Rescue mode is the same as a single-user mode. This mode can be used when a condition exists that prevents your system from completing the regular boot process. The system attempts to mount local file systems and start some system services. But rescue mode does not start the network service and does not allow other users to log on to the system. Changing to rescue mode prompts for the root password.
救援模式与单用户模式相同。当存在阻止系统完成常规引导过程的条件时,可以使用此模式。系统尝试挂载本地文件系统并启动一些系统服务。但是救援模式不启动网络服务,也不允许其他用户登录到系统。切换到拯救模式提示输入根密码
Booting into rescue mode
To boot the system into rescue mode please use following steps:
1. Boot the system from installation DVD – Boot the system from the installation DVD/ ISO image of the same major release as the system (this may require you to change the bios to boot from DVD). Once the system has successfully booted from the ISO image and Red Hat Enterprise Linux boot screen will appear. Choose the option Rescue installed system from the menu screen.注意点是iso镜像要用系统的主版本好一致
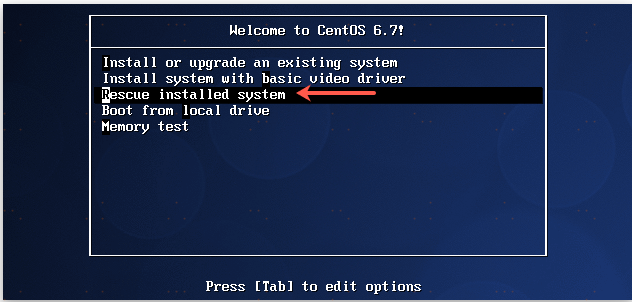
If the option “Rescue installed system is not available, which may be the case you will have to choose Rescue Mode by typing the following at the boot prompt and pressing [Enter]:
如果“Rescue installed system”选项不可用,您必须在引导提示符下输入以下内容并按[Enter]选择拯救模式:
[F1-Main] [F2-Options] [F3-General] [F4-Kernel] [F5-Rescue] boot: linux rescue
2. Choose the Language – Select desired language using arrow keys then press enter.

3. Choose Keyboard Type – Select desired keyboard type using arrow keys then press enter.
4. Network Interfaces – The network interfaces are unnecessary. Use arrow keys to highlight No then press enter. If you want to access the system over the network in rescue mode you can do it by configuring IP address as well. For the example in the post, we will go without network configuration.网络接口非必须,根据需要选择,但是如果选择网络模式,需要配置可用的ip地址

5. Next, a screen will appear telling you that the program will now attempt to find a Red Hat Enterprise Linux installation to rescue. Select “Continue” on this screen.

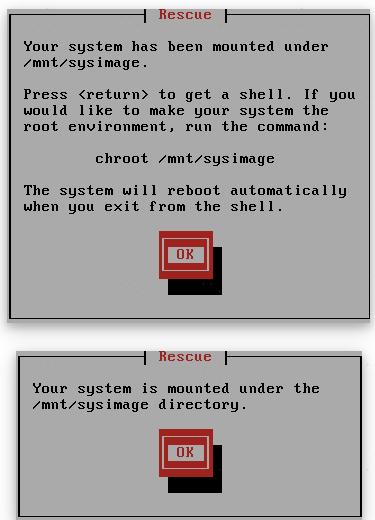
6. You are currently in Rescue Mode. If you allowed it, your root filesystem should be mounted as the /mnt/sysimage directory. For example, your /etc/fstab will be present at the /mnt/sysimage/etc/fstab location.
您当前处于救援模式。如果允许的话,应该将根文件系统挂载为/mnt/sysimage目录。例如,您的/etc/fstab将出现在/mnt/sysimage/etc/fstab位置
7. switch context – You can switch contexts so all the files will be available at their usual locations. Select start shell option.切换到原系统目录下命令
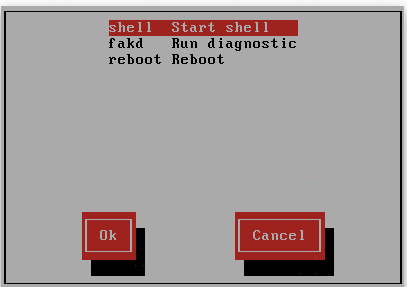
Execute below command in the shell. # chroot /mnt/sysimage
Exiting rescue mode
Although you are accessing the user-space files of your root filesystem, remember that you are still using the boot environment (such as the kernel and device inventory) from the rescue mode. Programs such as df or mount may not give the expected results. Leave the chroot context by using exit twice – first to exit the chroot and second one to exit rescue mode and reboot.
尽管您正在访问根文件系统的用户空间文件,但请记住,您仍然在使用救援模式下的引导环境(例如内核和设备目录)。诸如df或mount之类的程序可能不会给出预期的结果。通过使用两次exit离开chroot上下文——第一次是退出chroot,第二次是退出救援模式并重新启动
# exit ### Leaving chroot environment # exit ### Leaving rescue mode and rebooting