--------------siwuxie095
对象成员
在对象中包含其它对象是一种非常普遍的现象
以坐标系中的线段为例:说明对象成员的定义和使用方法

如果要定义一个如上图所示的线段类,每条线段都由两个点连接而形成,
这意味着,需要定义一个表示点的类,该点类包含横坐标和纵坐标,而
线段类包含两个坐标对象
可见,要描述清楚这个数学问题,至少要定义两个类:一个定义坐标的
点,另一个定义点上的线段
坐标类:Coordinate

线段类:Line

定义完成后,通过实例化来描述一条线段:

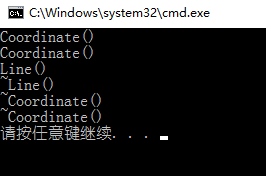
当实例化 Line 对象时,会先实例化 A 点,再实例化 B 点,
最后实例化 Line 对象
当销毁 Line 对象时,先销毁 Line 对象,再销毁 B 点,最后
销毁 A 点
「创建与销毁的过程正好相反」

这就像制造一辆汽车,肯定要先把各个零部件造好,然后再按照图纸
把汽车装配起来,当要拆除一辆汽车时,也是按照图纸把各个零件先
拆开,然后再分解各个零件



但刚才的构造函数并没有参数,作为线段类来说,它的两个点其实应该
可以由调用者来确定的,即 这两个点在 Line 对象实例化时就能通过给
构造函数传参,从而使这两个点生成在确定的位置上
坐标类 Coordinate 的构造函数应该有参数:

线段类 Line 的构造函数也应该有参数:

如果想将 x1、y1 传值给第一个点,x2、y2 传值给第二个点,单独写成
下面的形式是有问题的

需要对代码进行进一步的改进:给 Line 类的构造函数配备初始化列表,
在初始化列表中实例化 m_coorA 和 m_coorB,且将 Line 传入的 4 个
参数分配到两个对象成员中

程序 1:
Coordinate.h:
|
class Coordinate { public: Coordinate(); ~Coordinate(); void setX(int x); int getX(); void setY(int y); int getY(); private: int m_iX; int m_iY; }; |
Coordinate.cpp:
|
#include "Coordinate.h" #include <iostream> using namespace std;
Coordinate::Coordinate() { cout << "Coordinate()" << endl; }
Coordinate::~Coordinate() { cout << "~Coordinate()" << endl; }
void Coordinate::setX(int x) { m_iX = x; }
int Coordinate::getX() { return m_iX; }
void Coordinate::setY(int y) { m_iY = y; } int Coordinate::getY() { return m_iY; } |
Line.h:
|
#include "Coordinate.h" class Line { public: Line(); ~Line(); void setA(int x, int y); void setB(int x, int y); void printInfo(); private: Coordinate m_coorA; Coordinate m_coorB; }; |
Line.cpp:
|
#include "Line.h" #include <iostream> using namespace std;
Line::Line() { cout << "Line()" << endl; }
Line::~Line() { cout << "~Line()" << endl; }
void Line::setA(int x, int y) { m_coorA.setX(x); m_coorA.setY(y); }
void Line::setB(int x, int y) { m_coorB.setX(x); m_coorB.setY(y); }
void Line::printInfo() { cout << "(" << m_coorA.getX() << "," << m_coorA.getY() << ")" << endl; cout << "(" << m_coorB.getX() << "," << m_coorB.getY() << ")" << endl; } |
main.cpp:
|
#include <stdlib.h> #include "Line.h" #include <iostream> using namespace std;
//演示Line对象和其对象成员的调用顺序 int main(void) { // 或 Line *p = new Line; Line *p = new Line(); //Line类对象在创建时先执行对象成员的构造函数, //再执行对象的构造函数析构函数则相反 delete p; p = NULL; system("pause"); return 0; } |
运行一览:
程序 2:
Coordinate.h:
|
class Coordinate { public: Coordinate(int x,int y); ~Coordinate(); void setX(int x); int getX(); void setY(int y); int getY(); private: int m_iX; int m_iY; }; |
Coordinate.cpp:
|
#include "Coordinate.h" #include <iostream> using namespace std;
Coordinate::Coordinate(int x,int y) { m_iX = x; m_iY = y; cout << "Coordinate() " <<m_iX<<","<<m_iY<< endl; }
Coordinate::~Coordinate() { cout << "~Coordinate() " << m_iX << "," << m_iY << endl; }
void Coordinate::setX(int x) { m_iX = x; }
int Coordinate::getX() { return m_iX; }
void Coordinate::setY(int y) { m_iY = y; } int Coordinate::getY() { return m_iY; } |
Line.h:
|
#include "Coordinate.h"
class Line { public: Line(int x1,int y1,int x2,int y2); ~Line(); void setA(int x, int y); void setB(int x, int y); void printInfo(); private: Coordinate m_coorA; Coordinate m_coorB; }; |
Line.cpp:
|
#include "Line.h" #include <iostream> using namespace std;
//初始化列表 //如果对象成员所在类有默认构造函数那么这个地方就不需要初始化列表 Line::Line(int x1, int y1, int x2, int y2) :m_coorA(x1, y1), m_coorB(x2,y2) { cout << "Line()" << endl; }
Line::~Line() { cout << "~Line()" << endl; }
void Line::setA(int x, int y) { m_coorA.setX(x); m_coorA.setY(y); }
void Line::setB(int x, int y) { m_coorB.setX(x); m_coorB.setY(y); }
void Line::printInfo() { cout << "(" << m_coorA.getX() << "," << m_coorA.getY() << ")" << endl; cout << "(" << m_coorB.getX() << "," << m_coorB.getY() << ")" << endl; } |
main.cpp:
|
#include <stdlib.h> #include "Line.h" #include <iostream> using namespace std;
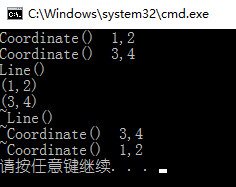
//让线段在创建时就将两个点一起确定下来 int main(void) { Line *p = new Line(1,2,3,4); p->printInfo(); delete p; p = NULL; system("pause"); return 0; } |
运行一览:
【made by siwuxie095】