一、什么是Exchange
RabbitMQ 是 AMQP(高级消息队列协议)的标准实现:
从 AMQP 协议可以看出,Queue、Exchange 和 Binding 构成了 AMQP 协议的核心
-
Producer:消息生产者,即投递消息的程序。
-
Broker:消息队列服务器实体。
-
Exchange:消息交换机,它指定消息按什么规则,路由到哪个队列。
-
Binding:绑定,它的作用就是把 Exchange 和 Queue 按照路由规则绑定起来。
-
Queue:消息队列载体,每个消息都会被投入到一个或多个队列。
-
-
Consumer:消息消费者,即接受消息的程序。
二、Exchange的类型
RabbitMQ常用的Exchange Type有fanout、direct、topic、headers这四种,本文主要通过direct方式,实现生产者与消费者实例
三、具体操作步骤
- 创建生产者 新建springboot web项目,file->new->project
- 在pom.xml文件添加引用
<!-- 添加springboot对amqp的支持 -->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-amqp</artifactId>
</dependency>
<!-- SLf4j 日志记录-->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.projectlombok</groupId>
<artifactId>lombok</artifactId>
<optional>true</optional>
<version>1.18.12</version>
</dependency>
- 在application.properties文件中添加连接MQ配置,注意端口是5672,不是15672,15672是web浏览端口
# 应用名称
spring.application.name=springboot-rabbitmq-receive
spring.rabbitmq.host=127.0.0.1
spring.rabbitmq.port=5672
spring.rabbitmq.username=guest
spring.rabbitmq.password=guest
- 创建RabbitMQ配置类,注意添加的注解是Configuration
package com.howdy.common.config;
import org.springframework.amqp.core.Queue;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
@Configuration //注意 这个地方不是 Configurable
public class RabbitMQConf {
@Bean
public Queue helloQueue() {
// 第一个参数是创建的queue的名字,第二个参数是是否支持持久化
return new Queue("hello_queue_test", true);
}
}
- 创建发送消息服务类
package com.howdy.common.service;
import lombok.extern.slf4j.Slf4j;
import org.springframework.amqp.core.AmqpTemplate;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Service;
@Service
@Slf4j
public class HelloSender {
@Autowired
private AmqpTemplate template;
public void Send() {
String msg = "hello rabbitmq...";
template.convertAndSend("hello_queue_test", msg);
log.info("hello_queue_test队列发送消息:" + msg);
}
}
- 创建测试方法类
package com.howdy.common.controller;
import com.howdy.common.service.HelloSender;
import org.junit.Test;
import org.junit.runner.RunWith;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.GetMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RestController;
@RestController
@RequestMapping("/test")
public class TestRabbitMQ {
@Autowired
private HelloSender helloSender;
@GetMapping("/testRabbit")
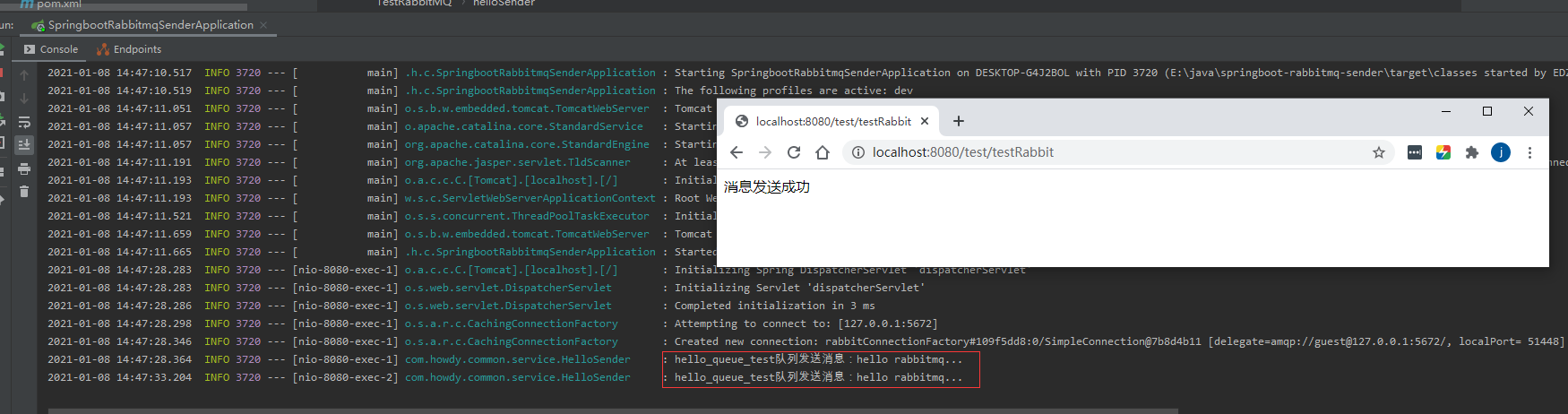
public String testRabbit(){
helloSender.Send();
return "消息发送成功";
}
}
- 生产者 完整目录结构

2、创建消费者项目,大部分与生产者相同,下面我只列出不同的地方
- 创建消费端,消费方法
package com.howdy.common.service;
import lombok.extern.slf4j.Slf4j;
import org.springframework.amqp.rabbit.annotation.RabbitHandler;
import org.springframework.amqp.rabbit.annotation.RabbitListener;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
@Component
@Slf4j
public class HelloReceive {
@RabbitHandler
@RabbitListener(queues = "hello_queue_test") //监听队列名为hello的队列
public void ProcessClient(String msg) {
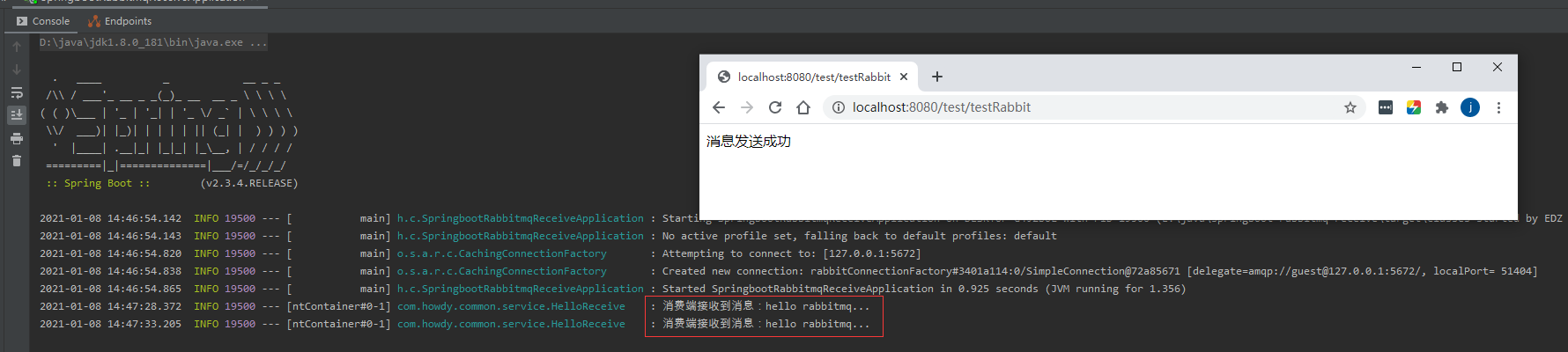
log.info("消费端接收到消息:"+msg);
}
}
- 完整目录结构
- 最后测试结果,如图: