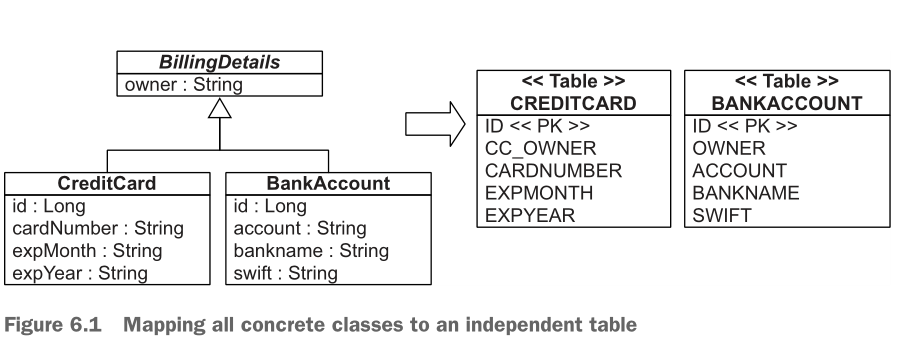
一、结构
二、代码
1.
1 package org.jpwh.model.inheritance.mappedsuperclass; 2 3 import javax.persistence.MappedSuperclass; 4 import javax.validation.constraints.NotNull; 5 6 @MappedSuperclass 7 public abstract class BillingDetails { 8 9 @NotNull 10 protected String owner; 11 12 // ... 13 14 protected BillingDetails() { 15 } 16 17 protected BillingDetails(String owner) { 18 this.owner = owner; 19 } 20 21 public String getOwner() { 22 return owner; 23 } 24 25 public void setOwner(String owner) { 26 this.owner = owner; 27 } 28 }
2.
1 package org.jpwh.model.inheritance.mappedsuperclass; 2 3 import org.jpwh.model.Constants; 4 5 import javax.persistence.AttributeOverride; 6 import javax.persistence.Column; 7 import javax.persistence.Entity; 8 import javax.persistence.GeneratedValue; 9 import javax.persistence.Id; 10 import javax.validation.constraints.NotNull; 11 12 @Entity 13 @AttributeOverride( 14 name = "owner", 15 column = @Column(name = "CC_OWNER", nullable = false)) 16 public class CreditCard extends BillingDetails { 17 18 @Id 19 @GeneratedValue(generator = Constants.ID_GENERATOR) 20 protected Long id; 21 22 @NotNull 23 protected String cardNumber; 24 25 @NotNull 26 protected String expMonth; 27 28 @NotNull 29 protected String expYear; 30 31 // ... 32 33 public CreditCard() { 34 super(); 35 } 36 37 public CreditCard(String owner, String cardNumber, String expMonth, String expYear) { 38 super(owner); 39 this.cardNumber = cardNumber; 40 this.expMonth = expMonth; 41 this.expYear = expYear; 42 } 43 44 public Long getId() { 45 return id; 46 } 47 48 public String getCardNumber() { 49 return cardNumber; 50 } 51 52 public void setCardNumber(String cardNumber) { 53 this.cardNumber = cardNumber; 54 } 55 56 public String getExpMonth() { 57 return expMonth; 58 } 59 60 public void setExpMonth(String expMonth) { 61 this.expMonth = expMonth; 62 } 63 64 public String getExpYear() { 65 return expYear; 66 } 67 68 public void setExpYear(String expYear) { 69 this.expYear = expYear; 70 } 71 72 }
3.
1 package org.jpwh.model.inheritance.mappedsuperclass; 2 3 import org.jpwh.model.Constants; 4 5 import javax.persistence.Entity; 6 import javax.persistence.GeneratedValue; 7 import javax.persistence.Id; 8 import javax.validation.constraints.NotNull; 9 10 @Entity 11 public class BankAccount extends BillingDetails { 12 13 @Id 14 @GeneratedValue(generator = Constants.ID_GENERATOR) 15 protected Long id; 16 17 @NotNull 18 protected String account; 19 20 @NotNull 21 protected String bankname; 22 23 @NotNull 24 protected String swift; 25 26 public BankAccount() { 27 super(); 28 } 29 30 public BankAccount(String owner, String account, String bankname, String swift) { 31 super(owner); 32 this.account = account; 33 this.bankname = bankname; 34 this.swift = swift; 35 } 36 37 public Long getId() { 38 return id; 39 } 40 41 public String getAccount() { 42 return account; 43 } 44 45 public void setAccount(String account) { 46 this.account = account; 47 } 48 49 public String getBankname() { 50 return bankname; 51 } 52 53 public void setBankname(String bankname) { 54 this.bankname = bankname; 55 } 56 57 public String getSwift() { 58 return swift; 59 } 60 61 public void setSwift(String swift) { 62 this.swift = swift; 63 } 64 }
三、存在的问题
1.it doesn’t support polymorphic associations very well。You can’t have another entity mapped with a foreign key “referencing BILLINGDETAILS ”—there is no such table. This would be problematic in the domain model, because BillingDetails is associated with User ; both the CREDITCARD and BANKACCOUNT tables would need a foreign key reference to the USERS table. None of these issues can be easily resolved, so you should consider an alternative mapping strategy.
2.查父类时要查每个表。Hibernate must execute a query against the superclass as several SQL SELECT s, one for each concrete subclass. The JPA query select bd from BillingDetails bd requires two SQL statements:
1 select 2 ID, OWNER, ACCOUNT, BANKNAME, SWIFT 3 from 4 BANKACCOUNT 5 select 6 ID, CC_OWNER, CARDNUMBER, EXPMONTH, EXPYEAR 7 from 8 CREDITCARD
3.several different columns, of different tables, share exactly the same semantics.
结论:We recommend this approach (only) for the top level of your class hierarchy,where polymorphism isn’t usually required, and when modification of the superclass in the future is unlikely.