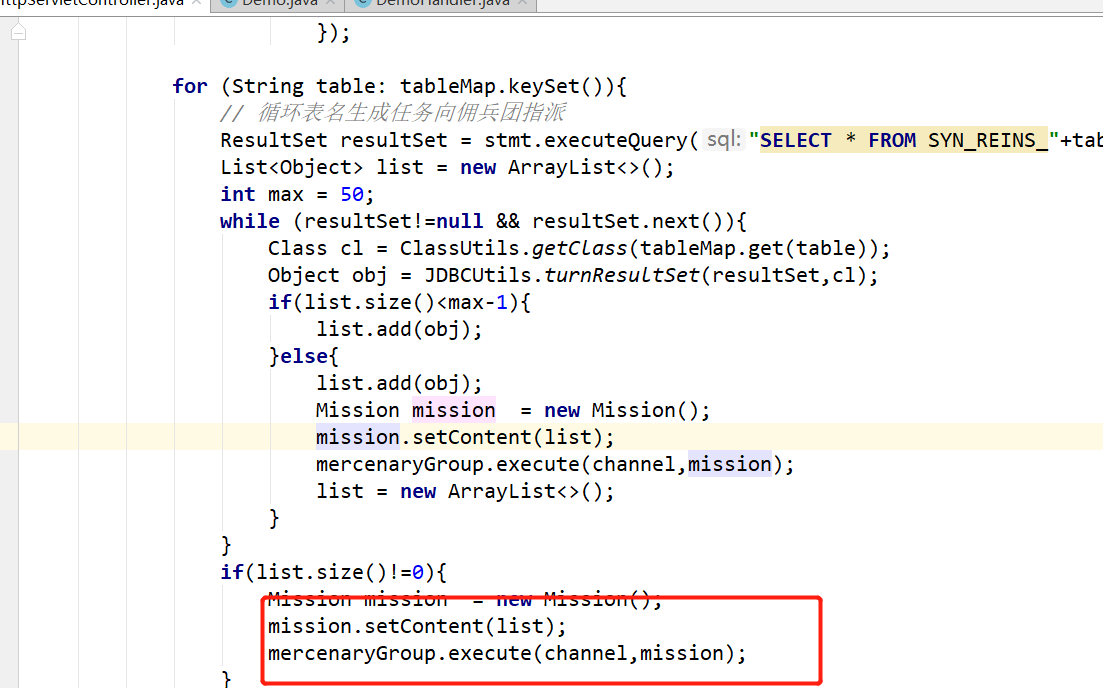
佣兵*对象是在多线程类中创建的,所以每次推送数据用的不是一个线程池。

多线程类:

1 class SynoInterfaceData extends Thread{ 2 private InterfaceLogService interfaceLogService; 3 private DataDictionaryService dataDictionaryService; 4 5 public static final Logger log = LoggerFactory.getLogger(ReinsHttpServletController.class); 6 private String startDate; 7 private String endDate; 8 private boolean backdoorFlag = false; 9 public SynoInterfaceData(InterfaceLogService interfaceLogService, 10 DataDictionaryService dataDictionaryService, 11 String startDate,String endDate, 12 boolean backdoorflag){ 13 this.interfaceLogService = interfaceLogService; 14 this.dataDictionaryService = dataDictionaryService; 15 this.startDate = startDate; 16 this.endDate = endDate; 17 this.backdoorFlag = backdoorflag; 18 } 19 @Override 20 public void run(){ 21 Connection conn = null; 22 Statement stmt = null; 23 String status = "SUCCESS"; 24 String requestString = ""; 25 ResourceBundle interfaceAddress = ResourceBundle.getBundle("interfaceAddress"); 26 try{ 27 log.info("准备金抽取数据开启数据库连接开始"); 28 conn = ConnectionUtil.openConnect(); 29 log.info("准备金抽取数据开启数据库连接开始"); 30 ConnectionUtil.beginTransaction(conn); 31 Map<String,String> tableMap = new HashMap<String,String>(){ 32 { 33 put("ZRJOUTSTANDINGACC","com.asd.modules.pojo.zrjoutstandingacc.model.Zrjoutstandingacc"); 34 put("ZRJOUTSTANDINGFAC","com.asd.modules.pojo.zrjoutstandingfac.Zrjoutstandingfac"); 35 put("ZRJOUTSTANDINGTREATY","com.asd.modules.pojo.zrjoutstandingtreaty.Zrjoutstandingtreaty"); 36 put("ZRJUNEARNEDACC","com.asd.modules.pojo.zrjunearnedacc.model.Zrjunearnedacc"); 37 put("ZRJUNEARNEDFAC","com.asd.modules.pojo.zrjunearnedfac.model.Zrjunearnedfac"); 38 put("ZRJUNEARNEDTREATY","com.asd.modules.pojo.zrjunearnedtreaty.model.Zrjunearnedtreaty"); 39 } 40 }; 41 42 stmt = conn.createStatement(); 43 //先删除对应日结日期的数据 44 for (String table:tableMap.keySet()){ 45 stmt.addBatch("DELETE FROM " + table + " WHERE PAYDATE BETWEEN '"+startDate+"' and '"+endDate+"' and uuid[1,4] != 'YYLF' " ); 46 } 47 stmt.executeBatch(); 48 ConnectionUtil.commitTransaction(conn); 49 stmt.close(); 50 51 stmt = conn.createStatement(); 52 // 方法订阅号 53 String channel = "default"; 54 // 用于记录任务完成情况的map 55 final Map<String,Integer> historyMap = new HashMap<>(); 56 for (String tableClass: 57 tableMap.values()) { 58 Class cl = ClassUtils.getClass(tableClass); 59 if(cl!=null){ 60 historyMap.put(cl.getSimpleName(),0); 61 } 62 } 63 // 防止 historyMap 多线程写入出现问题 64 final ReadWriteLock lock = new ReentrantReadWriteLock(); 65 // 组建佣兵* 66 MercenaryGroup mercenaryGroup 67 = new MercenaryGroup(new ReserveMissionHandler(), 68 100, 69 1, 70 new ReserveMissionListenner() { 71 public void handleAfter(Mission mission) { 72 List<Object> objects = (List<Object>) mission.getContent(); 73 String simpleClassName = objects.get(0).getClass().getSimpleName(); 74 try{ 75 lock.writeLock().lock(); 76 if(historyMap.containsKey(simpleClassName)){ 77 historyMap.put(simpleClassName,historyMap.get(simpleClassName)+objects.size()); 78 }else{ 79 historyMap.put(simpleClassName,objects.size()); 80 } 81 }catch (Exception e){ 82 throw e; 83 }finally { 84 lock.writeLock().unlock(); 85 } 86 } 87 }); 88 89 for (String table: tableMap.keySet()){ 90 // 循环表名生成任务向佣兵*指* 91 ResultSet resultSet = stmt.executeQuery("SELECT * FROM SYN_REINS_"+table+" WHERE PAYDATE BETWEEN '"+startDate+"' and '"+endDate+"' "); 92 List<Object> list = new ArrayList<>(); 93 int max = 50; 94 while (resultSet!=null && resultSet.next()){ 95 Class cl = ClassUtils.getClass(tableMap.get(table)); 96 Object obj = JDBCUtils.turnResultSet(resultSet,cl); 97 if(list.size()<max-1){ 98 list.add(obj); 99 }else{ 100 list.add(obj); 101 Mission mission = new Mission(); 102 mission.setContent(list); 103 mercenaryGroup.execute(channel,mission); 104 list = new ArrayList<>(); 105 } 106 } 107 if(list.size()!=0){ 108 Mission mission = new Mission(); 109 mission.setContent(list); 110 mercenaryGroup.execute(channel,mission); 111 } 112 // 原逻辑 113 //stmt.addBatch("INSERT INTO "+table+" SELECT * FROM SYN_REINS_"+table+" WHERE PAYDATE BETWEEN '"+startDate+"' and '"+endDate+"' "); 114 } 115 // 等待任务全部完成 116 mercenaryGroup.waitForDead(60000); 117 // 销毁佣兵* 118 mercenaryGroup.destory(); 119 120 System.out.println("全部任务执行完毕:开始时间:"+startDate+";结束时间:"+endDate+";startDate"+historyMap.toString()); 121 stmt.close(); 122 123 stmt = conn.createStatement(); 124 for(String tableName:historyMap.keySet()){ 125 String sql = "UPDATE ZRJREINSSTATUS SET STATUS='2',ZRJCOUNT="+historyMap.get(tableName)+" WHERE STARTDATE='"+startDate+"' AND ENDDATE='"+endDate+"' AND TABLENAME='"+tableName.toLowerCase()+"' "; 126 stmt.addBatch(sql); 127 } 128 //更新update 129 stmt.executeBatch(); 130 stmt.close(); 131 status = "SUCCESS"; 132 //执行完毕后通知再保系统 133 ConnectionUtil.commitTransaction(conn); 134 }catch (Exception e){ 135 e.printStackTrace(); 136 ConnectionUtil.rollBackTransaction(conn); 137 status=e.getMessage(); 138 }finally{ 139 requestString = XMLUtils.createRequestXML(XstreamUtils.getRequestHeaderXstream(),startDate,endDate,status); 140 String responseString = ""; 141 try { 142 responseString = HttpClientUtils.httpPostSend(interfaceAddress.getString("reinsinterface"),requestString); 143 } catch (Exception e1) { 144 e1.printStackTrace(); 145 }finally{ 146 if(backdoorFlag){ 147 return; 148 } 149 //生成并发送报文日志记录 150 RequestHead requestHead = HttpHeadUtils.getRequestHead(); 151 KeyInfo keyInfo = new KeyInfo(); 152 keyInfo.setBusstartdate(startDate); 153 String UUID = requestString.substring(requestString.indexOf("<uuid>")+6, requestString.lastIndexOf("</uuid>")); 154 String sender = requestString.substring(requestString.indexOf("<sender>")+8, requestString.lastIndexOf("</sender>")); 155 // String password = requestString.substring(requestString.indexOf("<password>")+10, requestString.lastIndexOf("</password>")); 156 String requestType = requestString.substring(requestString.indexOf("<request_type>")+14, requestString.lastIndexOf("</request_type>")); 157 requestHead.setUuid(UUID); 158 // requestHead.setPassword(password); 159 requestHead.setRequest_type(requestType); 160 requestHead.setSender(sender); 161 //传送开始时间 162 Date date = new Date(); 163 try { 164 interfaceLogService.addNewLog(requestString,responseString,requestHead,keyInfo,date); 165 }catch (Exception e){ 166 log.error("准备金发送业务系统报文保存失败",e); 167 } 168 169 } 170 System.out.println("--0--"+ requestString); 171 ConnectionUtil.closeConnect(conn); 172 ConnectionUtil.closeStatements(stmt); 173 } 174 } 175 176 }
调用同步异步方法:
@RequestMapping(value="ReinsServlet_backdoor",produces="application/json;charset=UTF-8") @ResponseBody public void backdoor( @RequestParam("startDate") String startDate, @RequestParam("endDate") String endDate){ if(startDate == null || endDate == null){ return; } //调用异步同步方法 Thread t = new SynoInterfaceData( interfaceLogService, dataDictionaryService, startDate,endDate,true); t.start(); }
