Introduction
The CoderLine SkinFramework allows you to add custom Form Borders to your WinForms .NET applications. Didn't you ever want to give your Windows a unique appearance like Microsoft does in their Office Suite (since 2007)?
Development Process
To get the expected result, I had to do much reading and “trial and error” work. The main reading sources are listed below:- http://geekswithblogs.net/kobush/articles/CustomBorderForms.aspx
- http://customerborderform.codeplex.com/
- And of course, the MSDN (especially about Windows Messages)
The first result of my SkinFramework which I finished as a school project in 2008 was quite unusable. It had been very slow and didn't render well if I maximized my window. So the project suspended a long time till a few days ago when a developer contacted me and asked about the project state and I got interested in this project again. Meanwhile I have developed on some GUI controls and also used some third party libraries. There were some libraries which also provide skinning functionalities. The main idea I copied from those libraries is not to derive from a special Form class to enable skinning. In my library, I want to provide a component which can be added to a form which manages the whole skinning.
The result of a few days developing is a ~2700 code line small library which allows creating custom form borders alias Skins.
What is the Main Idea to Enable Skinning?
A form can be split up into two sections, the client area and the non-client area. Simplified the client area is the section where you place your controls and the non-client area is the window borders, the caption buttons (minimize, maximize/restore, close), the icon including the system menu and the caption text:

The .NET 2.0 Framework doesn’t provide the functionality to draw into the non-client area nor place controls in it. We have to “hook” into the Windows Message loop and override the native implementations of all relevant messages. We can do this via overriding the Form’s WndProc Method and a lot of native Win32 calls.
/// <summary> /// Processes Windows messages. /// </summary> /// <param name="m">The Windows <see cref="T:System.Windows.Forms.Message"/> /// to process.</param> protected override void WndProc(ref Message m)
There is a huge list of Windows Messages (http://www.pinvoke.net/default.aspx/Constants.WM), but which ones are relevant for skinning? We can put our messages into 5 main sections:
General
WM_STYLECHANGED
When the user changes the windows style via the control panel, we have to update some stuff and redraw our window.
Handle Form Activation
We have to determine whether our form is currently active and focused or not. Depending on this value, we have to draw an inactive border. Those messages are needed to catch the form activation:
WM_ACTIVATEAPPWM_ACTIVATEWM_MDIACTIVATE
Handle Mouse Processing
We have to handle some mouse events to determine whether the cursor is above any caption button:
WM_NCLBUTTONDOWN
With this message, we can determine the button which is currently pressed.WM_NCMOUSEMOVE
With this message, we can determine the button which is currently hovered.WM_NCLBUTTONUP
As we handle theWM_NCLBUTTONDOWNto determine the pressed state, we need to handle this message to recognize if the button got released.WM_NCMOUSELEAVE, WM_MOUSELEAVE, WM_MOUSEHOVERThese three messages are needed to catch when the mouse leaves the non-client area so that we can reset all hover states.
Handle Form Sizing
To catch these events is very important. We have to update a lot of stuff as our form gets resized, minimized, maximized, etc.
WM_SHOWWINDOW
As we show our window, we have to update the region of our form (to provide a custom form shape as round corners)WM_SIZE
After the size of a form has changed, we have to update our form region too, especially if we switch from a maximized state to the normal one.WM_GETMINMAXINFO
This little message allows us to determine the bounds of our form if it gets maximized. Without processing this message, our form would overlap the taskbar if it gets maximized.WM_WINDOWPOSCHANGING, WM_WINDOWPOSCHANGEDTwo more messages to handle our form resizing.
Handle Non Client Processing
Overriding the following messages allows us to process special non-client actions.
WM_NCPAINT
What could it be? Yes, using the parameters of this message, we can get a Graphics Context to paint our non-client area. Without overriding this message, we would only get some default painted windows.WM_NCCALCSIZE
Using this message, we can determine how big our non-client area is. As you know, we have different non-client area sizes on differentFormBorderStyles.WM_NCHITTEST
This message determines where the cursor is currently positioned in the non-client area. If we set special result values, we enable window features as form-resizing, window moving, opening system menu…
Each message has special LPARAM and WPARAM values which contain important data to process the message (Cursor position, pointer to the graphics context...). Contact the MSDN to find out which message parameters contain which data.
IMPORTANT: I hope you recognized that the Message type is a struct and not a class. You have to pass it by reference (ref parameter) to other methods if you want to change result values.
The Native Window Class
The MSDN describes this class as follows:
"Provides a low-level encapsulation of a window handle and a window procedure." (http://msdn.microsoft.com/en-us/library/system.windows.forms.nativewindow.aspx - 23.02.2010)
But what can this little helper do for us? As described in the upper section, we have to override the windows messages by overriding the WndProc method of the Form class. This would enforce the end-user (developer) to use our SkinForm as the base class for his windows. But as I mentioned, I want to provide a component which enables this feature. This is the point where our NativeWindow comes into play. The NativeWindow class provides an awesome method called AssignHandle.
/// <summary> /// Assigns a handle to this window. /// </summary> /// <param name="handle">The handle to assign to this window.</param> public void AssignHandle(IntPtr handle)If we assign the handle of our
Form (Form.Handle) to a NativeWindow via this method, we can handle all its Windows Messages. We simply derive an own listener class from NativeWindow where we assign the handle of our Form which should get skinned. We can override the WndProc method of our listener and handle all messages for our Form in our NativeWindow. But how can this work? All windows messages are sent to a specific Handle. As we use the AssignHandle method, the NativeWindow becomes the owner of the Forms handle and receives all Messages sent to the form. So we don’t have to register hooks to catch the Windows Messages.
Here a little sample:
[System.Security.Permissions.PermissionSet (System.Security.Permissions.SecurityAction.Demand, Name = "FullTrust")] public class FormMessageListener : NativeWindow { private Form _parentForm; public FormMessageListener(Form parent) { // catch when the handle is created parent.HandleCreated += OnHandleCreated; parent.HandleDestroyed += OnHandleDestroyed; _parentForm = parent; } private void OnHandleCreated(object sender, EventArgs e) { // As the handle gets created, take it over AssignHandle(((Form)sender).Handle); } private void OnHandleDestroyed(object sender, EventArgs e) { // release the handle as needed ReleaseHandle(); } [System.Security.Permissions.PermissionSet (System.Security.Permissions.SecurityAction.Demand, Name = "FullTrust")] protected override void WndProc(ref Message m) { switch (m.Msg) { case 0x00A0: //ncmousemove // Print the Cursor position (in screen coordinates) Point screenPoint = new Point(m.LParam.ToInt32()); Debug.WriteLine(screenPoint); break; } base.WndProc(ref m); } }
Quite useful, eh?
To enable our skinning, we have to implement actions for all mentioned Windows messages – DONE. Include some wrappers and dynamic skin loading and our framework is done. This is why this library only needs about 2700 lines of code.
Class Diagram
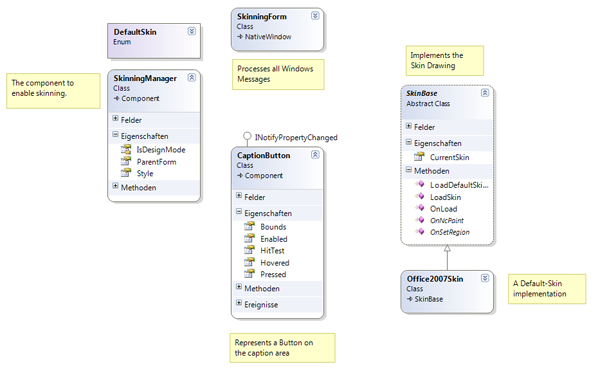
Note: No relations are displayed in this class diagram.
Useful Painting Helpers
Painting Definitions
As we provide an interface for creating new skins, we shouldn’t provide the access to internal classes and properties too. So we create a wrapper class containing all data needed for painting the controls.
For example, the painting definition for our form contains the following data:
- The Graphics to paint into
- The Bounds to paint into
- A list of painting definitions for our caption button
- The icon size
- The caption height
- Is the form active?
- Has the form a system menu /icon
- The caption text
This prevents the skin developer from doing nasty stuff using internal properties.
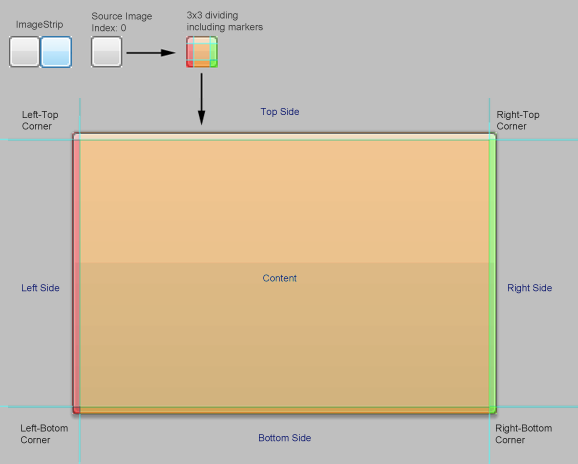
ImageStrip
I got this idea from Axialis Software: http://www.axialis.com/tutorials/image-strip.html (23.02.2010). This library uses image strips for skins. For example, the following image is used to draw the caption of an Office2007 Luna skin.
 (150% Zoom)
(150% Zoom)
You can read more about the ImageStrip class on my blog: http://www.coderline.net/desktopentwicklung/imagestrip-zeichnen/ (Currently in German only, sorry).
Control Paint Helper
As we read in the previous section, ImageStrips are used for drawing the Images itself. But now we need a class which handles the stretching of those images into target bounds. If we think of a button using an image as background source, we have to divide our source image into a 3x3 a matrix: 4 Corners (no stretching), 4 Sides (for horizontal and vertical stretching) and a content area.
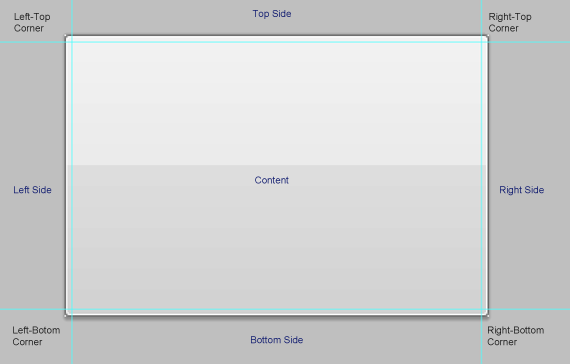
The ControlPaintHelper class manages all this dividing and drawing stuff. During creation, we specify the ImageStrip (the size of a single image, and the image itself) and the padding of the lines which divide our image into a 3x3 matrix. A little illustration how the paint helper works:
How To Use
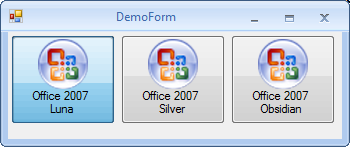
Currently three default Skins are available:
 |
Office 2007 Luna Blue |
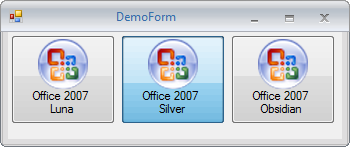 |
Office 2007 Silver |
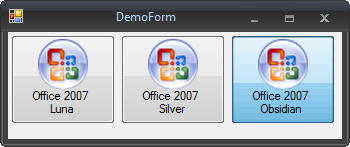 |
Office 2007 Obsidian Black |
To enable the skinning in your application, do these three simple steps:
- Add an instance of the
SkinningManagercomponent to yourForm - Set the
ParentFormproperty to the ownerForm - Set the
DefaultSkinproperty to load any default skin, or load any custom Skin using theSkinningManager.LoadSkin(SkinBase)method
What's Up Next?
The next step is to implement a skin which can load MsStyle documents. This will allow developers to use thousands of existing skins for their application.
Good resources for this task are:
- http://www.codeproject.com/KB/miscctrl/XPTaskBar.aspx
- http://www.codeproject.com/KB/miscctrl/uxtheme.aspx
Probably I will try to support alpha blending transparency. Resources for further reading:
- http://www.codeproject.com/KB/graphics/alphaBG.aspx
- http://www.codeproject.com/KB/GDI-plus/perpxalpha_sharp.aspx
- http://www.codeproject.com/KB/GDI-plus/CsTranspTutorial3.aspx
- SemiTranDlgWithCtrls.aspx
The last part is to provide a skin builder application which allows creating new skins in a friendly user interface. I’m not sure if I will implement such an app.
You're all invited to improve and extend this framework.
from: http://www.codeproject.com/Articles/61485/Winforms-SkinFramework