ipython是一个升级版的交互式python命令行工具.
ipython安装
pip install ipython
等到命令执行完成后显示successfully表示完装成功
在命令提示符下输入ipython就可以启动ipython了
其与原版python命令行工具不同在于ipython的提示符变成了in和out.
in为输入命令的地方,out为命令执行完成后输出的地方
ipython的特点
tab键自动补全一些常用的方法

支持一些系统命令
In [2]: pwd # 显示当前所在目录
Out[2]: '/root'
In [3]: cd .. # 返回当前目录的上一级目录
/
执行系统命令(!)
In [6]: !ifconfig
ens33: flags=4163<UP,BROADCAST,RUNNING,MULTICAST> mtu 1500
inet 192.168.81.10 netmask 255.255.255.0 broadcast 192.168.81.255
inet6 fe80::a545:8b99:d507:4d0f prefixlen 64 scopeid 0x20<link>
ether 00:0c:29:95:d5:31 txqueuelen 1000 (Ethernet)
RX packets 12851 bytes 9887304 (9.4 MiB)
RX errors 0 dropped 0 overruns 0 frame 0
TX packets 7172 bytes 1546188 (1.4 MiB)
TX errors 0 dropped 0 overruns 0 carrier 0 collisions 0
lo: flags=73<UP,LOOPBACK,RUNNING> mtu 65536
inet 127.0.0.1 netmask 255.0.0.0
inet6 ::1 prefixlen 128 scopeid 0x10<host>
loop txqueuelen 1 (Local Loopback)
RX packets 140 bytes 12132 (11.8 KiB)
RX errors 0 dropped 0 overruns 0 frame 0
TX packets 140 bytes 12132 (11.8 KiB)
TX errors 0 dropped 0 overruns 0 carrier 0 collisions 0
In [7]: !ip a
1: lo: <LOOPBACK,UP,LOWER_UP> mtu 65536 qdisc noqueue state UNKNOWN qlen 1
link/loopback 00:00:00:00:00:00 brd 00:00:00:00:00:00
inet 127.0.0.1/8 scope host lo
valid_lft forever preferred_lft forever
inet6 ::1/128 scope host
valid_lft forever preferred_lft forever
2: ens33: <BROADCAST,MULTICAST,UP,LOWER_UP> mtu 1500 qdisc pfifo_fast state UP qlen 1000
link/ether 00:0c:29:95:d5:31 brd ff:ff:ff:ff:ff:ff
inet 192.168.81.10/24 brd 192.168.81.255 scope global ens33
valid_lft forever preferred_lft forever
inet6 fe80::a545:8b99:d507:4d0f/64 scope link
valid_lft forever preferred_lft forever
In [8]: !cat /etc/sysconfig/selinux
# This file controls the state of SELinux on the system.
# SELINUX= can take one of these three values:
# enforcing - SELinux security policy is enforced.
# permissive - SELinux prints warnings instead of enforcing.
# disabled - No SELinux policy is loaded.
SELINUX=disabled
# SELINUXTYPE= can take one of three two values:
# targeted - Targeted processes are protected,
# minimum - Modification of targeted policy. Only selected processes are protected.
# mls - Multi Level Security protection.
SELINUXTYPE=targeted
?命令(内省,命令空间搜索)
In [12]: l1?
Type: list
String form: [1, 2, 3, 4]
Length: 4
Docstring:
list() -> new empty list
list(iterable) -> new list initialized from iterable's items
In [13]: def func():
...: print("hello world")
...:
In [14]: func?
Signature: func()
Docstring: <no docstring>
File: /<ipython-input-13-4475a92670e6>
Type: function
In [15]: func?? # 打印函数的源码
Signature: func()
Source:
def func():
print("hello world")
File: /<ipython-input-13-4475a92670e6>
Type: function
In [17]: l1.a*?
l1.append
In [18]: l1.p*?
l1.pop
In [19]: l1.__*__?
l1.__add__
l1.__class__
l1.__contains__
l1.__delattr__
l1.__delitem__
l1.__dir__
l1.__doc__
l1.__eq__
l1.__format__
l1.__ge__
l1.__getattribute__
l1.__getitem__
l1.__gt__
l1.__hash__
l1.__iadd__
l1.__imul__
l1.__init__
l1.__init_subclass__
l1.__iter__
l1.__le__
l1.__len__
l1.__lt__
l1.__mul__
l1.__ne__
l1.__new__
l1.__reduce__
l1.__reduce_ex__
l1.__repr__
l1.__reversed__
l1.__rmul__
l1.__setattr__
l1.__setitem__
l1.__sizeof__
l1.__str__
l1.__subclasshook__
%run命令执行文件代码
In [29]: !vi test.py
In [30]: !cat test.py
def func1():
print("hello world")
func1()
In [31]: %run "test.py"
hello world
%paste和%cpaste命令执行剪帖板代码
In [2]: %paste
def func1():
print("hello world")
func1()
## -- End pasted text --
hello world
与编辑器和IDE交互
魔术命令:%timeit %pdb
In [37]: %timeit a+b
47.1 ns ± 0.955 ns per loop (mean ± std. dev. of 7 runs, 10000000 loops each)
pdb是python debug的简写,一般用于排错
使用命令历史
使用上箭头或下箭头可以查看上一条命令或下一条命令的历史
输入与输出变量
In [40]: !ls
1 boot etc lib media opt root sbin sys tmp var
bin dev home lib64 mnt proc run srv test.py usr
In [41]: _ # 执行前面倒数第一条命令
Out[41]: 3
In [47]: !ls
1 boot etc lib media opt root sbin sys tmp var
bin dev home lib64 mnt proc run srv test.py usr
In [48]: print("hello world")
hello world
In [49]: !ls
1 boot etc lib media opt root sbin sys tmp var
bin dev home lib64 mnt proc run srv test.py usr
In [50]: __
Out[50]: 3
In [54]: _i48 # 执行第48条命令
Out[54]: 'print("hello world")'
目录书签系统%bookmark
In [55]: %bookmark local /usr/local # 定义local书签
In [56]: %bookmark selinux /etc/sysconfig/selinux # 定义selinux书签
In [57]: %bookmark -l # 显示所有的书签
Current bookmarks:
local -> /usr/local
selinux -> /etc/sysconfig/selinux
In [55]: %bookmark local /usr/local
In [56]: %bookmark sysconfig /etc/sysconfig
In [57]: %bookmark -l
Current bookmarks:
local -> /usr/local
sysconfig -> /etc/sysconfig
In [58]: pwd
Out[58]: '/'
In [59]: cd local
(bookmark:local) -> /usr/local
/usr/local
In [60]: pwd
Out[60]: '/usr/local'
In [61]: cd sysconfig
(bookmark:sysconfig) -> /etc/sysconfig
/etc/sysconfig
In [62]: pwd
Out[62]: '/etc/sysconfig'
ipython notebook
安装jupyter
pip install jupyter
运行界面
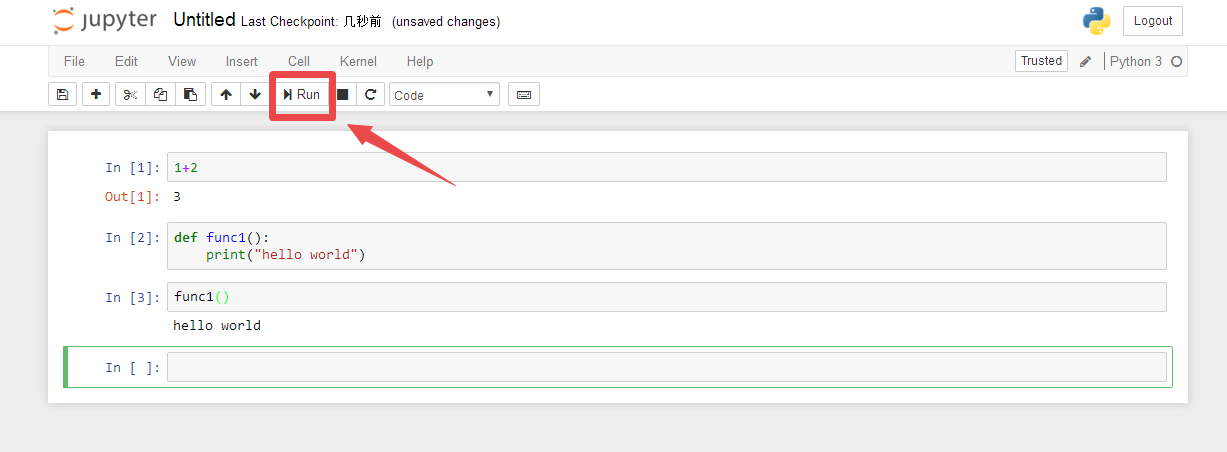
ipython常用的魔术命令
%quickref 显示ipython的快速参考
%magic 显示所有的魔术命令的详细文档
%debug 从最新的异常跟踪的底部进入交互式调试器
%hist 打印命令的输入(可选输出)历史
%pdb 在异常发生后自动进入调试器
%paste 执行剪贴板中的python代码
%cpaste 打开一个特殊提示符以便手工粘贴待执行的python代码
%reset 删除interactive命名空间中的全部变量/名称
%page OBJECT 通过分页器打印输出object
%run script.py 在ipython中执行一个python脚本文件
%prun statement 通过cprofile执行statement,并打印分析器的输出结果
%time statement 报告statement的执行时间
%timeit statement 多次执行statement以计算系统平均执行时间.对那么执行时间非常小的代码很有用
%who,%who_id,%whos 显示interactive命名空间中定义的变量,信息级别/冗余度可变
%xdel variable 删除variable,并尝试清除其在ipython中的对象上的一切引用
python调试器命令
h(help) 显示命令列表
help command 显示command的文档
c(continue) 恢复程序的执行
q(quit) 退出调试器,不再执行任何代码
b(break) n 在当前文件的第n行设置一个断点
b path/to/file.py:n 在指定文件的第n行设置一个断点
s(step) 单步进入函数调用
n(next) 执行当前行,并前进到当前级别的下一行
u(up)/d(down) 在函数调用栈中向上或向下移动
a(args) 显示当前函数的参数
debug statement 在新的递归调试器中调用语句statement
l(list) statement 显示当前行,以及当前栈级别上的上下文参考代码
w(where) 打印当前位置的完整栈跟踪(包括上下文参考代码)
ipython快捷键
Ctrl+p或者向上键头 向后搜索命令历史中以当前输入的文本开头的命令
Ctrl+n或者向上键头 向前搜索命令历史中以当前输入的文本开头的命令
Ctrl+r 按行读取的反向历史搜索(部分匹配)
Ctrl+Shift+variable 从剪贴板粘贴文本
Ctrl+c 中止当前正在执行的代码
Ctrl+a 把光标移动到行首
Ctrl+e 把光标移动到行尾
Ctrl+k 删除从光标开始到行尾的文本
Ctrl+u 清除当前行的所有内容
Ctrl+f 将光标向前移动一个字符
Ctrl+b 将光标向后移动一个字符
Ctrl+l 清屏