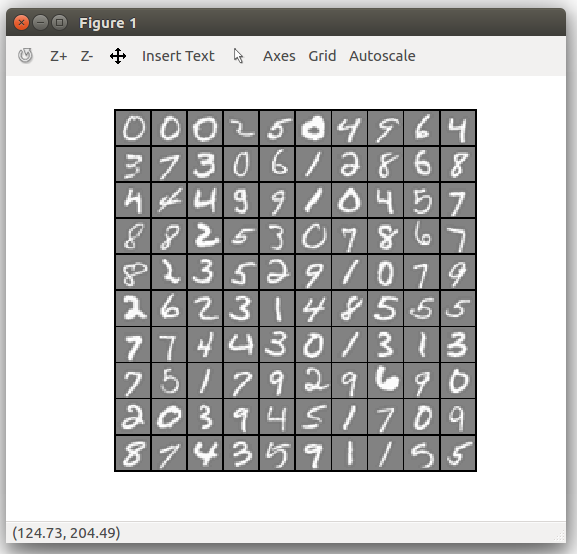
模拟人的神经元建立的感知机模型。
1.用神经元表示逻辑回归
需要注意的是输入层有4个unit,实际输入为3个,x0表示偏置,设为1.
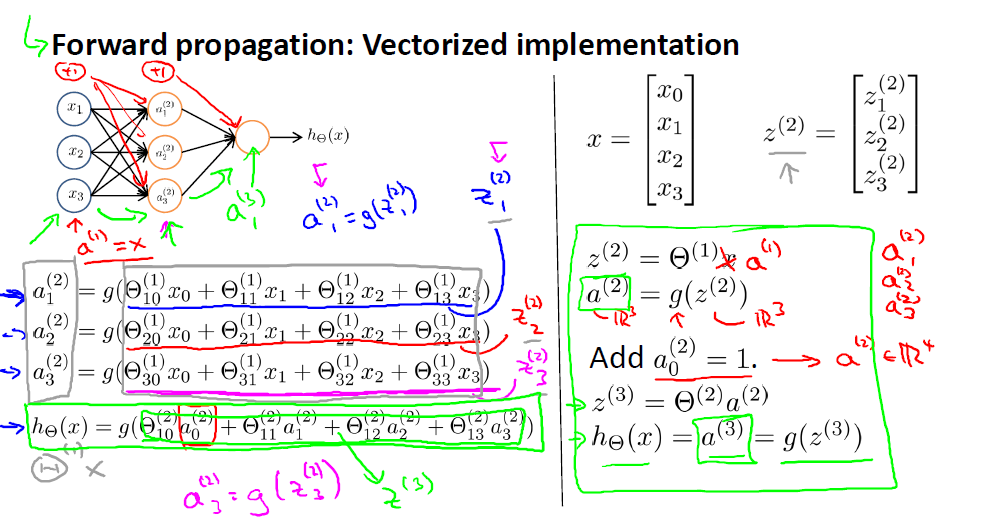
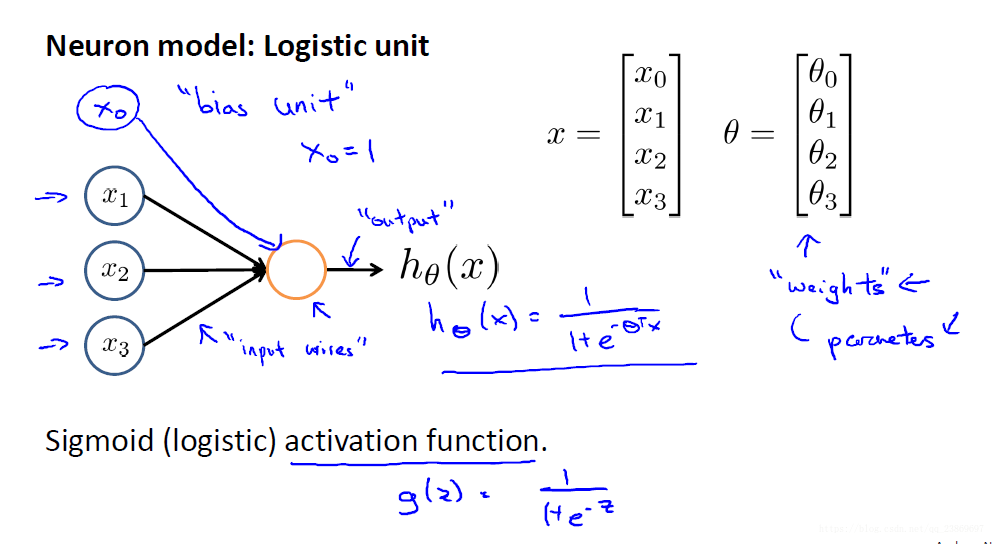
2.神经网络
主要是要注意每一层的偏置单元在向量化的时候对矩阵尺寸的影响。
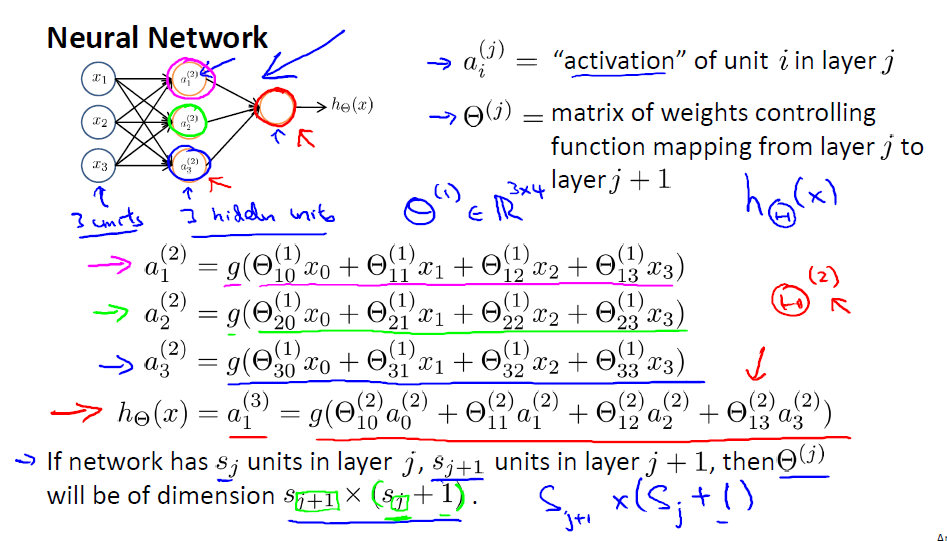
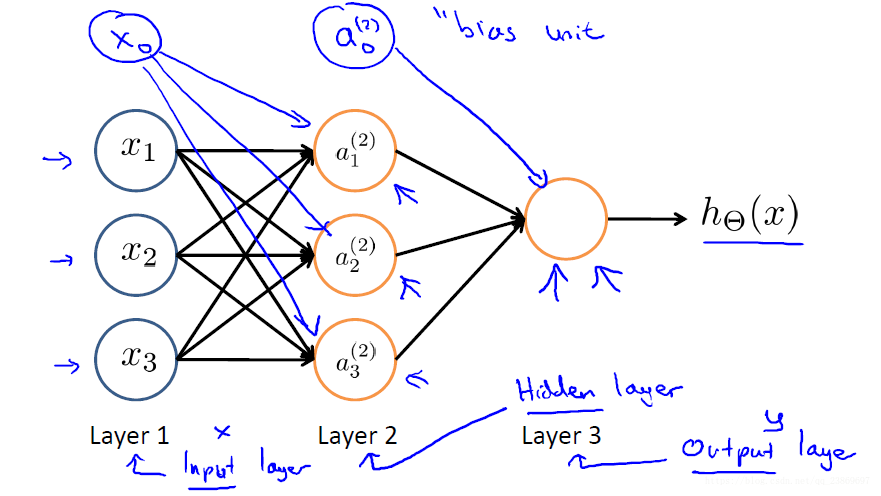
从图中我们很容易将表达式转为矩阵相乘的形式。我们在写表达式的时候总是倾向于使用简化的表达,, 其中, 所以在构建或者保存权重的时候要清楚权重矩阵的每一列或者每一行表示的是什么。要注意的地方就是权重的尺寸,这里权重矩阵的尺寸定义如下:
- 层有单元,层有个单元,那么的尺寸为
这里的有+1,表示还有一个偏置的权重。
3.神经网络学习特征
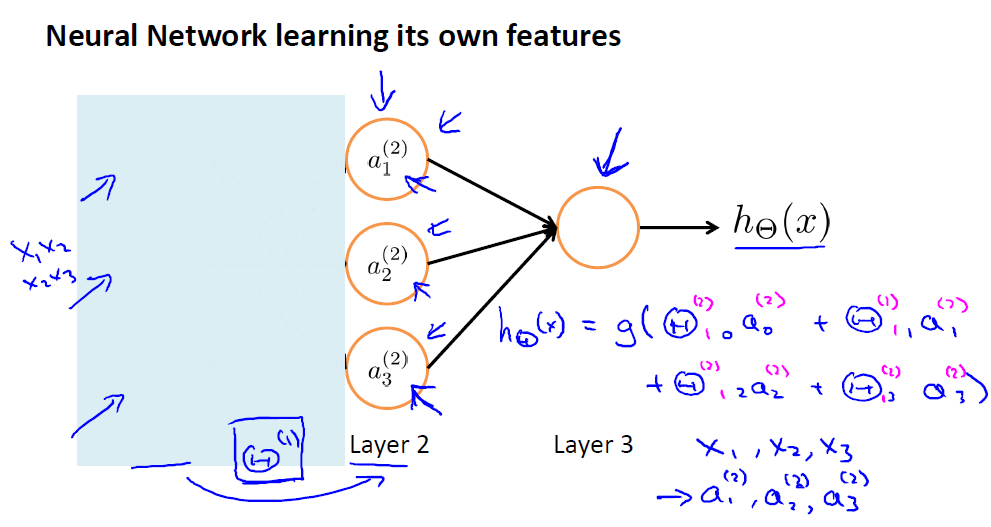
上面的三层神经网络结构,当我们把输入城挡住,剩下的结构就是使用网络结构表示的逻辑回归。这里可以把第二层的输入看做逻辑回归的输入,最后得到输出。与一般的直接把特征输入给逻辑回归模型不一样,这里的输入是已经过网络自主学习得到的,即第二层的输出。神经网络能够自主的抽象出更深层次的特征。
4.神经网络的结构
根据神经元之间不同的连接方式,我们能够得到不同的网络结构。
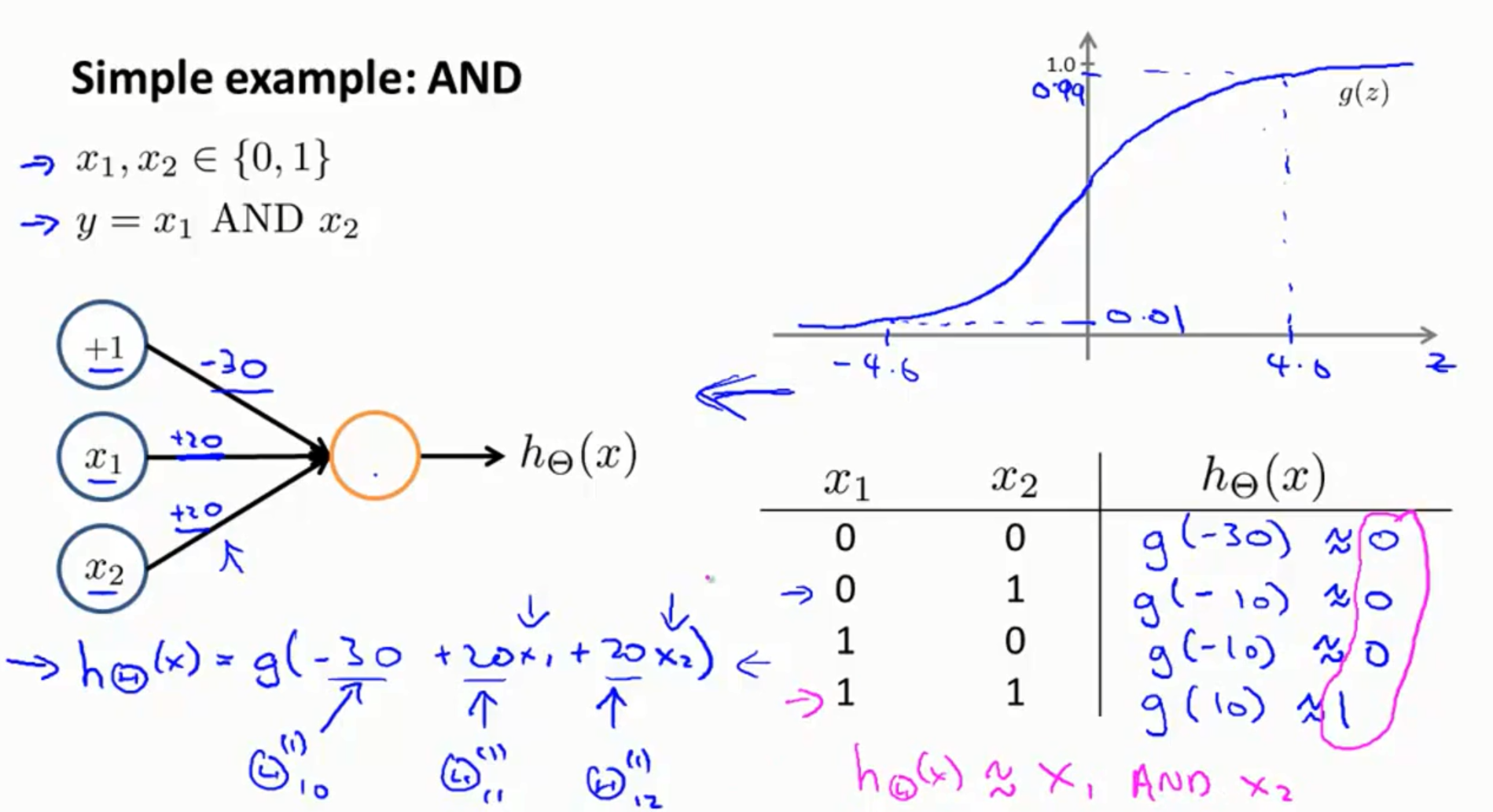
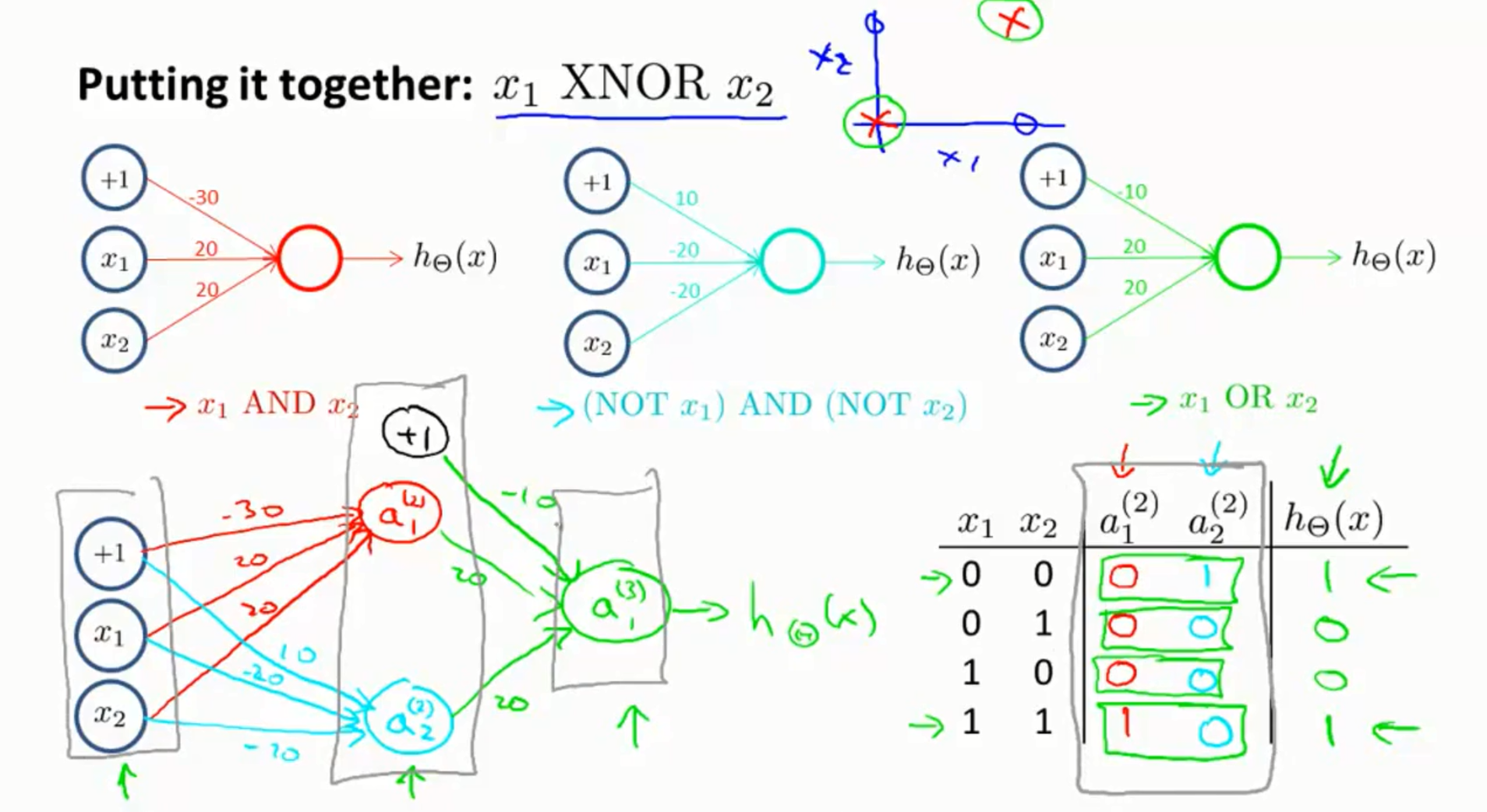
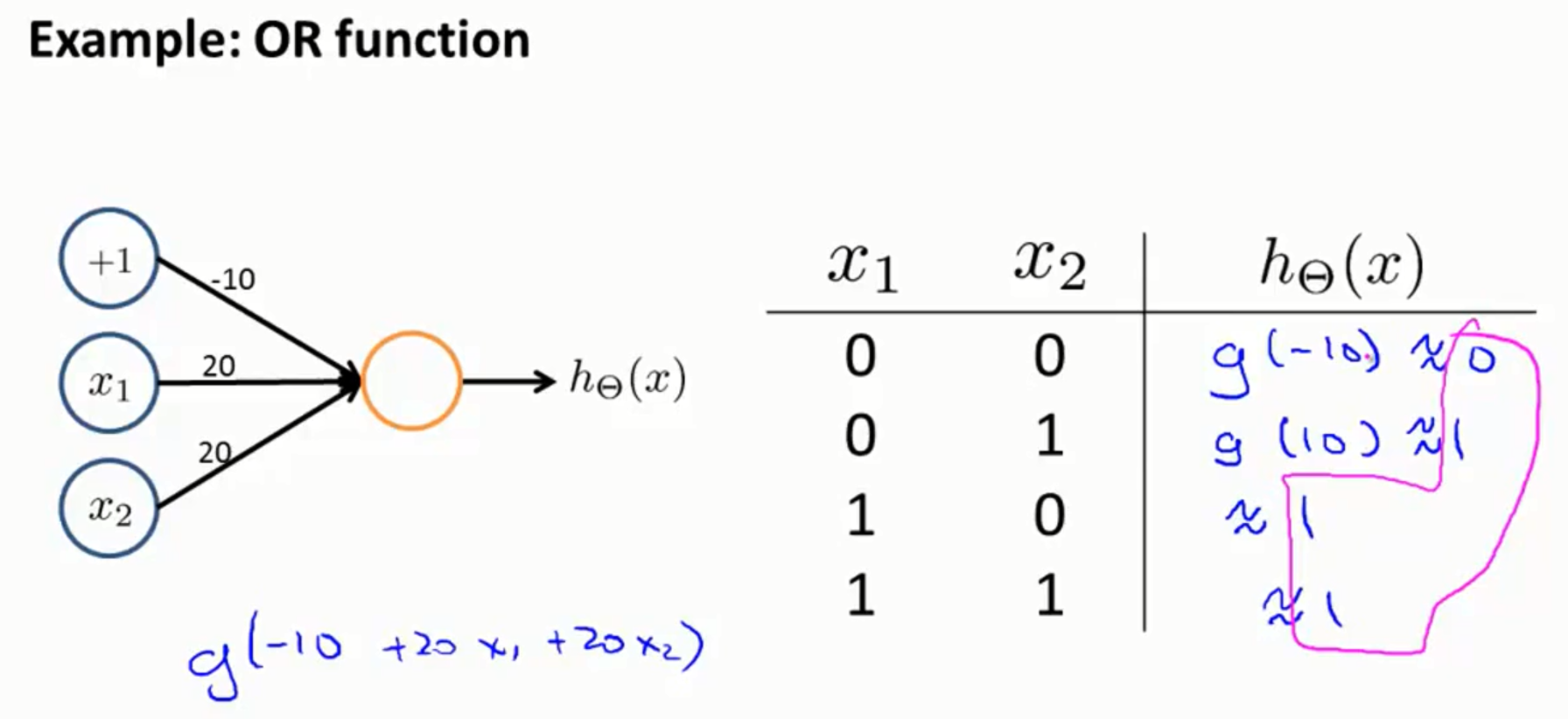
5.神经网络的应用实例:异或与异或非
先通过设定权重实现了与门和或门。
6.对分类问题:one-vs-all
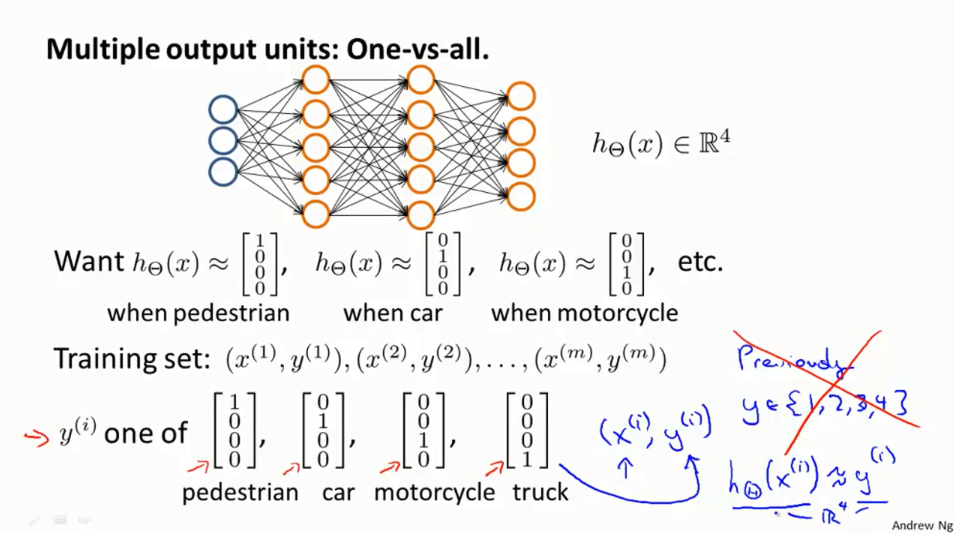
label通常情况下使用的是独热码。
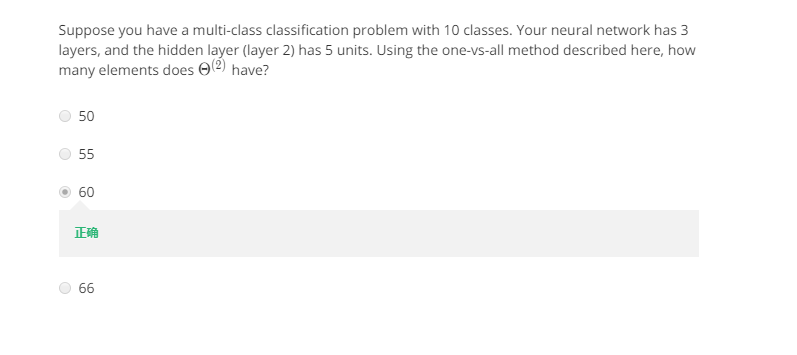
7.两道题:
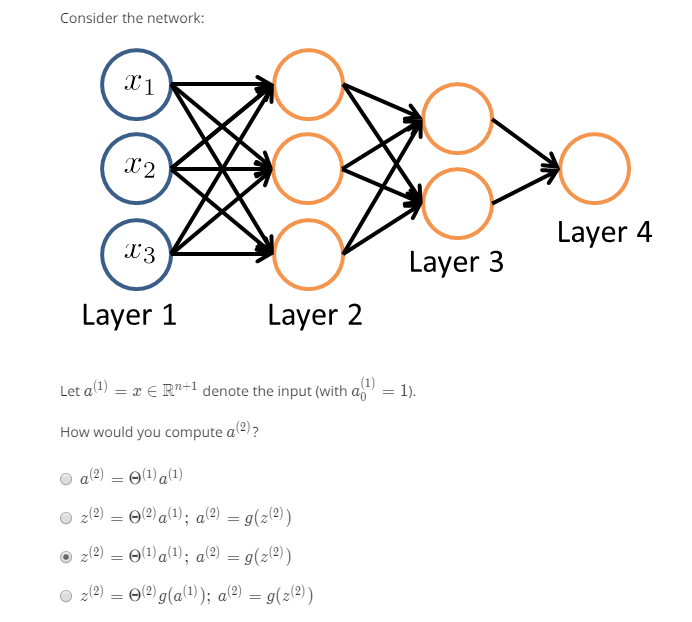
为什么会是60呢?
表示第二层到第三层之间的权重,参看上面的PPT,我们所讲的每一层有多少个unit是不包括偏置的,在神经网络的图上也不会画出来的,但是表达式中是存在的。根据上面的矩阵大小决定原则,第二层有5个unit,第三层有10个unit,那么尺寸应该是[10x(5+1)]=60.
8.编程练习:Multi-class Classi cation and Neural Networks
(1)目的:使用一对多逻辑回归和神经网络识别手写数字
(2)训练集
5000个训练样本,20x20像素的灰度图片,已经“unrolled”为大小1x400的向量。
所以训练集表示为一个5000x400的矩阵。
训练集的分类标注:用1~9标注手写体的1~9,10表示手写体0,大小为5000x1
(3) 数据的可视化
随机选取100个样本,使用画图命令画出图片
(4)逻辑回归分类
使用1对多逻辑回归模型建立一个多类别分类器。10个类别需要建立十个不同的逻辑回归分类器。
1) 向量化cost function
没有正则项的逻辑回归,其代价函数为:
定义输入矩阵X和
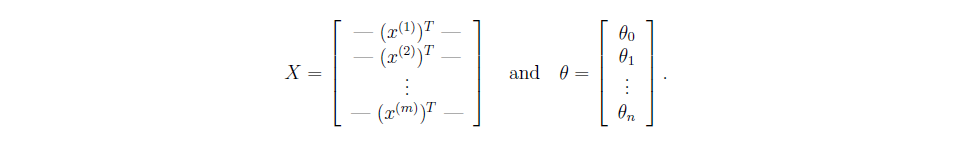
矩阵相乘就可以完成所有样本的计算,下面的等式用到了矩阵乘法中的一个定律.
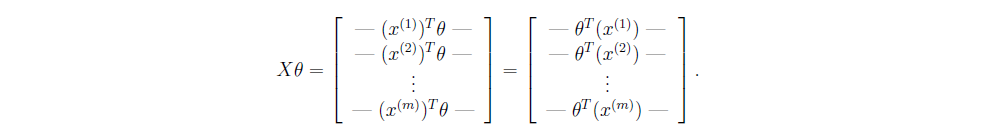
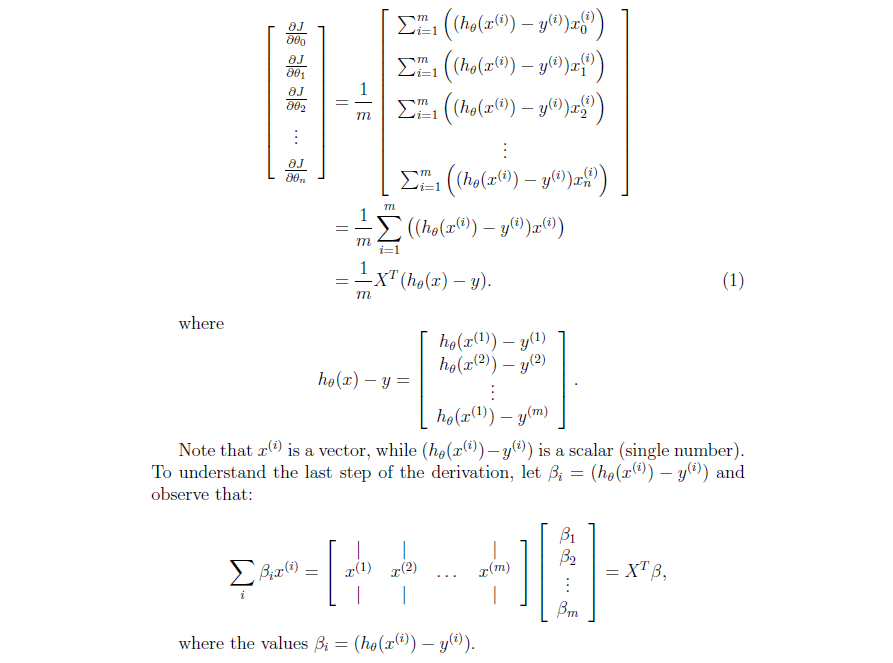
2) 向量化梯度
对上面的代价函数求导,得到第的导数为
使用向量表示如下:
h_t = sigmoid(X*theta)
J = 1/m*sum((-y).*log(h_t)-(1-y).*log(1-h_t))
grad_0 = 1/m*sum(h_t-y)
grad_j = 1/m*X'*(h_t-y)
grad = [grad_0;grad_j]3)带有正则项的逻辑回归向量化
代价函数为
这里的n表示未知参数的个数。一定要记住是从1开始的,所以要减去.看下面的代码,不然计算得到cost总是比预期的大。
h_t = sigmoid(X*theta);
J = 1/m*sum((-y).*log(h_t)-(1-y).*log(1-h_t))+(lambda/(2*m))*sum(theta(2:end,:).^2);
% theta(2:end,:) 表示从第二行开始的所有列,即从j=1开始是用于偏置项,不需要正则化。
所以正则化的逻辑回归代价函数的对的偏导数为:
grad_0 = 1/m*sum(h_t-y); % j=0时偏导
grad_0_j = 1/m*X'*(h_t-y)+lambda/m*theta; %这里也把j=0的项,是错误的
grad_1_j = grad_0_j(2:end,:) % 去掉j=0计算出来的梯度
grad = [grad_0;grad_1_j] % 把正确计算的j=0偏导加到所有的偏导数中4) One-vs-all分类器
function [all_theta] = oneVsAll(X, y, num_labels, lambda)
%ONEVSALL trains multiple logistic regression classifiers and returns all
%the classifiers in a matrix all_theta, where the i-th row of all_theta
%corresponds to the classifier for label i
% [all_theta] = ONEVSALL(X, y, num_labels, lambda) trains num_labels
% logistic regression classifiers and returns each of these classifiers
% in a matrix all_theta, where the i-th row of all_theta corresponds
% to the classifier for label i
% Some useful variables
m = size(X, 1);
n = size(X, 2);
% You need to return the following variables correctly
all_theta = zeros(num_labels, n + 1);
% Add ones to the X data matrix
X = [ones(m, 1) X];
% Set Initial theta
initial_theta = zeros(n + 1, 1);
% Set options for fminunc
options = optimset('GradObj', 'on', 'MaxIter', 50);
% % Run fmincg to obtain the optimal theta
for i = 1 : num_labels
c = i * ones(size(y));
[theta] = fmincg(@(t)(lrCostFunction(t, X, (y == c), lambda)), initial_theta, options);
all_theta(i, :) = theta;
end
% =========================================================================
end5) 使用训练好模型做预测
function p = predictOneVsAll(all_theta, X)
%PREDICT Predict the label for a trained one-vs-all classifier. The labels
%are in the range 1..K, where K = size(all_theta, 1).
% p = PREDICTONEVSALL(all_theta, X) will return a vector of predictions
% for each example in the matrix X. Note that X contains the examples in
% rows. all_theta is a matrix where the i-th row is a trained logistic
% regression theta vector for the i-th class. You should set p to a vector
% of values from 1..K (e.g., p = [1; 3; 1; 2] predicts classes 1, 3, 1, 2
% for 4 examples)
m = size(X, 1);
num_labels = size(all_theta, 1);
% You need to return the following variables correctly
p = zeros(size(X, 1), 1);
% Add ones to the X data matrix
X = [ones(m, 1) X];
% ====================== YOUR CODE HERE ======================
pred = sigmoid(X*all_theta');
[prop,p] = max(pred,[],2);
% =========================================================================
end
(5) 使用神经网络进行分类
直接载入训练好的权重,在计算的时候需要注意的是要添加偏置单元。
function p = predict(Theta1, Theta2, X)
%PREDICT Predict the label of an input given a trained neural network
% p = PREDICT(Theta1, Theta2, X) outputs the predicted label of X given the
% trained weights of a neural network (Theta1, Theta2)
% Useful values
m = size(X, 1);
num_labels = size(Theta2, 1);
% You need to return the following variables correctly
p = zeros(size(X, 1), 1);
% ====================== YOUR CODE HERE ======================
% Instructions: Complete the following code to make predictions using
% your learned neural network. You should set p to a
% vector containing labels between 1 to num_labels.
%
% Hint: The max function might come in useful. In particular, the max
% function can also return the index of the max element, for more
% information see 'help max'. If your examples are in rows, then, you
% can use max(A, [], 2) to obtain the max for each row.
a1 = [ones(m,1) X];
a2 = [ones(m,1) sigmoid(a1*Theta1')];
a3 = sigmoid(a2*Theta2');
[prop,p]=max(a3,[],2);
% =========================================================================
end