1.comparable接口
当我们运行关于treeMap示例代码1:
代码示例
package com.test.ComparatorTest;
import java.util.*;
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Map students = new TreeMap();
students.put(02,"邱烁铭");
students.put(01,"李家雄");
students.put(04,"李文高");
students.put(03,"周云龙");
Set st = students.keySet(); //获取键的集合
Iterator it = st.iterator(); //获取Iterator对象
while(it.hasNext()){
Object key = it.next();
Object value = students.get(key); //根据获取的键值找到对应的值
System.out.println(key + ":" + value);
}
}
}
结果如下:
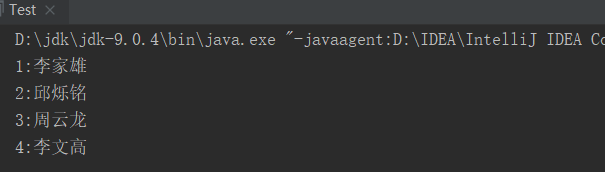
通过分析结果发现:
◆ 对插入的键值对按照键的升序进行了排序。
◆ TreeMap类是一个无序集合(输出顺序与插入顺序不同)
造成此种现象的玄机就在TreeMap类的put方法中,put方法的部分源码如下所示:
public V put(K key, V value){
……
Entry<K,V> t = root;
if (key == null)
throw new NullPointerException();
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
Comparable<? super K> k = (Comparable<? super K>) key;
do {
parent = t;
cmp = k.compareTo(t.key);
if (cmp < 0)
t = t.left;
else if (cmp > 0)
t = t.right;
else
return t.setValue(value);
} while (t != null);
……
}
TreeMap底层数据结构依赖于红黑树的实现,其核心在于比较待插入键值对中键的大小。因此,在put方法中我们将聚焦于compareTo方法。由于compareTo()是由变量k进行调用(k.compareTo()),不难发现,compareTo()是key强转后Comparable类型中的方法。查看comparable接口源码如下:
public interface Comparable<T> {
public int compareTo(T o);
}
comparable接口中只有一个compareTo(T o)的抽象方法。结合示例代码,我们put的键值对为Integer-String类型,通过观察Integer类发现其为comparable接口的实现类。Integer类部分源码如下所示:
public final class Integer extends Number implements Comparable<Integer> {
……
public int compareTo(Integer anotherInteger) {
return compare(this.value, anotherInteger.value);
}
public static int compare(int x, int y) {
return (x < y) ? -1 : ((x == y) ? 0 : 1);
}
……
}
总结:
实例1中TreeMap类元素之所以能够排序是因为每次向TreeMap集合中存入键值对时,就会将键值取出通过调用compareTo()方法与其他元素的键值进行比较,该方法是Comparable接口中定义的。因此想要对集合中的元素进行排序,就必须实现Comparable接口。JDK中大部分类都实现Comparable接口,拥有接口中的CompareTo()方法,如Integer,String和double等。
2.comparator接口
有时候,定义的类没有实现Comparable接口或者实现了Comparable接口而不想按照定义的compareTo()方法进行排序。例如,希望按照降序进行排序。这时可以通过自定义比较器方式对TreeMap集合中的元素排序,即实现Comparator接口,在创建TreeMap集合时指定比较器。如实例2所示:
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Map students = new TreeMap(new Decreasing());
students.put(02,"邱烁铭");
students.put(01,"李家雄");
students.put(04,"李文高");
students.put(03,"周云龙");
Set st = students.keySet();
Iterator it = st.iterator();
while(it.hasNext()){
Object key = it.next();
Object value = students.get(key);
System.out.println(key + ":" + value);
}
}
}
Decreasing比较器源码如下:
import java.util.Comparator;
public class Decreasing implements Comparator {
@Override
public int compare(Object o1, Object o2) {
int id1 = (Integer) o1;
int id2 = (Integer) o2;
return (id2 < id1) ? -1 : ((id1 == id2) ? 0 : 1);
}
}
运行结果如下:
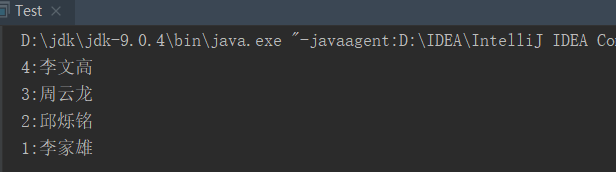
通过结果对比发现,集合按照key值的降序进行排列。实例2中定义了比较器Decreasing针对Integer类型的key进行比较。其实现过程分析如下:
由于我们在创建TreeMap对象使传入了比较器实例,因此在put方法中,将会运行以下代码:
public V put(K key, V value) {
…………
Entry<K,V> t = root;
Comparator<? super K> cpr = comparator;
if (cpr != null) {
do {
parent = t;
cmp = cpr.compare(key, t.key);
if (cmp < 0)
t = t.left;
else if (cmp > 0)
t = t.right;
else
return t.setValue(value);
} while (t != null);
}
…………
}
根据源码分析,在比较键值时,会调用自定义比较器Decreasing中的compare方法对待插入节点的键值与其他节点的键值进行比对。然后按照自定义比较器制定的规则将节点插入到合适的位置。
总结:
实例2中TreeMap类元素之所以能够排序是因为每次向TreeMap集合中存入键值对时,就会将键值取出通过调用compare()方法与其他元素的键值进行比较,该方法是实现了Comparator接口的自定义比较器定义的。自定义比较器实现compare方法,并在创建TreeMap对象时传入。在用户层面,就能按照定义的compare规则对TreeMap集合进行排序。