1 中国剩余定理:
设正整数m1, m2, m3 …… mk两两互素,则一次同余方程组 x ≡ ai (mod mi) i = 1, 2, 3, ……, k有整数解,且在mod m = m1* m2 * m3 …… mk下解是唯一的,即任意两个解都是mod m同余的
设Mi = m / mi; 那么

因为Mi(i = 1, 2, 3, …… , i != k) 是mk的倍数,可以约去,
而 中
中
其中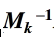 是
是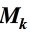 的逆,所以
的逆,所以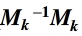 ≡ 1 (mod mk)
≡ 1 (mod mk)
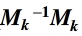 mod mk等于 1 ,所以
mod mk等于 1 ,所以 mod mk 等于ak
mod mk 等于ak
所以所求x是满足所有条件的解
#include <iostream> #include <stdio.h> #include <cmath> using namespace std;
const int MAXN = 100; int nn, a[MAXN], n[MAXN]; int egcd(int a, int b, int &x, int &y) { int d; if (b == 0) { x = 1; y = 0; return a; } else { d = egcd(b, a%b, x, y); int t = x; x = y; y = t - a / b * y; return d; } } int lmes() { int i, tm=1, mf, y, ret=0, m; for (i=0; i<nn; i++) tm *= n[i]; for (i=0; i<nn; i++) { m = tm/n[i]; egcd(m, n[i], mf, y); ret += (a[i]*m*(mf%n[i]))%tm; } return (ret+tm)%tm; } int main() { a[0] = 4; a[1] = 5; n[0] = 5; n[1] = 11; nn = 2; printf("%d ", lmes()); return 0; }
下边的代码是我参考上面那个写的针对多组数据的,道理同上
#include <stdio.h> int a[10], m[10], n; //a[i]是余数 void exGcd(int a, int b, int &x, int &y) { if(b == 0) { x = 1; y = 0; } else { exGcd(b, a%b, x, y); int t = x; x = y; y = t - a / b * y; } } int China() { int tm = 1, M, ret = 0, x, y; for(int i = 0; i < n; i++) tm *= m[i]; for(int i = 0; i < n; i++) { M = tm / m[i]; exGcd(M, m[i], x, y); x = (x % m[i] + m[i]) % m[i]; ret = (ret+ a[i] * M * x) % tm; } return (ret % tm + tm) % tm; } int main() { scanf("%d", &n); for(int i = 0; i < n; i++) scanf("%d", &a[i]); for(int i = 0; i < n; i++) scanf("%d", &m[i]); printf("%d", China()); return 0; }