上一篇:Angular2入门系列教程5-路由(一)-使用简单的路由并在在路由中传递参数
之前介绍了简单的路由以及传参,这篇文章我们将要学习复杂一些的路由以及传递其他附加参数。一个好的路由系统可以使我们的程序更好的工作。
假设你已经跟上了我们的进度。
我们来为我们的文章明细新增一个评论框;当我们在明细中点击评论的时候,在我们的明细页面显示评论,这里,我们就可以完全把明细页面看成一个独立的路由,可以建立自己的子路由页面,做一些评论,分享等操作。
那,首先在data目录下建立我们的评论实体Commen和评论服务Comment.service

1 export class Comment{ 2 id:number; 3 userName:string; 4 content:string; 5 blogId:number; 6 }

1 import {Comment} from './comment' 2 export let Comments:Comment[]=[]; 3 export class CommentService 4 { 5 public AddComment(com:Comment) 6 { 7 com.id=this.GetMaxId(); 8 Comments.push(com); 9 } 10 public GetBlogComments(blogId:number):Comment[] 11 { 12 return Comments.filter(x=>x.blogId==blogId); 13 } 14 private GetMaxId():number 15 { 16 var maxId=1; 17 Comments.forEach(x=>{ 18 if(x.id>maxId) 19 maxId=x.id; 20 }); 21 return maxId; 22 } 23 }
作为服务,我们的commen.service提供了获取相应博客的评论以及添加评论的功能!然后我们在app.module.ts中的provider数组中添加我们的CommnetService服务类
那么,数据准备好了,现在我们来建立我们的评论页面
在App文件夹下建立以下东西(希望你是用插件直接生成,这样可以节约很多时间,插件可以帮我们直接初始化这些组件,这样我们可以直接使用而不报错),但是我们先去处理路由问题,让我们可以在articleDetai中直接导航到这个组件
之前我们谈到的路由是要用<router-outlet></router-outlet>去显示组件,我们自然要在article.detail.html中添加这么一句话
然后为了我们能找文章明细中进行,导航,我们需要配置一下路由文件。这次,我们新建一个路由配置文件,我推荐这样做,因为,我们的程序始终是分模块的,不同模块用自己的路由就行了,而不是所有的路由都配置在一个文件中
我们在根目录(app.routing同级)下面建立articleDetail.routing.ts,键入一下代码

1 import { NgModule } from '@angular/core'; 2 import { RouterModule, Routes } from '@angular/router'; 3 4 import { CommentComponent } from './comment/comment.component'; 5 import { ArticledetailComponent } from './articledetail/articledetail.component'; 6 7 const articleDetailRoutes: Routes = [ 8 { 9 path: 'articledetail/:id', 10 component: ArticledetailComponent, 11 children: [ 12 { 13 path: 'comment', 14 component: CommentComponent 15 } 16 ] 17 } 18 ]; 19 @NgModule({ 20 imports: [ 21 RouterModule.forChild(articleDetailRoutes) 22 ], 23 exports: [ 24 RouterModule 25 ] 26 }) 27 export class ArticleDetailRoutingModule { }
我们看到有个children的节点,这个就是我们配置路由子节点的地方
然后我们将app.routing.ts中关于articledetail的路由删掉

1 const routes:Routes=[ 2 { path: 'article',component: ArticleComponent}, 3 { path: '',redirectTo:"/article",pathMatch: 'full'} 4 ];
然后,我们在app.moudule.ts中添加本次路由相关的信息

1 import { BrowserModule } from '@angular/platform-browser'; 2 import { NgModule } from '@angular/core'; 3 import { FormsModule } from '@angular/forms'; 4 import { HttpModule } from '@angular/http'; 5 import { AppRoutingModule } from './app.routing'; 6 import { ArticleDetailRoutingModule } from './articledetail.routing'; 7 8 import {BlogService} from './data/blog.service'; 9 import {CommentService} from './data/comment.service'; 10 11 import { AppComponent } from './app.component'; 12 import { ArticleComponent } from './article/article.component'; 13 import { ArticledetailComponent } from './articledetail/articledetail.component'; 14 import { CommentComponent } from './comment/comment.component'; 15 16 17 @NgModule({ 18 declarations: [ 19 AppComponent, 20 ArticleComponent, 21 ArticledetailComponent, 22 CommentComponent 23 24 ], 25 imports: [ 26 BrowserModule, 27 FormsModule, 28 HttpModule, 29 ArticleDetailRoutingModule, 30 AppRoutingModule 31 32 ], 33 providers: [BlogService,CommentService], 34 bootstrap: [AppComponent] 35 }) 36 export class AppModule { }
路由可以用了,我们现在来到articleDetail组件,具体编写一下怎么路由
在html中添加代码
<button class="btn" (click)="doComment()">评论</button>
然后在ts中编写事件
doComment()
{
this.router.navigate(["comment"],{relativeTo:this.aRoute});
}
好了,一切准备就绪,现在,我们的子路由可以用了,如果不出意外,点击评论按钮,你可以看到以下内容

到此,我们实现了多级路由,那么,现在来看看传递复杂参数,那,我们就把我们的博客的标题和id传过去吧
在articleDetail组件中的doComment编写
doComment()
{
this.router.navigate(["comment",{id:this.blog.id,title:this.blog.title}],{relativeTo:this.aRoute})
}
我们这里处理了两个参数,[]中"comment"表示要导航到的路由,{}里面的内容是我们传递的参数;relativeTo表示相对与aRoute的路径,我们先来看看这样做的效果
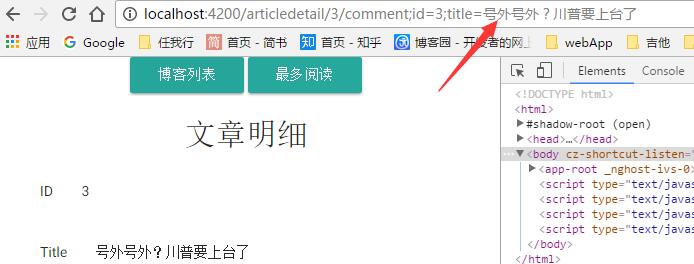
我们看到,在我们的地址栏,路由之外,用分号分割了我们传递的参数,这就是Angular2路由中传递参数的方式,之后我们要做的就是在我们的Comment里面接收这些参数,这里直接贴出我们的Comment组件的完整代码
comment.component.ts

1 import { Component, OnInit,Input } from '@angular/core'; 2 import {ActivatedRoute,Params,Router} from '@angular/router'; 3 import { Location } from '@angular/common'; 4 5 import {Comment} from '../data/comment'; 6 import {CommentService} from '../data/comment.service'; 7 8 import 'rxjs/add/operator/switchMap'; 9 10 @Component({ 11 selector: 'comment', 12 templateUrl: './comment.component.html' 13 }) 14 15 export class CommentComponent implements OnInit { 16 BlogTitle:string; 17 private comments:Comment[]; 18 private com:Comment=new Comment(); 19 private blogId:number; 20 constructor( 21 private cService: CommentService, 22 private aRoute: ActivatedRoute, 23 private router: Router, 24 private location: Location 25 ){} 26 ngOnInit() { 27 let id=this.aRoute.params 28 .subscribe(params=>{ 29 this.comments=this.cService.GetBlogComments(+params["id"]); 30 this.blogId=+params["id"]; 31 this.BlogTitle=params["title"]; 32 }) 33 } 34 sumComment() 35 { 36 if(this.com.userName&&this.com.content) 37 { 38 this.com.blogId=this.blogId; 39 this.cService.AddComment(this.com); 40 this.comments=this.cService.GetBlogComments(this.blogId); 41 console.log(this.comments); 42 this.com=new Comment(); 43 } 44 } 45 }
html

1 <div class="container"> 2 <h2>Blog: {{BlogTitle}}</h2> 3 <div class="comment"> 4 <div class="section"> 5 <div *ngFor="let com of comments"> 6 <div> 7 <span>名字:</span> 8 <span>{{com.userName}}</span> 9 </div> 10 <div > 11 <span>评论内容:</span> 12 <span>{{com.content}}</span> 13 </div> 14 <div class="divider"></div> 15 </div> 16 </div> 17 </div> 18 <div class="divider red"></div> 19 <div> 20 <div class="section"> 21 <div class=""> 22 来,评论一下 23 </div> 24 <div> 25 <input type="text" placeholder="你的名字" [(ngModel)]="com.userName" class=""> 26 <input type="text" placeholder="说点儿什么" [(ngModel)]="com.content" class=""> 27 </div> 28 <div> 29 <button class="btn" (click)="sumComment()">提交</button> 30 </div> 31 </div> 32 </div> 33 </div>
我们直接在代码里面通过route的params属性获取了路由参数,然后处理它;这里的params是一个Observable类型的,我们直接调用它的Subscribe方法(以后再介绍),获取到params,通过一些操作,将这些数据获取出来,显示在页面上,我们来看看我们做的效果
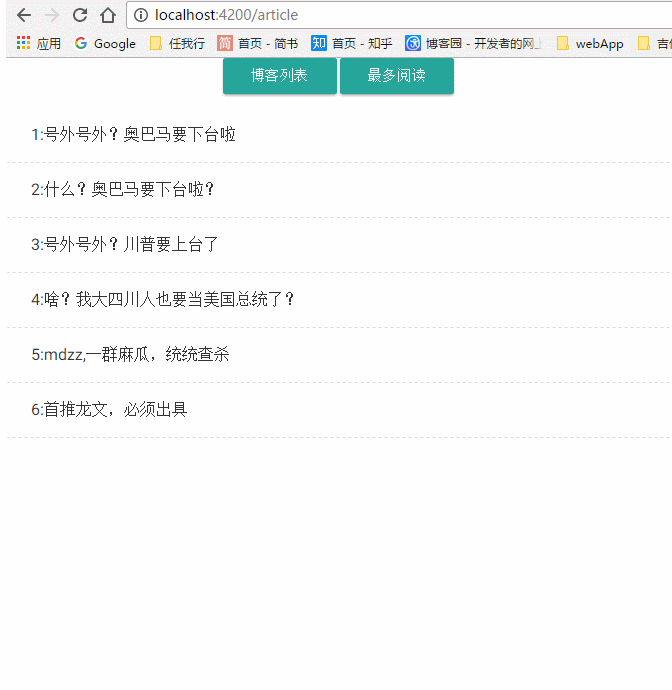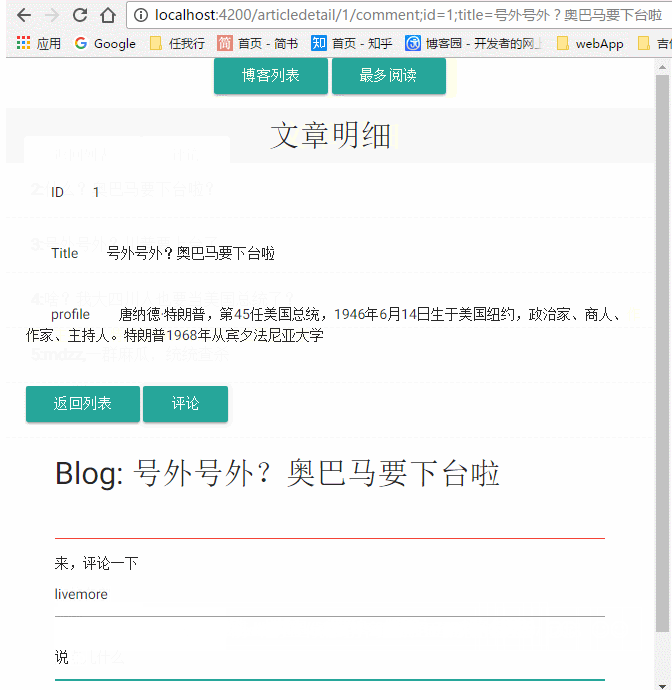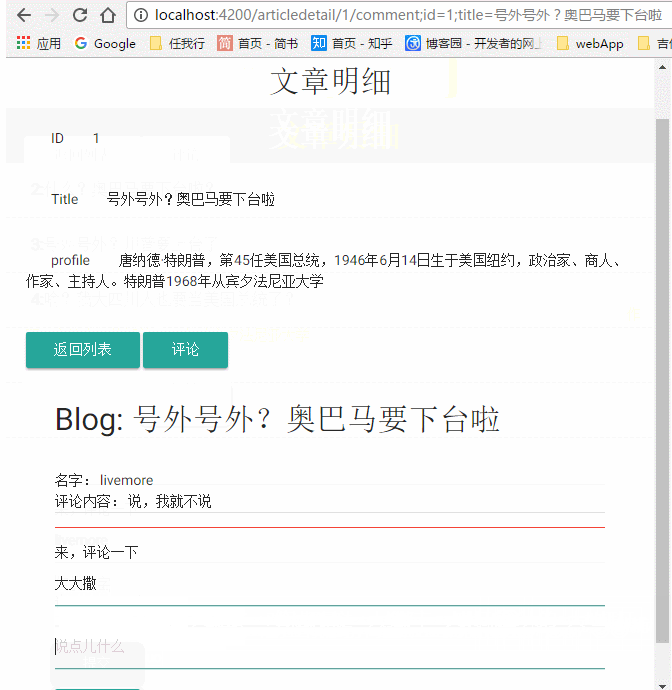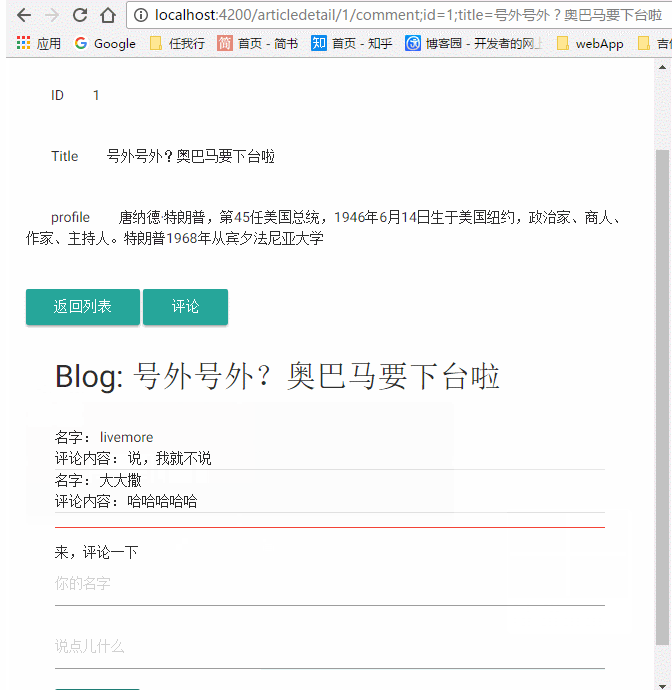
这就是我们本篇文章的内容!
也许,许多人会问了,我们可以直接在这里传递一个类的数据么,比如我们就直接传递blog:this.blog ,把整个Blog传递过去,那我只能告诉不可以,为什么?我们来看看Angular2路由参数的定义吧

这里的定义是key:string,也就是,我们的参数只能传递string类型的过去
我们并不推荐用这种方式传递很多参数到子组件中去,我们可以采用其他方式,比如localStorage;如果你非要这么做,也有解决方法,用JSON.stringify将你的类变成json字符串,到子组件接收之后,再用JSON.parse重新变成一个Object!(很蠢不是么?)
关于路由暂时就介绍这么多,Angular2有更多关于路由的知识,有兴趣的同学可以直接到官网去看,或者,我把这个系列写完了再回头写一个!在我看来,我们日常开发用不到那么多东西,就不在这里介绍了
更新ing。。。
项目已经放到了gitbub上,地址 https://github.com/SeeSharply/LearnAngular
本文章的提交 https://github.com/SeeSharply/LearnAngular/tree/8021af04eb463c31c110e058753ab19d918391af
