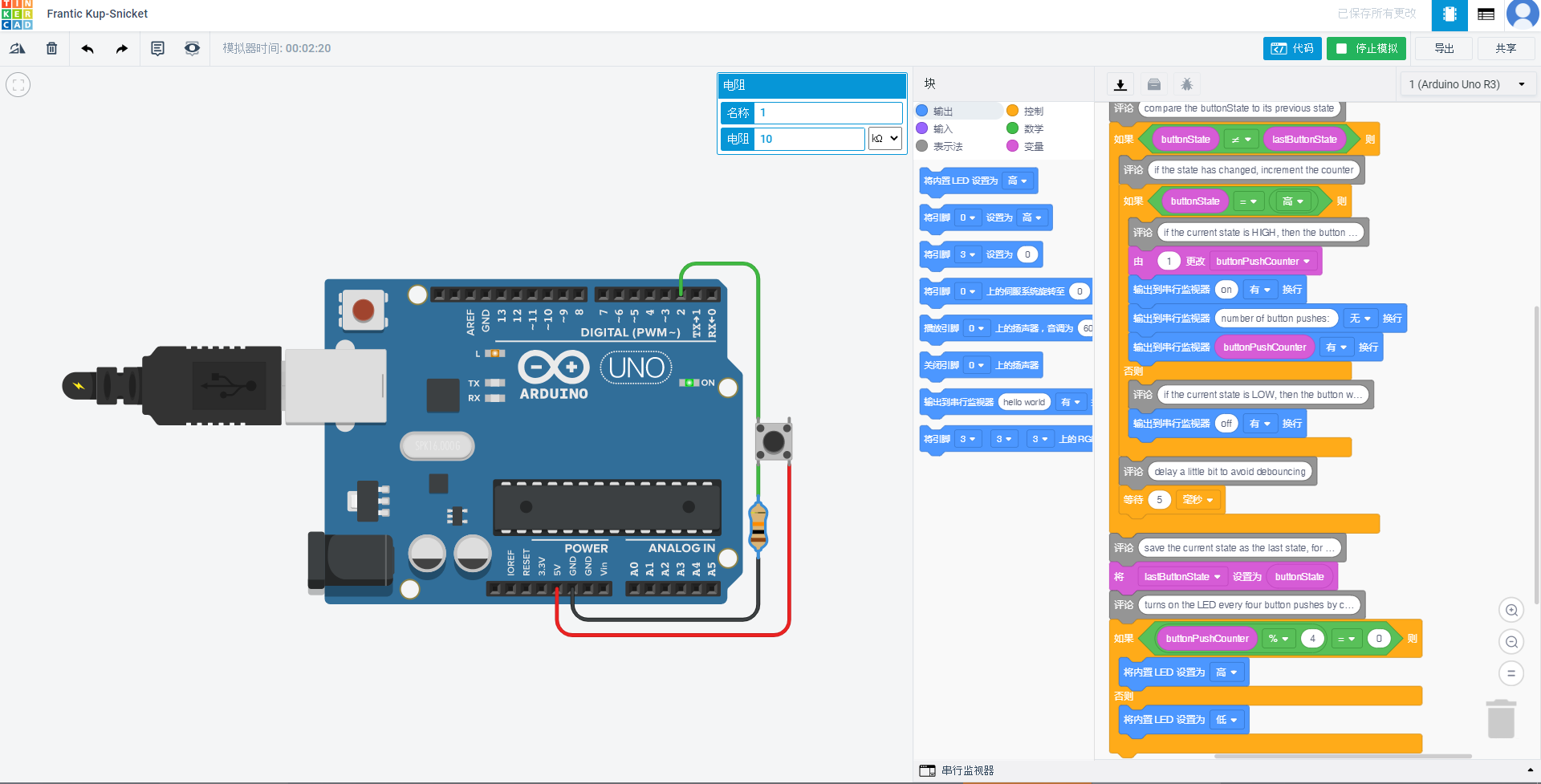
/* State change detection (edge detection) 状态变化检测(边缘检测) Often, you don't need to know the state of a digital input all the time, but you just need to know when the input changes from one state to another. For example, you want to know when a button goes from OFF to ON. This is called state change detection, or edge detection. 通常,您不需要知道状态一直使用数字输入,但您只需要知道输入何时从一种状态变为另一个。 例如,您想知道什么时候按钮从OFF变为ON。 这就是所谓的状态变化检测或边缘检测。 This example shows how to detect when a button or button changes from off to on and on to off. 本示例说明如何检测按钮或按钮从关闭变为打开,然后从打开变为关闭。 The circuit: * pushbutton attached to pin 2 from +5V * 10K resistor attached to pin 2 from ground * LED attached from pin 13 to ground (or use the built-in LED on most Arduino boards) 电路: * 按钮从5V连接到引脚2 * 10K电阻从地连接到引脚2 * LED从引脚13接地(或使用大多数Arduino板上的内置LED) This example code is in the public domain. http://www.arduino.cc/en/Tutorial/ButtonStateChange */ int buttonState = 0; int lastButtonState = 0; int buttonPushCounter = 0; void setup() { pinMode(2, INPUT); Serial.begin(9600); pinMode(13, OUTPUT); } void loop() { // read the pushbutton input pin buttonState = digitalRead(2); // compare the buttonState to its previous state if (buttonState != lastButtonState) { // if the state has changed, increment the counter if (buttonState == HIGH) { // if the current state is HIGH, then the button // went from off to on buttonPushCounter += 1; Serial.println("on"); Serial.print("number of button pushes: "); Serial.println(buttonPushCounter); } else { // if the current state is LOW, then the button // went from on to off Serial.println("off"); } // delay a little bit to avoid debouncing delay(5); // Wait for 5 millisecond(s) } // save the current state as the last state, for // the next time through the loop lastButtonState = buttonState; // turns on the LED every four button pushes by // checking the modulo of the button push counter. // the modulo function gives you the remainder of // the devision of two numbers //通过检查按钮按下计数器的模数,每四个按钮按下一次即可打开LED一次。 //模函数返回两个数相除的余数 if (buttonPushCounter % 4 == 0) { digitalWrite(13, HIGH); } else { digitalWrite(13, LOW); } }