python高级(02)--生成器和迭代器
python的迭代协议
# 什么是迭代协议
# 迭代器是什么? 迭代器是访问集合内元素的一种方式, 一般用来遍历数据
# 迭代器和以下标的访问方式不一样, 迭代器是不能返回的, 迭代器提供了一种惰性方式数据的方式
# [] list , __iter__
from collections.abc import Iterable, Iterator
a = [1, 2]
print(isinstance(a, Iterable))
print(isinstance(a, Iterator))
to_iterator = iter(a)
print(isinstance(to_iterator, Iterator))
什么是迭代器和可迭代对象
from collections.abc import Iterator
class Company(object):
def __init__(self, employee_list):
self.employee = employee_list
def __iter__(self):
return MyIterator(self.employee)
# def __getitem__(self, item):
# return self.employee[item]
class MyIterator(Iterator):
def __init__(self, employee_list):
self.iter_list = employee_list
self.index = 0
def __next__(self):
# 真正返回迭代值的逻辑
try:
word = self.iter_list[self.index]
except IndexError:
raise StopIteration
self.index += 1
return word
if __name__ == "__main__":
company = Company(["tom", "bob", "jane"])
my_itor = iter(company)
# while True:
# try:
# print (next(my_itor))
# except StopIteration:
# pass
# next(my_itor)
for item in company:
print(item)
生成器的使用
# 生成器函数,函数里只要有yield关键字
def gen_func():
yield 1
yield 2
yield 3
def fib(index):
if index <= 2:
return 1
else:
return fib(index - 1) + fib(index - 2)
def fib2(index):
re_list = []
n, a, b = 0, 0, 1
while n < index:
re_list.append(b)
a, b = b, a + b
n += 1
return re_list
def gen_fib(index):
n, a, b = 0, 0, 1
while n < index:
yield b
a, b = b, a + b
n += 1
if __name__ == "__main__":
# 生成器对象, python编译字节码的时候就产生了
gen = gen_func()
for val in gen:
print(val)
print(fib(10))
print(fib2(10))
g_fib = gen_fib(10)
for i in g_fib:
print(i)
生成器的原理
# 1.python中函数的工作原理
"""
"""
import inspect
frame = None
def foo():
bar()
def bar():
global frame
frame = inspect.currentframe()
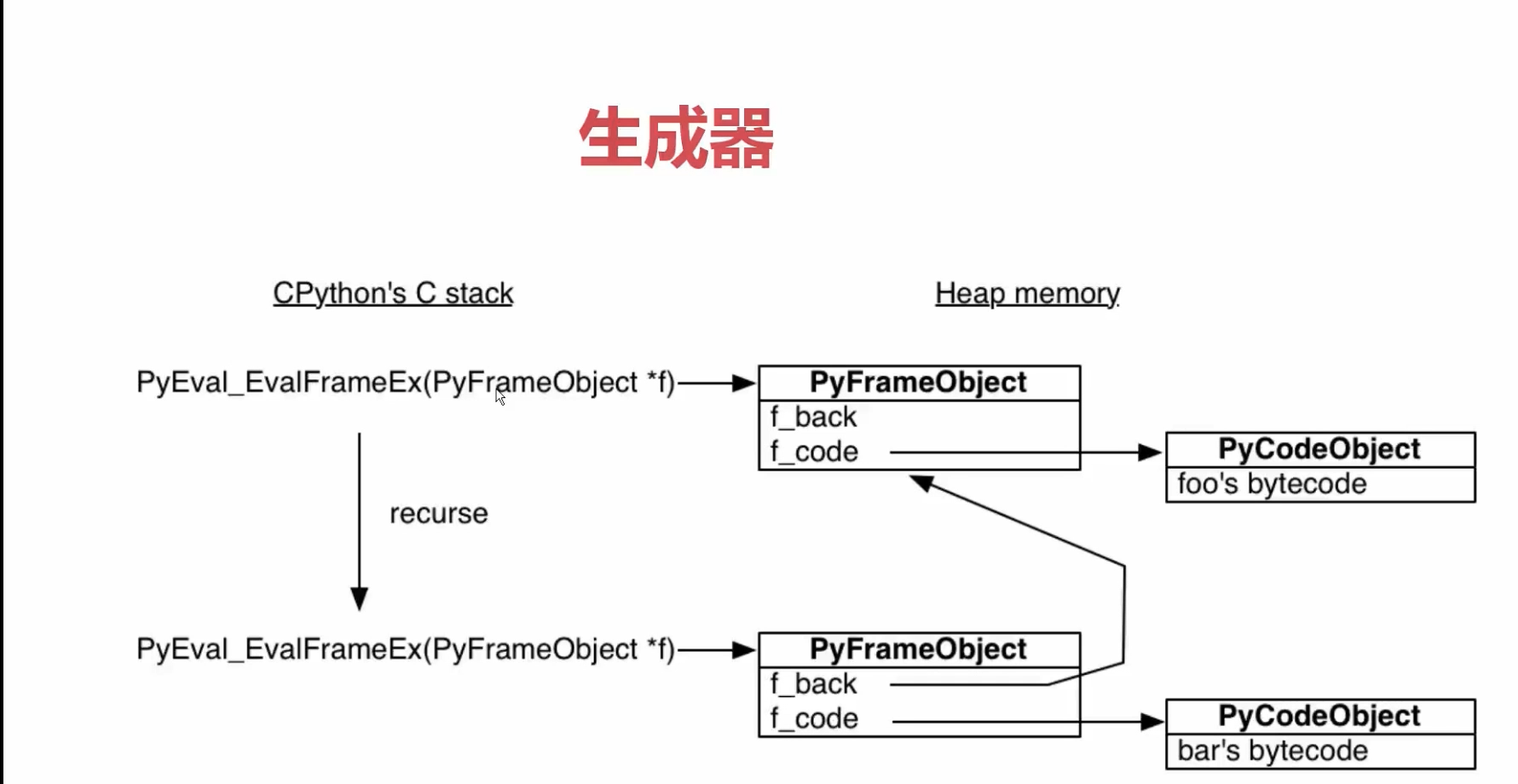
# python.exe会用一个叫做 PyEval_EvalFramEx(c函数)去执行foo函数, 首先会创建一个栈帧(stack frame)
"""
python一切皆对象,栈帧对象, 字节码对象
当foo调用子函数 bar, 又会创建一个栈帧
所有的栈帧都是分配在堆内存上,这就决定了栈帧可以独立于调用者存在
"""
# import dis
# print(dis.dis(foo))
foo()
print(frame.f_code.co_name)
caller_frame = frame.f_back
print(caller_frame.f_code.co_name)
def gen_func():
yield 1
name = 'suki'
sex = 'female'
yield 2
age = 30
return 'snoopy'
import dis
gen = gen_func()
print(dis.dis(gen), '
')
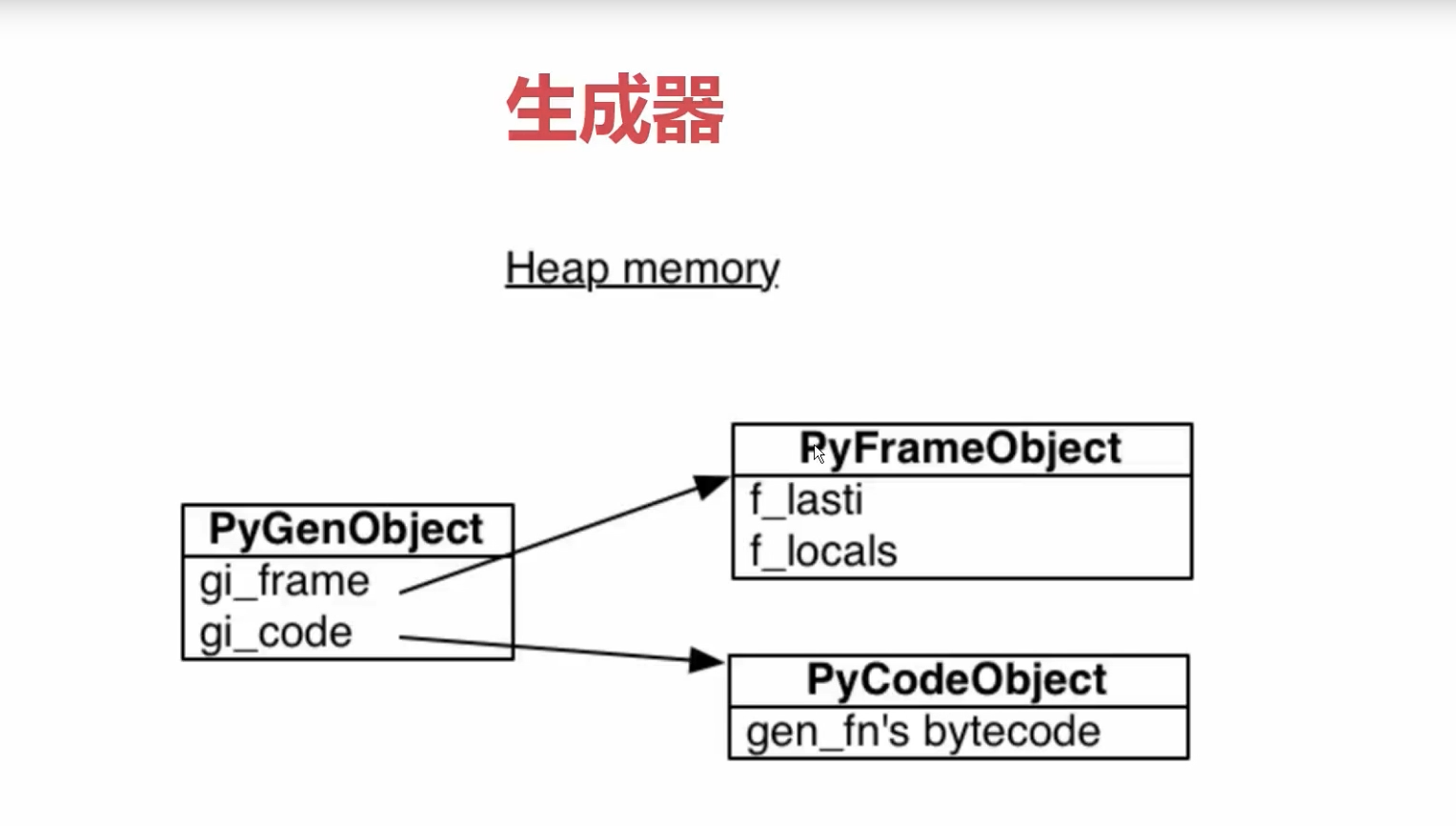
print(gen.gi_frame.f_lasti)
print(gen.gi_frame.f_locals)
next(gen)
print(gen.gi_frame.f_lasti)
print(gen.gi_frame.f_locals)
next(gen)
print(gen.gi_frame.f_lasti)
print(gen.gi_frame.f_locals)
通过UserList来看生成器的应用
class Company:
def __getitem__(self, item):
pass
from collections import UserList
生成器实现大文件读取
# 500G, 特殊 一行
def my_read_lines(f, new_line):
buf = ""
while True:
while new_line in buf:
pos = buf.index(new_line)
yield buf[:pos]
buf = buf[pos + len(new_line):]
chunk = f.read(4096)
if not chunk:
yield buf
break
buf += chunk
with open('input.txt') as f:
for line in my_read_lines(f, '{|}'): # {|}为分隔符
print(line)

