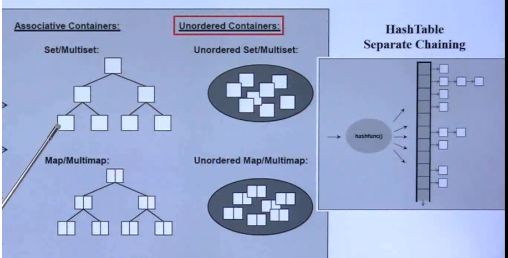
关联容器
map,set
map
map是一种关联式容器包含 键/值 key/value 相当于python中的字典
不允许有重复的key
map 无重复,有序
Map是STL的一个关联容器,它提供一对一(其中第一个可以称为关键字,每个关键字只能在map中出现一次,第二个可能称为该关键字的值)的数据 处理能力,这里说下map内部数据的组织,map内部自建一颗红黑树(一 种非严格意义上的平衡二叉树),这颗树具有对数据自动排序的功能,所以在map内部所有的数据都是有序的,后边我们会见识到有序的好处。
1、map简介
map是一类关联式容器。它的特点是增加和删除节点对迭代器的影响很小,除了那个操作节点,对其他的节点都没有什么影响。
对于迭代器来说,可以修改实值,而不能修改key。
2、map的功能
自动建立Key - value的对应。key 和 value可以是任意你需要的类型。
根据key值快速查找记录,查找的复杂度基本是log(n) 如果有1000个记录,最多查找10次,1,000,000个记录,最多查找20次。
快速插入Key -Value 记录。
快速删除记录
根据Key 修改value记录。
遍历所有记录。
map的插入,有4种
map插入,删除

#include <iostream> #include <map> #include <string> using namespace std; void printMap(map<int ,string> &map1) { if (!map1.size()) { cout<< "map为空" << endl; } else { cout<< "迭代器遍历 map: "; for (map<int, string>::iterator it = map1.begin(); it != map1.end(); it++) { cout << "key = " << it->first << " values = " << it->second << endl; } } } void test11() { // 插入,四种常用的方法 // 方法一 map<int, string> map1; map1.insert(pair<int ,string>(1, "teacher2")); map1.insert(pair<int ,string>(2, "teacher2")); // 方法二 map1.insert(make_pair(3, "teacher3")); map1.insert(make_pair(4, "teacher4")); // 方法三 map1.insert(map<int, string>::value_type(5, "teacher5")); map1.insert(map<int, string>::value_type(6, "teacher6")); // 方法四 map1[7] = "teacher7"; map1[8] = "teacher8"; // 遍历 printMap(map1); // map1.erase(map1.begin(), map1.end()); 共有4中删除方法 // 删除 for (auto it = map1.begin(); it != map1.end(); it++) { map1.erase(it); } printMap(map1); /* void erase( iterator pos ); void erase( iterator start, iterator end ); size_type erase( const KEY_TYPE &key ); erase()函数删除在pos位置的元素,或者删除在start和end之间的元素,或者删除那些值为key的所有元素。 */ } int main() { test11(); return 0; }
map 的4中insert方法探究

void printMap(map<int ,string> &map1) { if (!map1.size()) { cout<< "map为空" << endl; } else { cout<< "迭代器遍历 map: "; for (map<int, string>::iterator it = map1.begin(); it != map1.end(); it++) { cout << "key = " << it->first << " values = " << it->second << endl; } } } // 插入的四种方法的 不同处 // 前三种返回的都是 pair<iterator, bool>,若key已经存在,则报错 // 方法四 若key已经存在,则修改 void test12() { // 插入,四种常用的方法 // 方法一 map<int, string> map1; // 无重复,有序 // typdef pair<iterator, bool> pairib; map1.insert(pair<int ,string>(1, "teacher1")); // 接收 insert的返回值是一个 /* * iterator insert( iterator pos, const pair<KEY_TYPE,VALUE_TYPE> &val ); * void insert( input_iterator start, input_iterator end ); * pair<iterator, bool> insert( const pair<KEY_TYPE,VALUE_TYPE> &val ); * insert()函数: * * 插入val到pos的后面,然后返回一个指向这个元素的迭代器。 * 插入start到end的元素到map中。 * 只有在val不存在时插入val。返回值是一个指向被插入元素的迭代器和一个描述是否插入的bool值。 */ pair< map<int, string>::iterator, bool> MyPair1 = map1.insert(pair<int ,string>(2, "teacher2")); cout << "显示 insert 的返回值"<<endl; cout << "MyPair1.second = " << MyPair1.second << endl<< endl; cout << "插入的key, value为: "; cout <<"MyPair1.first->first = " << MyPair1.first->first <<endl; // 这个看仔细了,是两个 cout <<"MyPair1.first->second = " << MyPair1.first->second<< endl<<endl; // 这一步判断必须写,不写就无法判断是否插入成功 if (MyPair1.second == true) { cout << "key 1插入成功" << endl; cout << "MyPair1.second = " << MyPair1.second << endl; } else { cout << "插入失败:失败数据为: "; cout <<"MyPair1.first->first = " << MyPair1.first->first <<endl; // 这个看仔细了,是两个 cout <<"MyPair1.first->second = " << MyPair1.first->second<< endl; } cout << endl; map1[7] = "teacher7"; map1[7] = "teacher77"; // 这一步会插入失败 // 方法二 pair< map<int, string>::iterator, bool> MyPair2 = map1.insert(make_pair(3, "teacher3")); map1.insert(make_pair(4, "teacher4")); // 方法三 map1.insert(map<int, string>::value_type(5, "teacher55")); // 这一个会插入失败 auto MyPair3 = map1.insert(map<int, string>::value_type(5, "teacher5")); if (MyPair3.second == true) { cout << "key 1插入成功" << endl; cout << "MyPair3.second = " << MyPair3.second << endl; } else { cout << "插入失败:失败数据为: "; cout <<"MyPair3.first->first = " << MyPair3.first->first <<endl; // 这个看仔细了,是两个 cout <<"MyPair3.first->second = " << MyPair3.first->second<< endl; } cout <<endl; // 方法四 map1[7] = "teacher7"; map1[7] = "teacher77"; // 这一步会插入失败 // 遍历容器 printMap(map1); } int main() { test12(); return 0; }
map 的fing 和equal_range
pair equal_range( const KEY_TYPE &key );
equal_range()函数返回两个迭代器——一个指向第一个键值为key的元素,另一个指向最后一个键值为key的元素
使用是 auto pair = map1.equal_range(key)
第一个迭代器的内容
pair.first->first
pair.first->first
第二个迭代器的内容
pair.second->first
pair.second->first
find
// iterator find( const KEY_TYPE &key );
// find()函数返回一个迭代器指向键值为key的元素,如果没找到就返回指向map尾部的迭代器。

#include <iostream> #include <map> #include <string> using namespace std; void printMap(map<int ,string> &map1) { if (!map1.size()) { cout<< "map为空" << endl; } else { cout<< "迭代器遍历 map: "; for (map<int, string>::iterator it = map1.begin(); it != map1.end(); it++) { cout << "key = " << it->first << " values = " << it->second << endl; } } } void test113() { // 插入,四种常用的方法 // 方法一 map<int, string> map1; map1.insert(pair<int ,string>(1, "teacher2")); map1.insert(pair<int ,string>(2, "teacher2")); // 方法二 map1.insert(make_pair(3, "teacher3")); map1.insert(make_pair(4, "teacher4")); // 方法三 map1.insert(map<int, string>::value_type(5, "teacher5")); map1.insert(map<int, string>::value_type(6, "teacher6")); // 方法四 map1[7] = "teacher7"; map1[8] = "teacher8"; // 遍历 printMap(map1); // map查找, 异常处理 // iterator find( const KEY_TYPE &key ); // find()函数返回一个迭代器指向键值为key的元素,如果没找到就返回指向map尾部的迭代器。 cout << " 探究map1.find() 的返回值"<<endl; map<int, string>::iterator it = map1.find(100); // 返回的是迭代器 if (it == map1.end()) { cout <<"查找key 为100的值失败" <<endl; } else { cout << "查找成功:"; cout << it->first <<" = " << it->second <<endl; } map<int, string>::iterator it2 = map1.find(6); if (it2 == map1.end()) { cout <<"查找key 为6的值失败" <<endl; } else { cout << "查找key为6的值成功:"; cout << it2->first <<" = " << it2->second <<endl; } cout <<" 探究map1.equal_range(5)的返回值"<<endl; // pair equal_range( const KEY_TYPE &key ); // equal_range()函数返回两个迭代器——一个指向第一个键值为key的元素,另一个指向最后一个键值为key的元素。 // equal_range() 异常处理 // map1.equal_range(5); // 返回两个迭代器,形成一个pair pair<map<int, string>::iterator, map<int, string>::iterator> MyPair = map1.equal_range(5); // 返回两个迭代器,形成一个pair // 第一个迭代器 小于等于5的,第二个为大于等于5的 // 使用第一个迭代器 if (MyPair.first == map1.end()) { cout << "第一个迭代器小于等于5的不存在"<<endl; } else { cout << "第一个迭代器小于等于的迭代器位置为: " << MyPair.first->first<<endl; } // 使用第二个迭代器 if (MyPair.second == map1.end()) { cout << "第二个迭代器大于等于的不存在"<<endl; } else { cout << "第二个迭代器大于等于的迭代器位置为: " << MyPair.second->first<<endl; } } int main() { test113(); return 0; }
multimap
C++ Multimaps和maps很相似,但是MultiMaps允许重复的元素。

// // Created by lk on 18-6-3. // #include <iostream> #include <string> #include <map> using namespace std; //C++ Multimaps和maps很相似,但是MultiMaps允许重复的元素。 /* Mulitmap案例 1个key可以对应多个value === 分组 公司有销售部sale(员工两名), 技术研发部(development 1人),财务部(Financial,2人) 公司人员信息: 姓名, 年龄,电话, 工资等 通过mulitmap进行 信息的插入,保存,显示, 分部门显示员工信息 */ class Person { public: Person() { name = ""; age = 0; tel = ""; salary = 0; } Person(string name, int age, string tel, double salary) { this->name = name; this->age = age; this->tel = tel; this->salary = salary; } public: int getAge() { return age; } void alterMessage(string name) { this->name = name; } public: friend ostream& operator<<(ostream &out, const Person &obj) // 后面的const什么时候加 { out << "name = " << obj.name << " age = " << obj.age << " tel = " << obj.tel << " salary = " << obj.salary << endl; return out; } private: string name; // 用不用动态陪内存 问题 int age; string tel; double salary; }; // 看看返回值 是引用还是啥 multimap<string, Person> InsertMessage() { multimap<string, Person> map2; Person p1("王1", 21, "111", 121); Person p2("王2", 22, "222", 122); Person p3("张3", 23, "223", 123); Person p4("张4", 24, "224", 1234); Person p5("赵5", 25, "225", 12345); // sale部门 // map2.insert(make_pair("sale", p1)); map2.insert(pair<string, Person>("sale", p1) ); map2.insert(make_pair("sale", p2)); //development部门 map2.insert(make_pair("development", p3)); map2.insert(make_pair("development", p4)); //Financial部门 map2.insert(make_pair("Financial", p5)); return map2; } // 遍历multimap 哪里需要加const注意 void ErgodicMultimap(multimap<string, Person> &map2) { string flag; for(multimap<string, Person>::iterator it = map2.begin(); it != map2.end(); it++) { if (it->first != flag) { cout << " " << it->first<<" 部门信息: "<< endl; flag = it->first; } cout << it->second; } cout << "遍历结束"<<endl; } void test12_1() { multimap<string, Person> map2 = InsertMessage(); // 遍历 ErgodicMultimap(map2); // 按部门显示人数 int tag = map2.count("development"); cout<<"development部门人数==>" << tag << endl; multimap<string, Person>::iterator it = map2.find("development"); // 显示部门人员信息 cout <<"development部门员工信息"<<endl; while (it != map2.end() && tag) { cout << it->second <<endl; it++; tag--; } } // 修改multimap // 把 age = 23的修改成 name23 void test12_2() { multimap<string, Person> map2 = InsertMessage(); // 按照条件 检索修改 for(multimap<string, Person>::iterator it = map2.begin(); it != map2.end(); it++) { // 修改信息 if(it->second.getAge() == 23) { it->second.alterMessage("name23"); } } ErgodicMultimap(map2); } int main() { test12_1(); // test12_2(); return 0; }
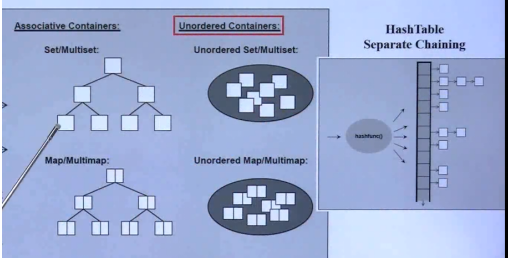
set
和map实现原理差不多,都是用红黑树
set是有序,不可重复的集合
// 重要
// 1 集合 元素唯一 自动排序,不能按照数组[]的方式插入元素
// 红黑树 平衡二叉树

// // Created by lk on 18-6-3. // #include <iostream> #include <algorithm> #include <cstdlib> #include <cstring> #include <set> using namespace std; // 重要 // 1 集合 元素唯一 自动排序,不能按照数组[]的方式插入元素 // 红黑树 平衡二叉树 void printSet(set<int> &set1) { cout << "set遍历:"; for (auto it = set1.begin(); it != set1.end(); it++) { cout << *it << ' '; } cout << endl; } // 基本操作 void test91() { set<int> set1; // 从小到大,无重复 for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++) { int tem = rand() % 200; set1.insert(tem); } set1.insert(100); set1.insert(100); // 遍历 printSet(set1); // set1.erase(set1.begin(), set1.end());// 删除元素、一个一个删除也可以 } // 对基本的数据类型,set可以排序,对复杂的用谓词,仿函数等 void test92() { set<int> set1; set<int, less<int>> set2; // 1和2都是从小到大,默认情况 set<int, greater<int>> set3; // 从大到小 for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++) { int tem = rand() % 200; set3.insert(tem); } // 非默认的 要写全 cout << "最大值优先 set遍历:"; for (set<int, greater<int>>::iterator it = set3.begin(); it != set3.end(); it++) { cout << *it << ' '; } } class Student { private: //public: int age; char name[32]; public: friend struct FunStudent; // 这里的友元 仿函数 Student() { age = 0; strcpy(name, ""); } Student(const char *name, int age) { this->age = age; strcpy(this->name, name); } void print() const // 这里要加 const,表示这个 本身不可修改 { cout << "name: " << name << " age: " << age << endl; } friend ostream &operator<<(ostream &out, const Student &obj) { out << " name: " << obj.name << " age: " << obj.age << endl; return out; } }; // 仿函数 struct FunStudent { bool operator()(const Student &Lobj, const Student &Robj) { if (Lobj.age < Robj.age) // 如果左边的年龄小,就返回真,按照从小到大 return true; else if (Lobj.age == Robj.age) // 如果年龄相同,看姓名 { if (strcmp(Lobj.name, Robj.name)) return true; else return false; } else return false; } }; // 对复杂的数据类型 Teacher, student void test93() { Student s1("s1", 18), s2("s2", 19), s3("s3", 20), s4("s4", 20); // 如果两个20能插入成功吗, 不能,所以要修改仿函数 // set<Student> set_Stu; // 按照什么排序?, 就要用到仿函数 set<Student, FunStudent> set_Stu; set_Stu.insert(s4); set_Stu.insert(s3); set_Stu.insert(s1); set_Stu.insert(s2); for (auto it = set_Stu.begin(); it != set_Stu.end(); it++) { // it->print(); cout << (*it); // 都对, 不过记得要加const } } // 如何判断insert函数的返回值 //typedef pair<iterator, bool> _pairib; void test94() { Student s1("s1", 18), s2("s2", 19), s3("s3", 20), s4("s4", 20); // 如果两个20能插入成功吗, 不能,所以要修改仿函数 // set<Student> set_Stu; // 按照什么排序?, 就要用到仿函数 set<Student, FunStudent> set_Stu; set_Stu.insert(s4); set_Stu.insert(s3); set_Stu.insert(s1); set_Stu.insert(s2); // auto i = set_Stu.insert(s2); // cout << i.second; // 或者 pair<set<Student, FunStudent>::iterator, bool> pair1 = set_Stu.insert(s2); cout << *pair1.first; // 返回s2的值 cout << pair1.second; // pair1.second为真插入成功, for (auto it = set_Stu.begin(); it != set_Stu.end(); it++) { // it->print(); cout << (*it); // 都对, 不过记得要加const } } // find查找, equal_rande, // 返回结果是pair 的使用 void test95() { set<int> set1; for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) { set1.insert(i + 1); } // 非默认的 要写全 cout << "最大值优先 set遍历:"; for (set<int>::iterator it = set1.begin(); it != set1.end(); it++) { cout << *it << ' '; } cout << endl; set<int>::iterator it = set1.find(5); // 找元素为5的位置 cout << " 等于5的迭代器的位置: " << *it << endl; int num1 = set1.count(5); cout << "5的个数 num1 : " << num1 << endl; auto it0 = set1.lower_bound(9); // 找大于等于5的迭代器的位置 cout << "大于等于9的位置 的值 it0: " << *it0 << endl; pair<set<int>::iterator, set<int>::iterator> MyPair = set1.equal_range(5); auto it3 = MyPair.first; // 5 auto it4 = MyPair.second; // 6 // 如果5被删除了这里是什么 set1.erase(5); 6, 6 cout << "it3 : " << *it3 << " it4 : " << *it4 << endl; } int main() { // test91(); // 基本操作 // test92(); // 对基本的数据类型,set可以排序,对复杂的用谓词,仿函数等 // test93(); // 对复杂的数据类型 Teacher, student // test94(); 重要 // 如何判断insert函数的返回值 test95(); // 重要 // find查找, equal_rande, return 0; }
几种容器的比较
1)vector
内部数据结构:数组。
在末尾增加或者删除元素所需时间与元素数目无关,在中间或者开头增加或者删除元素所需时间是随元素数目呈线性变化。
2):deque
内部数据结构是:数组
随机访问每个元素,所需要的时间为常量。在开头和末尾增加元素所需时间与元素数目无关,在中间增加或删除所需时间随元素数目呈线性变化。
3)list
内部数据结构:双向环状链表
不能随机访问一个元素,可双向遍历,在开头,末尾和中间的任何地方增加或者删除元素所需时间都是常量。
4)set
键和值相等。
键唯一
元素默认按升序排列、
5)map
键唯一,
元素默认按键的升序排列
关于迭代器失效的问题、小心使用STL中的erase
这段代码会出错, 要写成 iter = vect.erase(iter)

再删除时, 最好都这样写,对于多有的容器

