面向对象分析与设计概览…
良好的对象设计意味着什么?
是构建高质量软件系统的基本要求,如
Architectural cohesion 架构性的内聚
Reusability 可重用性
Maintenance 可维护性
Scalability 可扩展性
Flexibility 灵活性
UML、面向对象语言(C++/Java)重要吗?足够了吗?
UML是标准的图形表示工具,是一种思考的工具、沟通的形式,是有用的
但是,对象思想才是重点和难点
“Owning a hammer doesn’t make you a home builder“拥有一把 锤子未必能成为建筑师”
系统设计中的关键问题
应该如何为对象类分配职责(responsibility)?
对象之间应该如何协作?
什么样的类应该做什么样的事情?
某些针对设计问题的、经过反复验证的解决方案,可以(或者已经)被 表示成为最佳实践的原则、启示或者模式(pattern),如何用、如何自创?
软件开发过程模型
瀑布模型
螺旋模型
增量模型
迭代模型
喷泉模型
敏捷模型
SMF(微软)
RUP等
课程的关键 Key importance:
A critical ability in OO development is to skillfully assign responsibilities to software objects. 面向对象开发需要掌握的极为重要的能力:为软件对象分配职责。 方法:
Responsibility-driven design 职责驱动的设计
Performed during Design workflow 在设计的过程中完成职责分配
Follows GRASP principles 遵循GRASP原则
General Responsibility Assignment Software Pattern 通用职责分配软件模式
Successful designs become Patterns 成功的设计可以成为模式
A named description of a problem, solution, when to apply the solution, and how to apply the solution in new contexts 一个命名的描述:问题、解决方案、何 时适用、如何应用在新的环境
相关的知识点
用例 Use Cases
文字描述的重要交易和业务场景 Text description of vital transactions and scenarios
用例不是面向对象的,但面向对象分析设计都会用到 Not OO but usually used in OOAD
Topics and skills covered
OOAD elements
OOAD + UML is our focus
What is Analysis ?什么是分析
Analysis is investigation of the problem and requirements, rather than a solution.分析是对问题和要求的调查, 而不是解决方案。
For example, if a new online trading system is desired,
how will it be used? What are its functions?
requirements analysis :an investigation of the requirements
What is design?
Design is a conceptual solution that fulfills the requirements 概念性的、满足 需求的解决方案
分析与设计的类比:
用户需求:我要一辆能开动的汽车
系统功能:引擎、方向盘、油箱轮胎、车架、车门….
What is implement? 实现
Implementation is expression of the design in code
Emphasis on utilizing the language of choice to implement design classes while exploring visibility, navigability, etc.
What is deployment? 部署
Deployment is the actual installation in the host environment
Relationship of the Analysis and Design 分析与设计的关系
记住这句话:
“ do the right thing (analysis), and do the thing right (design) ” 做正确的事情(分析)、正确地做事情(设计)
What is OOA 面向对象分析?
finding and describing the objects or concepts in the problem domain 发现并描 述问题领域里的对象或者概念(概念类)
What is OOD 面向对象设计?
defining software objects and how they collaborate to fulfill the requirements 定义软件对象、以及它们之间如何协作完成功能的(设计类) For example, Airplane example of object and class discovery
OOA:
in the case of the flight information system, some of the concepts include: Plane, Flight, and Pilot.
OOD:
a Plane software object may have a tailNumber attribute and a getFlightHistory() method
then, implement…
OOAD Simple Example
Rudimentary process 最基本的过程
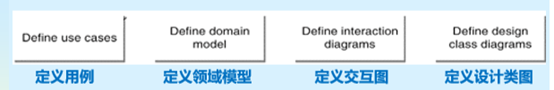
Dice game example
software simulates(模仿)a player rolling two dices. If the total is (>=) seven, they win; otherwise, they lose
Step1: Use Case
Player is requested to roll the dice.
System presents results:
If the dice face value totals (>=)seven, player wins; otherwise, player loses
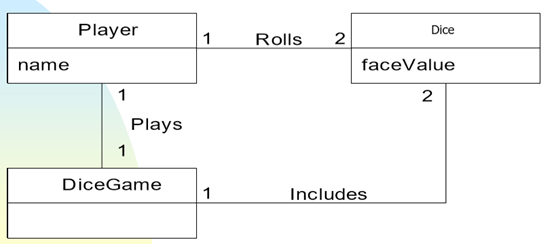
Step2: Domain Model 领域模型
OOA的结果体现在领域模型中,显示重要的领域概念或者对象
What is domain model?
a visual representation of conceptual classes or real-situation objects in a domain [MO95, Fowler96]. 问题领域的概念类以及真实对象的可视化表示
Domain models have also been called conceptual models , domain object models, and analysis object models. 领域模型也被称为 概念模型、领域对象模 型、分析对象模型
In our example,
Player,
Dice,
DiceGame
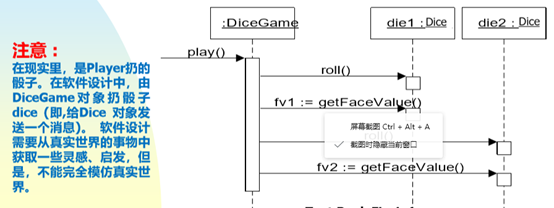
Step3: Interactions
Assignment of responsibilities among objects
Sequence or Communication diagrams
Step4: Design Class Diagrams (DCD)
Software classes(软件类) with methods according to responsibilities and attributes according to visibility
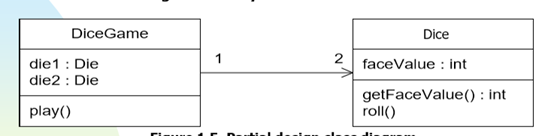
Cf:
the domain model showing real-world classes
this diagram shows software classes
LRG: lower representational gap,低表示差异
概念类与软件类,有很大的相似度
OOAD概述小结
领域、领域模型、概念类
系统、设计类==软件类
低表示差异LRG: 概念类可以直接作为软件类
概念类没有操作、软件类有操作
分析、设计,面向对象分析、面向对象设计
OOAD的简单完整过程示意
掌握面向对象思想,重于UML工具、OO语言