在 React Native 中,你并不需要学习什么特殊的语法来定义样式。我们仍然是使用 JavaScript 来写样式。
所有的核心组件都接受名为style的属性。这些样式名基本上是遵循了 web 上的 CSS 的命名,
只是按照 JS 的语法要求使用了驼峰命名法,例如将background-color改为backgroundColor。
style属性可以是一个普通的 JavaScript 对象。这是最简单的用法,因而在示例代码中很常见。
你还可以传入一个数组——在数组中位置居后的样式对象比居前的优先级更高,
这样你可以间接实现样式的继承。

import React, { Component } from 'react';
import { AppRegistry, StyleSheet, Text, View } from 'react-native';
export default class LotsOfStyles extends Component {
render() {
return (
<View>
<Text style={styles.red}>just red</Text>
<Text style={styles.bigBlue}>just bigBlue</Text>
<Text style={[styles.bigBlue, styles.red]}>bigBlue, then red</Text>
<Text style={[styles.red, styles.bigBlue]}>red, then bigBlue</Text>
</View>
);
}
}
const styles = StyleSheet.create({
bigBlue: {
color: 'blue',
fontWeight: 'bold',
fontSize: 30,
},
red: {
color: 'red',
},
});
指定宽高
最简单的给组件设定尺寸的方式就是在样式中指定固定的width和height。
React Native 中的尺寸都是无单位的,表示的是与设备像素密度无关的逻辑像素点。

import React, { Component } from 'react';
import { AppRegistry, View } from 'react-native';
export default class FixedDimensionsBasics extends Component {
render() {
return (
<View>
<View style={{ 50, height: 50, backgroundColor: 'powderblue'}} />
<View style={{ 100, height: 100, backgroundColor: 'skyblue'}} />
<View style={{ 150, height: 150, backgroundColor: 'steelblue'}} />
</View>
);
}
}
弹性(Flex)宽高
在组件样式中使用flex可以使其在可利用的空间中动态地扩张或收缩。一般而言我们会使用flex:1来指定某
个组件扩张以撑满所有剩余的空间。如果有多个并列的子组件使用了flex:1,则这些子组件会平分父容器中
剩余的空间。如果这些并列的子组件的flex值不一样,则谁的值更大,谁占据剩余空间的比例就更大
(即占据剩余空间的比等于并列组件间flex值的比)。
值得注意的事情是:
组件能够撑满剩余空间的前提是其父容器的尺寸不为零。如果父容器既没有固定的width和height,
也没有设定flex,则父容器的尺寸为零。其子组件如果使用了flex,也是无法显示的。
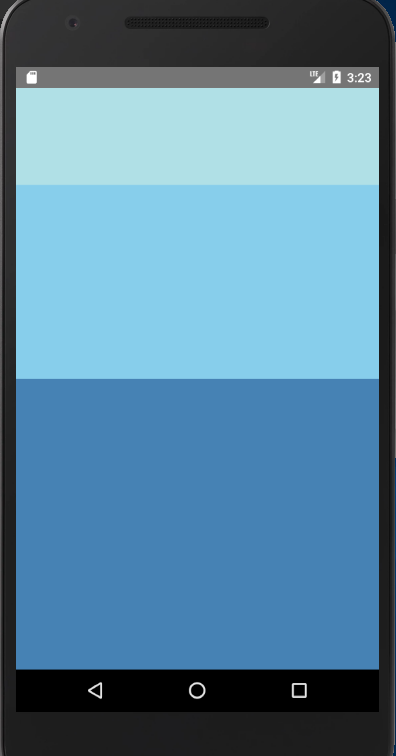
import React, { Component } from 'react';
import { AppRegistry, View } from 'react-native';
export default class FlexDirectionBasics extends Component {
render() {
return (
<View style={{flex: 1, flexDirection: 'row'}}>
<View style={{ 50, height: 50, backgroundColor: 'powderblue'}} />
<View style={{ 50, height: 50, backgroundColor: 'skyblue'}} />
<View style={{ 50, height: 50, backgroundColor: 'steelblue'}} />
</View>
)
}
}
使用Flexbox布局
我们在 React Native 中使用 flexbox 规则来指定某个组件的子元素的布局。Flexbox 可以在不同屏幕尺寸上提供一致的布局结构。
一般来说,使用flexDirection、alignItems和 justifyContent三个样式属性就已经能满足大多数布局需求。
React Native 中的 Flexbox 的工作原理和 web 上的 CSS 基本一致,当然也存在少许差异。
首先是默认值不同:flexDirection的默认值是column而不是row,而flex也只能指定一个数字值。
Flex Direction
在组件的style中指定flexDirection可以决定布局的主轴。子元素是应该沿着水平轴(row)方向排列,
还是沿着竖直轴(column)方向排列呢?默认值是竖直轴(column)方向。

Justify Content
在组件的 style 中指定justifyContent可以决定其子元素沿着主轴的排列方式。子元素是应该靠近主
轴的起始端还是末尾段分布呢?亦或应该均匀分布?对应的这些可选项有:flex-start、center、flex-end、
space-around、space-between以及space-evenly。
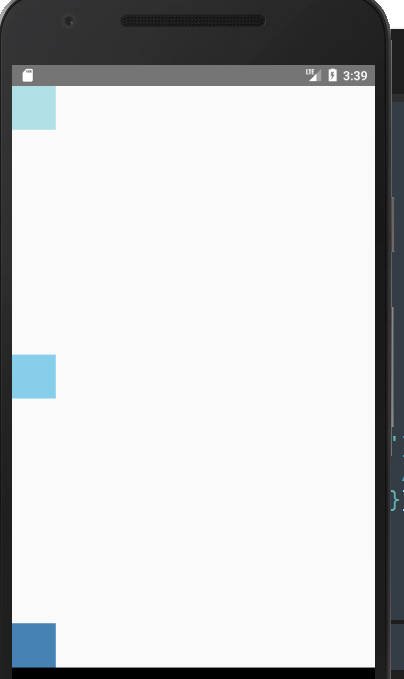
import React, { Component } from 'react';
import { AppRegistry, View } from 'react-native';
export default class JustifyContentBasics extends Component {
render() {
return (
// 尝试把`justifyContent`改为`center`看看
// 尝试把`flexDirection`改为`row`看看
<View style={{
flex: 1,
flexDirection: 'column',
justifyContent: 'space-between',
}}>
<View style={{ 50, height: 50, backgroundColor: 'powderblue'}} />
<View style={{ 50, height: 50, backgroundColor: 'skyblue'}} />
<View style={{ 50, height: 50, backgroundColor: 'steelblue'}} />
</View>
);
}
};
Align Items
在组件的 style 中指定alignItems可以决定其子元素沿着次轴(与主轴垂直的轴,比如若主轴方向为row,则次轴方向为column)
的排列方式。子元素是应该靠近次轴的起始端还是末尾段分布呢?亦或应该均匀分布?
对应的这些可选项有:flex-start、center、flex-end以及stretch。
注意:要使stretch选项生效的话,子元素在次轴方向上不能有固定的尺寸。
以下面的代码为例:只有将子元素样式中的 50去掉之后,alignItems: 'stretch'才能生效。

import React, { Component } from 'react';
import { AppRegistry, View } from 'react-native';
export default class AlignItemsBasics extends Component {
render() {
return (
// 尝试把`alignItems`改为`flex-start`看看
// 尝试把`justifyContent`改为`flex-end`看看
// 尝试把`flexDirection`改为`row`看看
<View style={{
flex: 1,
flexDirection: 'column',
justifyContent: 'center',
alignItems: 'stretch',
}}>
<View style={{ 50, height: 50, backgroundColor: 'powderblue'}} />
<View style={{height: 50, backgroundColor: 'skyblue'}} />
<View style={{height: 100, backgroundColor: 'steelblue'}} />
</View>
);
}
};
本质就是flex布局
更多布局知识见这篇文档:https://reactnative.cn/docs/layout-props/