前言
开门见山,开篇明意。这篇博客主要讲解一下Android中ProgressBar控件以及间接继承它的两个子控件SeekBar、RatingBar的基本用法,因为其有继承关系,存在一些共有特性,所以在一篇博客中讲解。下面先简单描述一下这三个控件:
- ProgressBar是一个进度条控件,一般在需要做某个比较耗时的操作的时候,向用户展示执行进度,以免用户以为已经失去响应。
- SeekBar是一个拖动条控件,拖动条通过滑块表示数值,而用户可以在一定范围内拖动这个滑块而改变其数值。
- RatingBar是一个星级评分控件,向用户展示一个评分样式的控件,用户可以选择星级来为其评分。
ProgressBar
ProgressBar,进度条,是AndroidUI界面中一个非常实用的组件,通常用于向用户显示某个耗时操作完成的百分比。因此它需要动态的显示进度,从而避免长时间的执行某个耗时的操作,而让用户感觉程序失去了相应,从而提高界面的友好性。
从官方文档上看,为了适应不同的应用环境,Android内置了几种风格的进度条,可以通过Style属性设置ProgressBar的风格。支持如下属性,后面在示例中会一一展示:
- @android:style/Widget.ProgressBar.Horizontal:水平进度条(可以显示刻度,常用)。
- @android:style/Widget.ProgressBar.Small:小进度条。
- @android:style/Widget.ProgressBar.Large:大进度条。
- @android:style/Widget.ProgressBar.Inverse:不断跳跃、旋转画面的进度条。
- @android:style/Widget.ProgressBar.Large.Inverse:不断跳跃、旋转动画的大进度条。
- @android:style/Widget.ProgressBar.Small.Inverse:不断跳跃、旋转动画的小进度条。
只有Widget.ProgressBar.Horizontal风格的进度条,才可以设置进度的递增,其他的风格展示为一个循环的动画,而设置Widget.ProgressBar.Horizontal风格的进度条,需要用到一些属性设置递增的进度,这些属性都有对应的setter、getter方法,这些属性如下:
- android:max:设置进度的最大值。
- android:progress:设置当前第一进度值。
- android:secondaryProgress:设置当前第二进度值。
- android:visibility:设置是否显示,默认显示。
对于Widget.ProgressBar.Horizontal风格的进度条而言,在代码中动态设置移动量,除了可以使用setProgress(int)方法外,Android还为我们提供了另外一个incrementProgressBy(int)方法,它与setProgress(int)的根本区别在于,setProgress(int)是直接设置当前进度值,而incrementProgressBy(int)是设置当前进度值的增量(正数为增,负数为减)。与setProgress(int)和incrementProgressBy(int)对应的还有setSecondaryProgress(int)和incrementSecondaryProgressBy(int)方法,用于设置第二进度值。
下面通过一个示例,来讲解一下上面的style设置样式的展示想过,以及动态控制进度条增减的实现。
布局代码:
1 <?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?> 2 <LinearLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android" 3 android:layout_width="match_parent" 4 android:layout_height="match_parent" 5 android:orientation="vertical" > 6 7 <TextView 8 android:layout_width="wrap_content" 9 android:layout_height="wrap_content" 10 android:text="android:style/Widget.ProgressBar.Small" /> 11 12 <ProgressBar 13 style="@android:style/Widget.ProgressBar.Small" 14 android:layout_width="wrap_content" 15 android:layout_height="wrap_content" /> 16 17 <TextView 18 android:layout_width="wrap_content" 19 android:layout_height="wrap_content" 20 android:text="android:style/Widget.ProgressBar.Large" /> 21 22 <ProgressBar 23 android:id="@+id/pbLarge" 24 style="@android:style/Widget.ProgressBar.Large" 25 android:layout_width="wrap_content" 26 android:layout_height="wrap_content" /> 27 28 <TextView 29 android:layout_width="wrap_content" 30 android:layout_height="wrap_content" 31 android:text="android:style/Widget.ProgressBar.Inverse" /> 32 33 <ProgressBar 34 style="@android:style/Widget.ProgressBar.Inverse" 35 android:layout_width="wrap_content" 36 android:layout_height="wrap_content" /> 37 38 <TextView 39 android:layout_width="wrap_content" 40 android:layout_height="wrap_content" 41 android:text="android:style/Widget.ProgressBar.Small.Inverse" /> 42 43 <ProgressBar 44 style="@android:style/Widget.ProgressBar.Small.Inverse" 45 android:layout_width="wrap_content" 46 android:layout_height="wrap_content" /> 47 48 <TextView 49 android:layout_width="wrap_content" 50 android:layout_height="wrap_content" 51 android:text="android:style/Widget.ProgressBar.Large.Inverse" /> 52 53 <ProgressBar 54 style="@android:style/Widget.ProgressBar.Large.Inverse" 55 android:layout_width="wrap_content" 56 android:layout_height="wrap_content" /> 57 58 <TextView 59 android:layout_width="wrap_content" 60 android:layout_height="wrap_content" 61 android:text="android:style/Widget.ProgressBar.Horizontal" /> 62 63 <ProgressBar 64 android:id="@+id/pbHor" 65 style="@android:style/Widget.ProgressBar.Horizontal" 66 android:layout_width="match_parent" 67 android:layout_height="wrap_content" 68 android:max="100" 69 android:progress="20" 70 android:secondaryProgress="60" /> 71 72 <LinearLayout 73 android:layout_width="match_parent" 74 android:layout_height="match_parent" 75 android:orientation="horizontal" > 76 <!-- 设置一个按钮控制水平进度的递增 --> 77 <Button 78 android:id="@+id/btnAdd" 79 android:layout_width="wrap_content" 80 android:layout_height="wrap_content" 81 android:text=" + " /> 82 <!-- 设置一个按钮控制水平进度的递减 --> 83 <Button 84 android:id="@+id/btnReduce" 85 android:layout_width="wrap_content" 86 android:layout_height="wrap_content" 87 android:layout_marginLeft="30dp" 88 android:text=" - " /> 89 <!-- 设置一个按钮控制Style为large的进度显示与隐藏 --> 90 <Button 91 android:id="@+id/btnVisible" 92 android:layout_width="wrap_content" 93 android:layout_height="wrap_content" 94 android:layout_marginLeft="30dp" 95 android:text="VisibleLarge" /> 96 </LinearLayout> 97 98 </LinearLayout>
实现代码:
1 package com.bgxt.progressbarseriesdemo; 2 3 import android.app.Activity; 4 import android.os.Bundle; 5 import android.view.View; 6 import android.view.View.OnClickListener; 7 import android.widget.Button; 8 import android.widget.ProgressBar; 9 10 public class ProgressBarActivity extends Activity { 11 12 private Button btnAdd, btnReduce, btnVisible; 13 private ProgressBar pbHor, pbLarge; 14 15 @Override 16 protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) { 17 super.onCreate(savedInstanceState); 18 setContentView(R.layout.activity_progressbar); 19 20 btnAdd = (Button) findViewById(R.id.btnAdd); 21 btnReduce = (Button) findViewById(R.id.btnReduce); 22 btnVisible = (Button) findViewById(R.id.btnVisible); 23 pbHor = (ProgressBar) findViewById(R.id.pbHor); 24 pbLarge = (ProgressBar) findViewById(R.id.pbLarge); 25 26 btnAdd.setOnClickListener(mathClick); 27 btnReduce.setOnClickListener(mathClick); 28 btnVisible.setOnClickListener(new View.OnClickListener() { 29 30 @Override 31 public void onClick(View v) { 32 // 判断Large进度条是否显示,显示则隐藏,隐藏则显示 33 if (pbLarge.getVisibility() == View.VISIBLE) { 34 pbLarge.setVisibility(View.GONE); 35 } else { 36 pbLarge.setVisibility(View.VISIBLE); 37 } 38 39 } 40 }); 41 } 42 43 private View.OnClickListener mathClick = new OnClickListener() { 44 45 @Override 46 public void onClick(View v) { 47 switch (v.getId()) { 48 case R.id.btnAdd: 49 // 如果是增加按钮,因为进度条的最大值限制在100,第一刻度限制在90. 50 // 在此限度内,以1.2倍递增 51 // 使用setProgress() 52 if (pbHor.getProgress() < 90) { 53 pbHor.setProgress((int) (pbHor.getProgress() * 1.2)); 54 } 55 if (pbHor.getSecondaryProgress() < 100) { 56 pbHor.setSecondaryProgress((int) (pbHor 57 .getSecondaryProgress() * 1.2)); 58 } 59 break; 60 case R.id.btnReduce: 61 // 如果是增加按钮,因为进度条的最大值限制在100,第一刻度限制在10.第二刻度限制在20 62 // 在此限度内,以10点为基数进行递减。 63 // 使用incrementXxxProgressBy(int) 64 if (pbHor.getProgress() > 10) { 65 pbHor.incrementProgressBy(-10); 66 } 67 if (pbHor.getSecondaryProgress() > 20) { 68 pbHor.incrementSecondaryProgressBy(-10); 69 } 70 break; 71 } 72 } 73 }; 74 75 }
展示效果:初始--递增--隐藏
SeekBar
SeekBar,拖动条控件 ,间接继承自ProgressBar,所以与进度条类似,但是进度条采用颜色填充来表名进度完成的程度,而拖动条则通过滑动的位置来标识数值。
SeekBar继承自ProgressBar,所以也继承了它的属性设置,上面介绍的一些属性在SeekBar中都可以用到。因为SeekBar涉及到一个滑块的概念,所以新增了属性android:thumb来通过设置一个Drawable对象,指定自定义滑块的外观,当然如果不设定也可以默认使用Android自带的风格。
当用户按住滑块进行滑动的时候,会触发一个SeekBar.OnSeekBarChangeListener事件,这是一个接口,需要开发人员实现三个方法:
- onProgressChanged(SeekBar seekBar,int progress,boolean fromUser):滑块在移动的时候响应。seekBar为触发事件的SeekBar控件,progress为当前SeekBar的滑块数值,fromUser为是否用户拖动产生的响应。
- onStartTrackingTouch(SeekBar seekBar):滑块开始移动的时候响应。
- onStopTrackingTouch(SeekBar seekBar):滑块结束移动的时候相应。
下面通过一个示例来讲解一下SeekBar的基本用法。
1 <?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?> 2 <LinearLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android" 3 android:layout_width="match_parent" 4 android:layout_height="match_parent" 5 android:orientation="vertical" > 6 <TextView 7 8 android:id="@+id/textview1" 9 android:layout_width="match_parent" 10 android:layout_height="30dp" /> 11 12 <TextView 13 android:id="@+id/textview2" 14 android:layout_width="match_parent" 15 android:layout_height="30dp" /> 16 17 <SeekBar 18 android:layout_marginTop="30dp" 19 android:id="@+id/seekbar1" 20 android:layout_width="match_parent" 21 android:layout_height="wrap_content" 22 android:max="100" 23 android:progress="30" /> 24 <!--设置一个拖动条,滑块为定义的bar图片--> 25 <SeekBar 26 android:layout_marginTop="30dp" 27 android:id="@+id/seekbar2" 28 android:layout_width="match_parent" 29 android:layout_height="wrap_content" 30 android:max="100" 31 android:progress="20" 32 android:thumb="@drawable/bar" 33 android:secondaryProgress="80" /> 34 35 </LinearLayout>
实现代码:
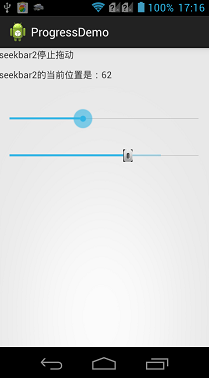
1 package com.bgxt.progressbarseriesdemo; 2 3 import android.app.Activity; 4 import android.os.Bundle; 5 import android.widget.SeekBar; 6 import android.widget.TextView; 7 import android.widget.SeekBar.OnSeekBarChangeListener; 8 9 public class SeekBarActivity extends Activity { 10 private TextView textview1, textview2; 11 private SeekBar seekbar1, seekbar2; 12 @Override 13 protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) { 14 // TODO Auto-generated method stub 15 super.onCreate(savedInstanceState); 16 setContentView(R.layout.activity_seekbar); 17 18 textview1 = (TextView) findViewById(R.id.textview1); 19 textview2 = (TextView) findViewById(R.id.textview2); 20 seekbar1 = (SeekBar) findViewById(R.id.seekbar1); 21 seekbar2 = (SeekBar) findViewById(R.id.seekbar2); 22 23 seekbar1.setOnSeekBarChangeListener(seekBarChange); 24 seekbar2.setOnSeekBarChangeListener(seekBarChange); 25 } 26 private OnSeekBarChangeListener seekBarChange = new OnSeekBarChangeListener() { 27 28 @Override 29 public void onStopTrackingTouch(SeekBar seekBar) { 30 if (seekBar.getId() == R.id.seekbar1) { 31 textview1.setText("seekbar1停止拖动"); 32 } else { 33 textview1.setText("seekbar2停止拖动"); 34 } 35 } 36 37 @Override 38 public void onStartTrackingTouch(SeekBar seekBar) { 39 if (seekBar.getId() == R.id.seekbar1) { 40 textview1.setText("seekbar1开始拖动"); 41 } else { 42 textview1.setText("seekbar2开始拖动"); 43 } 44 } 45 46 @Override 47 public void onProgressChanged(SeekBar seekBar, int progress, 48 boolean fromUser) { 49 if (seekBar.getId() == R.id.seekbar1) { 50 textview2.setText("seekbar1的当前位置是:" + progress); 51 } else { 52 textview2.setText("seekbar2的当前位置是:" + progress); 53 } 54 55 } 56 }; 57 }
效果展示:
RatingBar
RatingBar,星级评分控件,RatingBar与SeekBar的用法非常相似,并且具有相同的父类AbsSeekBar,AbsSeekbar又继承自ProgressBar。而RatingBar与SeekBar最大的区别在于:RatingBar通过星形图标来表示进度。
RatingBar扩展了AbsSeekbar,所以新增了一些固有的属性,也屏蔽了一些无用的属性,如在RatingBar中就不存在第二进度的概念,新增的属性有如下几个:
- android:isIndicator:设置是否允许用户修改,true为不允许,默认为false,允许。
- android:numStars:设置评分控件一共展示多少个星星,默认5个。
- android:rating:设置初始默认星级数。
- android:stepSize:设置每次需要修改多少个星级。
对于RatingBar而言,当改变其星级选项的时候,会触发一个RatingBar.OnRatingBarChangeListener事件,这是一个接口,需要实现其中的onRatingChanged(RatingBar ratingBar,float rating,boolean fromUser)方法,其中ratingBar表示触发事件的控件,rating表示当前的星级,fromUser表示是否用户触发的修改事件。
在这里需要注意的一点就是,因为继承关系,RatingBar也有Progress属性,但是还有另外一个属性rating表示星级。这两个属性代表的意义是有区别的,区别在于Progress属性针对的是Max属性设置的值而言的,而rating是单纯的表示第几颗星。
下面通过一个示例来展示一下评分控件的基本使用。
布局代码:
1 <?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?> 2 <LinearLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android" 3 android:layout_width="match_parent" 4 android:layout_height="match_parent" 5 android:orientation="vertical" > 6 7 <TextView 8 android:layout_width="match_parent" 9 android:layout_height="wrap_content" 10 android:text="评分控件的使用" 11 android:textSize="20dp" /> 12 13 <RatingBar 14 android:id="@+id/rbRating" 15 android:layout_width="wrap_content" 16 android:layout_height="wrap_content" /> 17 18 <RatingBar 19 android:id="@+id/rbRating1" 20 android:layout_width="wrap_content" 21 android:layout_height="wrap_content" 22 android:isIndicator="false" 23 android:max="100" 24 android:numStars="4" 25 android:rating="2.5" 26 android:stepSize="0.5" /> 27 28 </LinearLayout>
实现代码:
1 package com.bgxt.progressbarseriesdemo; 2 3 import android.app.Activity; 4 import android.os.Bundle; 5 import android.widget.RatingBar; 6 import android.widget.RatingBar.OnRatingBarChangeListener; 7 import android.widget.Toast; 8 9 public class RatingBarActivity extends Activity implements OnRatingBarChangeListener { 10 11 private RatingBar rbRating,rbRating1; 12 @Override 13 protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) { 14 super.onCreate(savedInstanceState); 15 setContentView(R.layout.activity_ratingbar); 16 rbRating=(RatingBar)findViewById(R.id.rbRating); 17 rbRating1=(RatingBar)findViewById(R.id.rbRating1); 18 //手动设置第一个RatingBar的属性值 19 rbRating.setMax(100); 20 rbRating.setProgress(20); 21 rbRating.setOnRatingBarChangeListener(this); 22 rbRating1.setOnRatingBarChangeListener(this); 23 } 24 @Override 25 public void onRatingChanged(RatingBar ratingBar, float rating, 26 boolean fromUser) { 27 //分别显示Progress属性和rating属性的不同 28 int progress=ratingBar.getProgress(); 29 Toast.makeText(RatingBarActivity.this, "progress:"+progress+" rating :"+rating,Toast.LENGTH_SHORT).show(); 30 } 31 32 }
展示效果:
总结
以上就详细说明了ProgressBar控件以及其两个子控件的用法,此处不包括控件样式的设置,对于控件的展示效果,以后再进行详解。
请支持原创,尊重原创,转载请注明出处。谢谢。