海量日志采集Flume(HA)
1.介绍:
Flume是Cloudera提供的一个高可用的,高可靠的,分布式的海量日志采集、聚合和传输的系统,Flume支持在日志系统中定制各类数据发送方,用于收集数据;同时,Flume提供对数据进行简单处理,并写到各种数据接受方(可定制)的能力。
2.日志采集
Flume—对哪个ip 哪个端口进行监控 --- 数据监控—接收数据----内存—存储本地硬盘
3.数据处理
Flume提供对数据进行简单处理,并写到各种数据接受方(可定制)的能力。 Flume提供了从Console(控制台)、RPC(Thrift-RPC)、Text(文件)、Tail(UNIX tail)、Syslog(Syslog日志系统,支持TCP和UDP等2种模式),exec(命令执行)等数据源上收集数据的能力。
4.Flume原理:
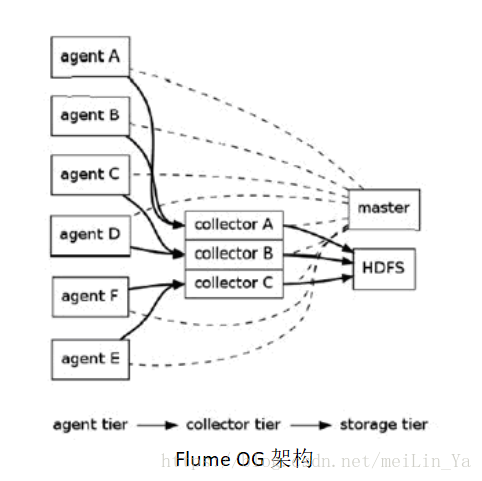
Flume OG:
Flume逻辑上分三层架构:Agent,Collector,Storage。采用多Master,为保持数据一致项,使用zookeeper,保持数据高可用和一致性。
特点:
· 3个角色:代理节点(agent),收集节点(collector),主节点(master).
· agent、collector 由 source、sink 组成,代表在当前节点数据是从 source 传送到 sink。
Flume NG

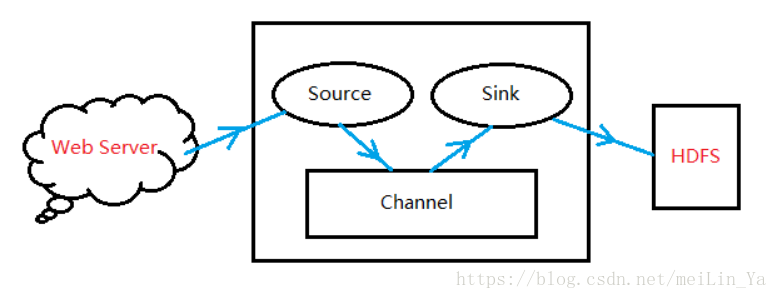
· Source:完成对日志数据的收集,分成 transtion 和 event 打入到Channel之中。
Source类型 | 说明 |
Avro Source | 支持Avro协议(实际上是Avro RPC),提供一个Avro的接口,需要往设置的地址和端口发送Avro消息,Source就能接收到,如:Log4j Appender通过Avro Source将消息发送到Agent |
Thrift Source | 支持Thrift协议,提供一个Thrift接口,类似Avro |
Exec Source | Source启动的时候会运行一个设置的UNIX命令(比如 cat file),该命令会不断地往标准输出(stdout)输出数据,这些数据就会被打包成Event,进行处理 |
JMS Source | 从JMS系统(消息、主题)中读取数据,类似ActiveMQ |
Spooling Directory Source | 监听某个目录,该目录有新文件出现时,把文件的内容打包成Event,进行处理 |
Netcat Source | 监控某个端口,将流经端口的每一个文本行数据作为Event输入 |
Sequence Generator Source | 序列生成器数据源,生产序列数据 |
Syslog Sources | 读取syslog数据,产生Event,支持UDP和TCP两种协议 |
HTTP Source | 基于HTTP POST或GET方式的数据源,支持JSON、BLOB表示形式 |
Legacy Sources | 兼容老的Flume OG中Source(0.9.x版本) |
自定义Source | 使用者通过实现Flume提供的接口来定制满足需求的Source。 |
· Channel:主要提供一个队列的功能,对source提供中的数据进行简单的缓存。
Channel类型 | 说明 |
Memory Channel | Event数据存储在内存中 |
JDBC Channel | Event数据存储在持久化存储中,当前Flume Channel内置支持Derby |
File Channel | Event数据存储在磁盘文件中 |
Spillable Memory Channel | Event数据存储在内存中和磁盘上,当内存队列满了,会持久化到磁盘文件(当前试验性的,不建议生产环境使用) |
Pseudo Transaction Channel | 测试用途 |
Custom Channel | 自定义Channel实现 |
· Sink:取出Channel中的数据,进行相应的存储文件系统,数据库,或者提交到远程服务器。
Sink类型 | 说明 |
HDFS Sink | 数据写入HDFS |
Logger Sink | 数据写入日志文件 |
Avro Sink | 数据被转换成Avro Event,然后发送到配置的RPC端口上 |
Thrift Sink | 数据被转换成Thrift Event,然后发送到配置的RPC端口上 |
IRC Sink | 数据在IRC上进行回放 |
File Roll Sink | 存储数据到本地文件系统 |
Null Sink | 丢弃到所有数据 |
HBase Sink | 数据写入HBase数据库 |
Morphline Solr Sink | 数据发送到Solr搜索服务器(集群) |
ElasticSearch Sink | 数据发送到Elastic Search搜索服务器(集群) |
Kite Dataset Sink | 写数据到Kite Dataset,试验性质的 |
Custom Sink | 自定义Sink实现 |

Flume安装和使用:
安装
运行配置:
a1.sources = r1
a1.sinks = k1
a1.channels = c1
# Describe configure the source
a1.sources.r1.type = avro
a1.sources.r1.bind = 0.0.0.0
a1.sources.r1.port = 4141
# Describe the sink
a1.sinks.k1.type = logger
# Use a channel which buffers events in memory
a1.channels.c1.type = memory
a1.channels.c1.capacity = 1000
a1.channels.c1.transactionCapacity = 100
# Bind the source and sink to the channel
a1.sources.r1.channels = c1
a1.sinks.k1.channel = c1运行:
在/home/bigdata/flume1.6目录下运行
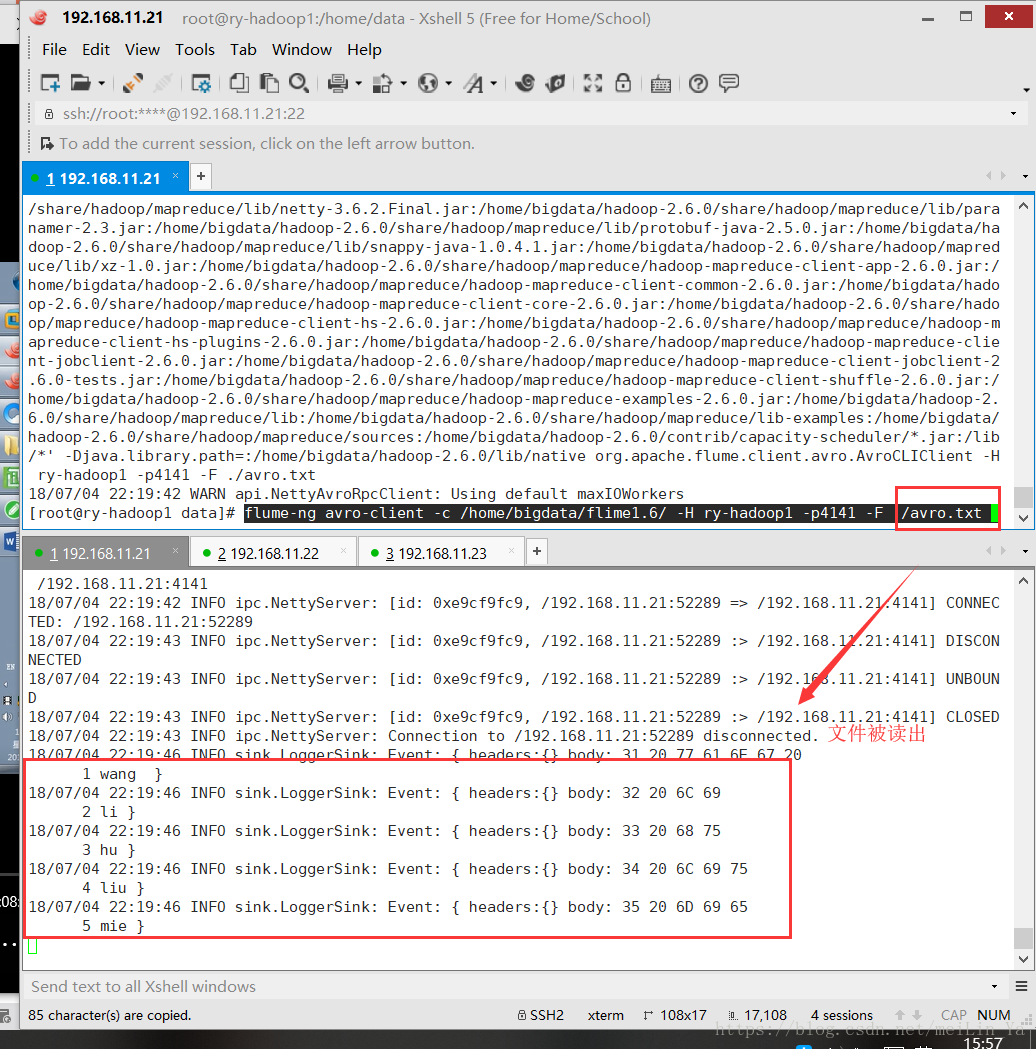
flume-ng agent -n a1 -c . -f ./conf/avro.conf -Dflume.root.logger=INFO,console当flume可以运行我们就体会下收集不同数据源(source)日志,并存放到hdfs上
source: avro
flume-ng avro-client -c /home/bigdata/flime1.6/ -H ry-hadoop1 -p4141 -F ./avro.txt source: Exec
b1.sources=r1
b1.channels=c1
b1.sinks=k1
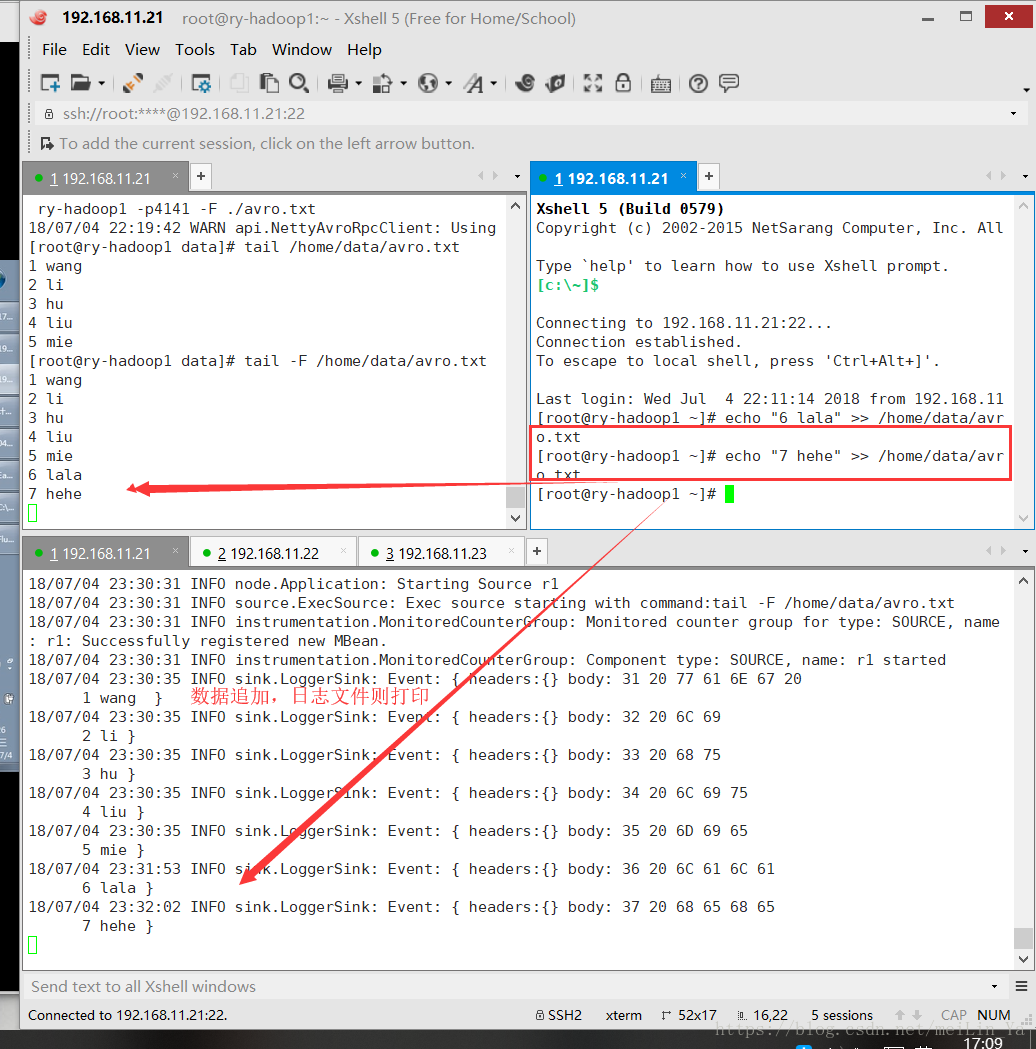
b1.sources.r1.type=exec
b1.sources.r1.command=tail -F /home/data/avro.txt
b1.channels.c1.type=memory
b1.channels.c1.capacity=1000
b1.channels.c1.transactionCapacity=100
b1.sinks.k1.type=logger
b1.sources.r1.channels=c1
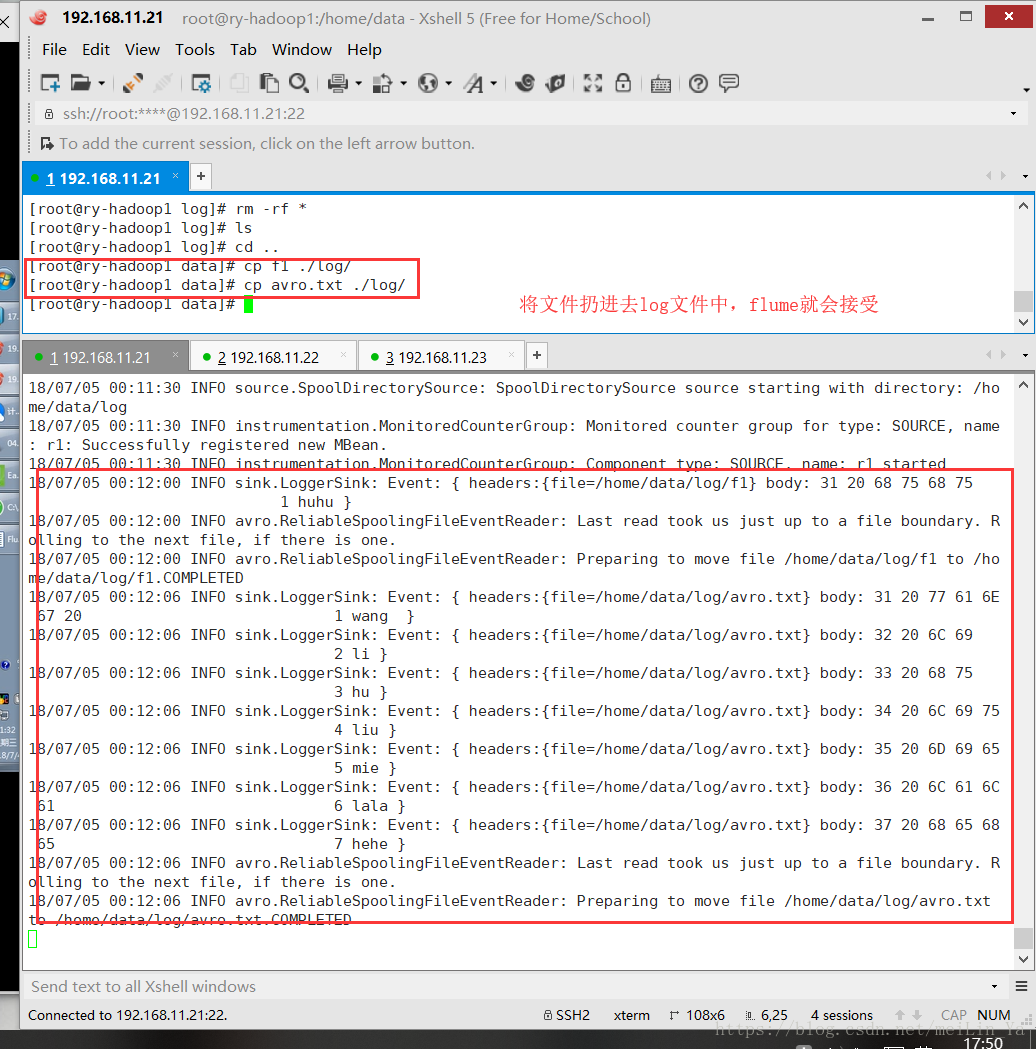
b1.sinks.k1.channel=c1source: spooldir只能对一级目录进行收集
在数据Linux本地建一个文件夹log
agent.sources=r1
agent.channels=c1
agent.sinks=k1
agent.sources.r1.type=spooldir
agent.sources.r1.spooldir=/home/data/log
agent.sources.r1.fileHeader=true
agent.channels.c1.type=memory
agent.channels.c1.capacity=1000
agent.channels.c1.transactionCapacity=100
agent.sinks.k1.type=logger
agent.sources.r1.channels=c1
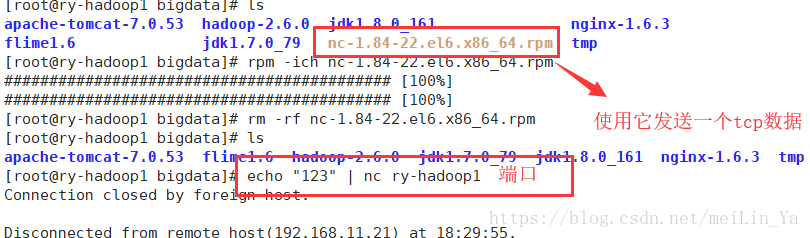
agent.sinks.k1.channel=c1flume-ng agent -n agent -c /home/bigdata/flime1.6/ -f /home/bigdata/flime1.6/conf/spoolDir.conf -Dflume.root.logger=INFO,consolesource: TCP
a1.sources = r1
a1.sinks = k1
a1.channels = c1
# Describe/configure the source
a1.sources.r1.type = syslogtcp
a1.sources.r1.port = 5140
a1.sources.r1.host = 0.0.0.0
# Describe the sink
a1.sinks.k1.type = logger
# Use a channel which buffers events in memory
a1.channels.c1.type = memory
a1.channels.c1.capacity = 1000
a1.channels.c1.transactionCapacity = 100
# Bind the source and sink to the channel
a1.sources.r1.channels = c1
a1.sinks.k1.channel = c1
source:JSONHandler
a1.sources = r1
a1.sinks = k1
a1.channels = c1
# Describe/configure the source
a1.sources.r1.type = org.apache.flume.source.http.HTTPSource
a1.sources.r1.port = 8888
# Describe the sink
a1.sinks.k1.type = logger
# Use a channel which buffers events in memory
a1.channels.c1.type = memory
a1.channels.c1.capacity = 1000
a1.channels.c1.transactionCapacity = 100
# Bind the source and sink to the channel
a1.sources.r1.channels = c1
a1.sinks.k1.channel = c1
source 就讲5个。
然后讲存储
hdfsSinK.conf
配置:
a1.sources = r1
a1.sinks = k1
a1.channels = c1
# Describe/configure the source
a1.sources.r1.type = syslogtcp
a1.sources.r1.port = 5140
a1.sources.r1.host = 0.0.0.0
# Describe the sink
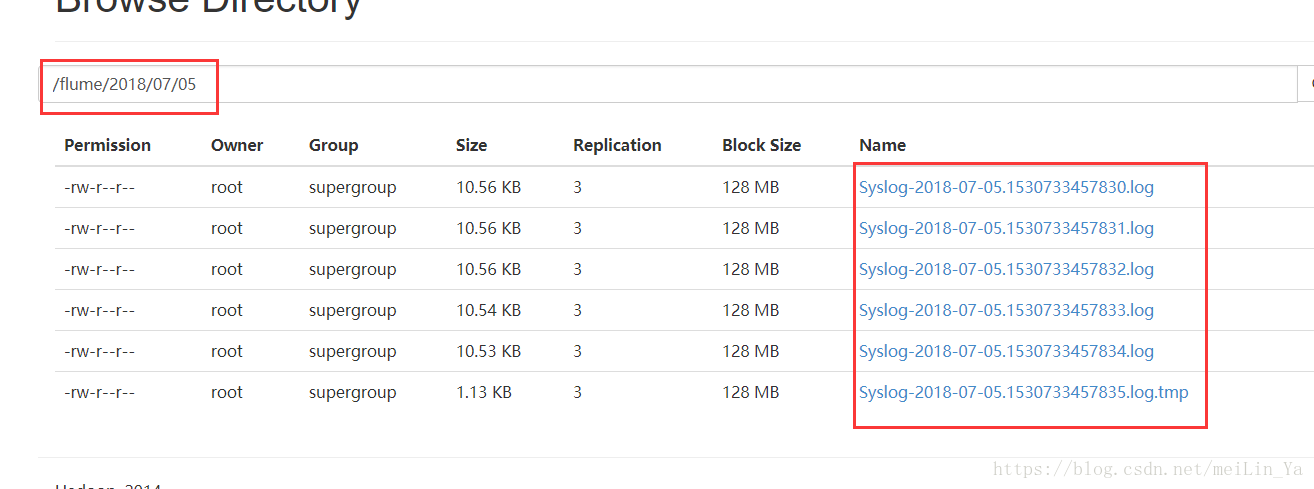
a1.sinks.k1.type = hdfs
a1.sinks.k1.hdfs.path = hdfs://ry-hadoop1:8020/flume
a1.sinks.k1.hdfs.filePrefix = Syslog
a1.sinks.k1.hdfs.fileSuffix = .log
a1.sinks.k1.hdfs.round = true
a1.sinks.k1.hdfs.roundValue = 1
a1.sinks.k1.hdfs.roundUnit = minute
a1.sinks.k1.hdfs.fileType=DataStream
a1.sinks.k1.hdfs.writeFormat=Text
a1.sinks.k1.hdfs.rollInterval=0
a1.sinks.k1.hdfs.rollSize=10240
a1.sinks.k1.hdfs.rollCount=0
a1.sinks.k1.hdfs.idleTimeout=60
# Use a channel which buffers events in memory
a1.channels.c1.type = memory
a1.channels.c1.capacity = 1000
a1.channels.c1.transactionCapacity = 100
# Bind the source and sink to the channel
a1.sources.r1.channels = c1
a1.sinks.k1.channel = c1运行:
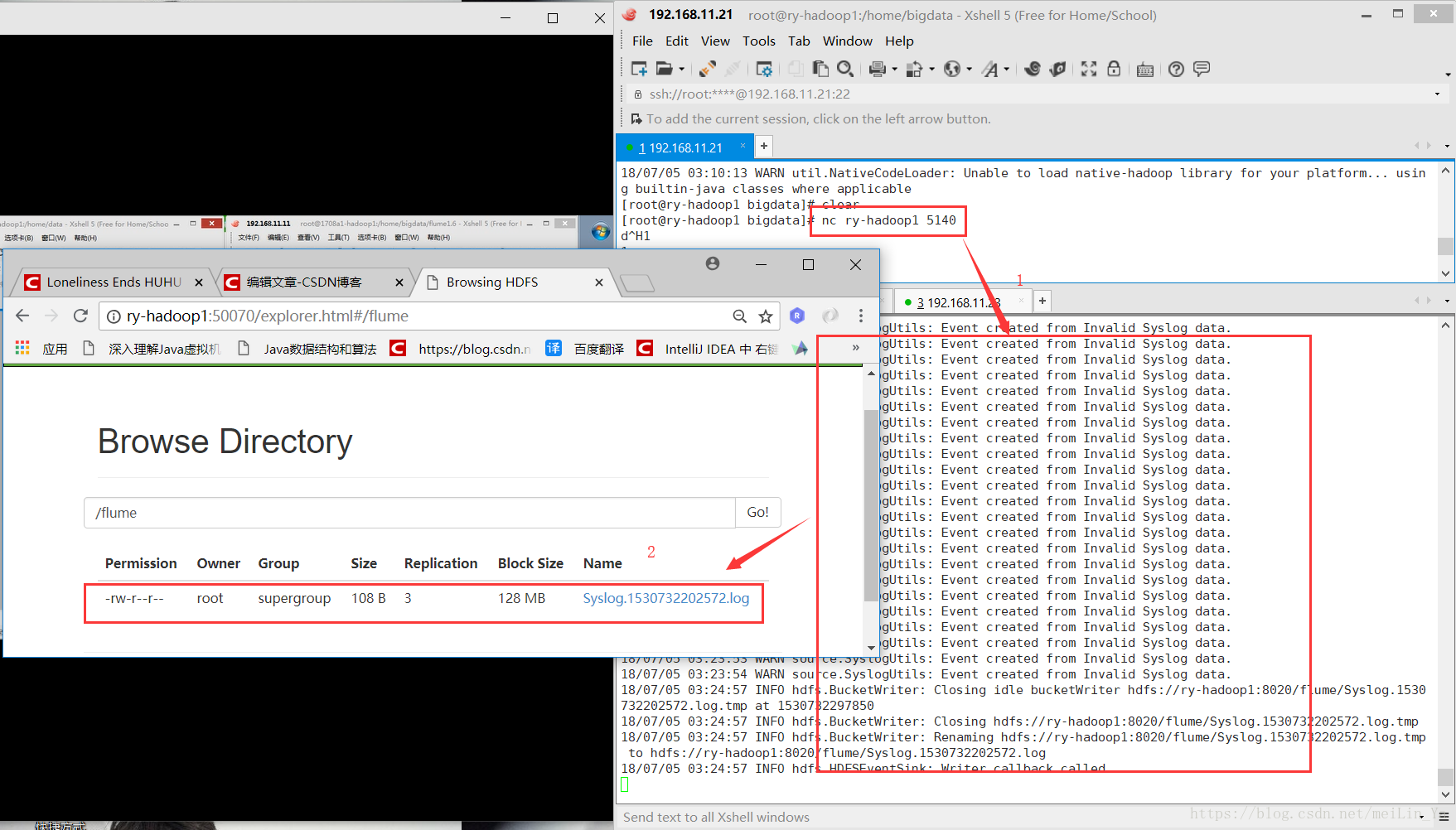
flume-ng agent -n a1 -c . -f ./conf/hdfsSink.conf -Dflume.root.logger=INFO,console写一个shell脚本,循环输出tcp数据,然后收集在hdfs种
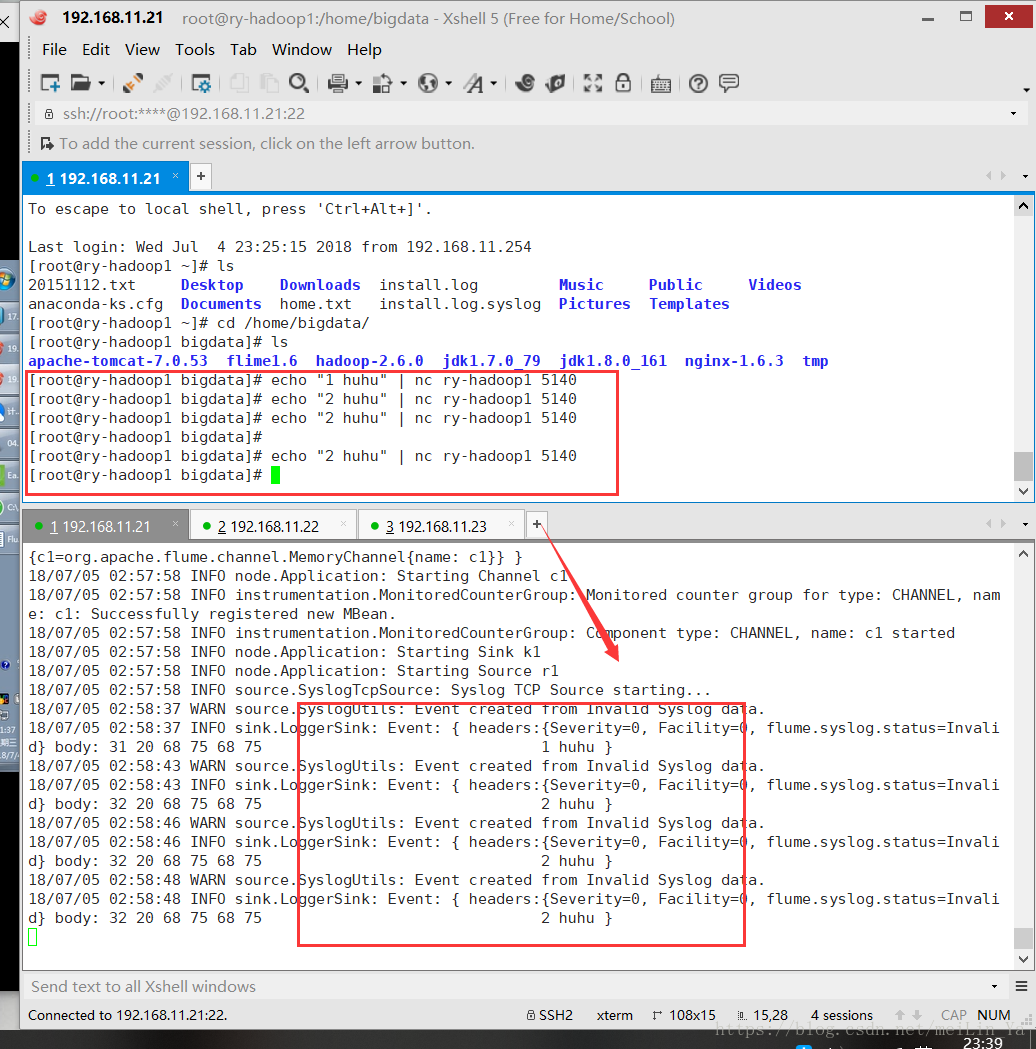
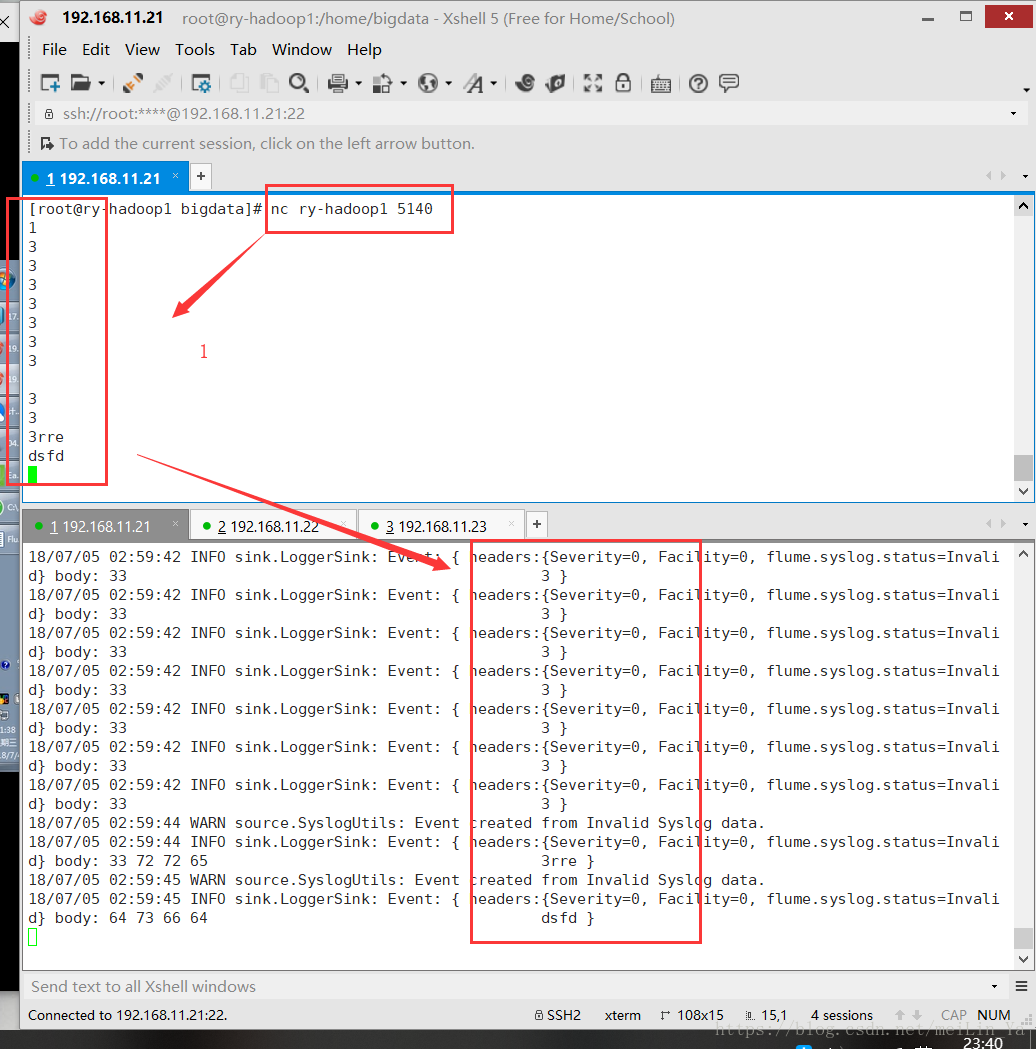
#!/bin/sh
int=1
while(( $int<=500000 ))
do
echo "this is message"$int | nc ry-hadoop1 5140
echo "this is message"$int
let "int++"
done
设定收集日志的具体时间。
那么有个问题,当hadoop维护期间不能存储数据时,我们的日志文件存在哪里呢?
本地,那么我们看看如何存在本地
通道类型为文本形式
a1.sources = r1
a1.sinks = k1
a1.channels = c1
# Describe/configure the source
a1.sources.r1.type = syslogtcp
a1.sources.r1.port = 5140
a1.sources.r1.host = 0.0.0.0
# Describe the sink
a1.sinks.k1.type = file_roll
a1.sinks.k1.sink.directory = /home/data/log/
a1.sinks.k1.sink.serializer=TEXT
# Use a channel which buffers events in memory
a1.channels.c1.type = memory
a1.channels.c1.capacity = 1000
a1.channels.c1.transactionCapacity = 100
# Bind the source and sink to the channel
a1.sources.r1.channels = c1
a1.sinks.k1.channel = c1channels通道类型为文件形式
a1.sources = s1
a1.channels = c1
a1.sinks = k1
# For each one of the sources, the type is defined
a1.sources.s1.type = syslogtcp
a1.sources.s1.host = localhost
a1.sources.s1.port = 5180
# Each sink's type must be defined
a1.sinks.k1.type = logger
# Each channel's type is defined.
a1.channels.c1.type = file
a1.channels.c1.checkpointDir = /home/data/log/checkpoint
a1.channels.c1.dataDir = /home/data/log/data
#Bind the source and sinks to channels
a1.sources.s1.channels = c1
a1.sinks.k1.channel = c1flume的HA:
Flume支持Fan out流从一个源到多个通道。有两种模式的Fan out,分别是复制和复用。在复制的情况下,流的事件被发送到所有的配置通道。在复用的情况下,事件被发送到可用的渠道中的一个子集。Fan out流需要指定源和Fan out通道的规则。大白话来说就是,当你采集日志的时候可以通过一个agent进行保存多份日志。启动多台集群讲多台的flume连接起来,可以同时接收到其中一台的数据进行备份,这个有点类似zookeeper。
1) Replicating Channel Selector 多个Channel
在3台机器上启动flume的avor,然后复制master连接启动source为:replicating的flume
a1.sources = r1
a1.sinks = k1
a1.channels = c1
# Describe/configure the source
a1.sources.r1.type = avro
a1.sources.r1.bind = 0.0.0.0
a1.sources.r1.port = 5555
# Describe the sink
a1.sinks.k1.type = logger
# Use a channel which buffers events in memory
a1.channels.c1.type = memory
a1.channels.c1.capacity = 1000
a1.channels.c1.transactionCapacity = 100
# Bind the source and sink to the channel
a1.sources.r1.channels = c1
a1.sinks.k1.channel = c1在master启动连接:
a1.sources = r1
a1.channels = c1 c2
a1.sinks = k1 k2
# Describe/configure the source
a1.sources.r1.type = syslogtcp
a1.sources.r1.host = 0.0.0.0
a1.sources.r1.port = 5140
a1.sources.r1.channels = c1 c2
a1.sources.r1.selector.type = replicating
# Describe the sink
a1.sinks.k1.type = avro
a1.sinks.k1.channel = c1
a1.sinks.k1.hostname = master
a1.sinks.k1.port = 5555
a1.sinks.k2.type = avro
a1.sinks.k2.channel = c2
a1.sinks.k2.hostname = slave1
a1.sinks.k2.port = 5555
# Use a channel which buffers events in memory
a1.channels.c1.type = memory
a1.channels.c1.capacity = 1000
a1.channels.c1.transactionCapacity = 100
a1.channels.c2.type = memory
a1.channels.c2.capacity = 1000
a1.channels.c2.transactionCapacity = 100当你写一条数据进入日志时,其他3台机器都会有反应
1) MulChnSel_a1.conf
输入数据映射的匹配。
a1.sources = s1
a1.channels = c1 c2
a1.sinks = k1 k2
# For each one of the sources, the type is defined
a1.sources.s1.type = org.apache.flume.source.http.HTTPSource
a1.sources.s1.port = 8887
a1.sources.s1.channels = c1 c2
a1.sources.s1.selector.type = multiplexing
a1.sources.s1.selector.header = company
a1.sources.s1.selector.mapping.ali = c1
a1.sources.s1.selector.mapping.baidu = c2
a1.sources.s1.selector.default = c2
# Each sink's type must be defined
a1.sinks.k1.type = avro
a1.sinks.k1.hostname = master
a1.sinks.k1.port = 5555
a1.sinks.k1.channel = c1
a1.sinks.k2.type = avro
a1.sinks.k2.hostname = slave1
a1.sinks.k2.port = 5555
a1.sinks.k2.channel = c2
# Each channel's type is defined.
a1.channels.c1.type = memory
a1.channels.c1.capacity = 1000
a1.channels.c1.transactionCapacity = 100
a1.channels.c2.type = memory
a1.channels.c2.capacity = 1000
a1.channels.c2.transactionCapacity = 100
3)Flume Sink Processors
failover的机器是一直发送给其中一个sink,当这个sink不可用的时候,自动发送到下一个sink。
a1.sources = r1
a1.sinks = k1 k2
a1.channels = c1 c2
#这个是配置failover的关键,需要有一个sink group
a1.sinkgroups = g1
a1.sinkgroups.g1.sinks = k1 k2
#处理的类型是failover
a1.sinkgroups.g1.processor.type = failover
#优先级,数字越大优先级越高,每个sink的优先级必须不相同
a1.sinkgroups.g1.processor.priority.k1 = 5
a1.sinkgroups.g1.processor.priority.k2 = 10
#设置为10秒,当然可以根据你的实际状况更改成更快或者很慢
a1.sinkgroups.g1.processor.maxpenalty = 10000
# Describe/configure the source
a1.sources.r1.type = syslogtcp
a1.sources.r1.port = 5140
a1.sources.r1.channels = c1 c2
a1.sources.r1.selector.type = replicating
# Describe the sink
a1.sinks.k1.type = avro
a1.sinks.k1.channel = c1
a1.sinks.k1.hostname = m1
a1.sinks.k1.port = 5555
a1.sinks.k2.type = avro
a1.sinks.k2.channel = c2
a1.sinks.k2.hostname = m2
a1.sinks.k2.port = 5555
# Use a channel which buffers events in memory
a1.channels.c1.type = memory
a1.channels.c1.capacity = 1000
a1.channels.c1.transactionCapacity = 100
a1.channels.c2.type = memory
a1.channels.c2.capacity = 1000
a1.channels.c2.transactionCapacity = 100
在hadoop1创建Flume_Sink_Processors_avro.conf配置文件
a1.sources = r1
a1.sinks = k1
a1.channels = c1
# Describe/configure the source
a1.sources.r1.type = avro
a1.sources.r1.channels = c1
a1.sources.r1.bind = 0.0.0.0
a1.sources.r1.port = 5555
# Describe the sink
a1.sinks.k1.type = logger
# Use a channel which buffers events in memory
a1.channels.c1.type = memory
a1.channels.c1.capacity = 1000
a1.channels.c1.transactionCapacity = 100
# Bind the source and sink to the channel
a1.sources.r1.channels = c1
a1.sinks.k1.channel = c1启动:
flume-ng agent -c . -f /home/bigdata/flume/conf/Flume_Sink_Processors_avro.conf -n a1 -Dflume.root.logger=INFO,console测试:
然后在hadoop1或hadoop2的任意一台机器上,测试产生log
# echo "idoall.org test1 failover" | nc localhost 51404) Load balancing Sink Processor
load balance type和failover不同的地方是,load balance有两个配置,一个是轮询,一个是随机。两种情况下如果被选择的sink不可用,就会自动尝试发送到下一个可用的sink上面。
a1.sources = r1
a1.sinks = k1 k2
a1.channels = c1
#这个是配置Load balancing的关键,需要有一个sink group
a1.sinkgroups = g1
a1.sinkgroups.g1.sinks = k1 k2
a1.sinkgroups.g1.processor.type = load_balance
a1.sinkgroups.g1.processor.backoff = true
a1.sinkgroups.g1.processor.selector = round_robin
# Describe/configure the source
a1.sources.r1.type = syslogtcp
a1.sources.r1.port = 5140
a1.sources.r1.channels = c1
# Describe the sink
a1.sinks.k1.type = avro
a1.sinks.k1.channel = c1
a1.sinks.k1.hostname = m1
a1.sinks.k1.port = 5555
a1.sinks.k2.type = avro
a1.sinks.k2.channel = c1
a1.sinks.k2.hostname = m2
a1.sinks.k2.port = 5555
# Use a channel which buffers events in memory
a1.channels.c1.type = memory
a1.channels.c1.capacity = 1000
a1.channels.c1.transactionCapacity = 100启动:
#flume-ng agent -c . -f /home/bigdata/flume/conf/Load_balancing_Sink_Processors_avro.conf -n a1 -Dflume.root.logger=INFO,console测试:
输入太快产生的日志可能会落到一台机器上
echo "idoall.org test1" | nc localhost 5140flume的海量日志离线采集于存储。不同的数据源,不同的数据存储方式(本地和hdfs),均衡负载的存储方式,存储时间,存储数据大小等等的设定。