一:数学原理
在临近点插值的数学基础上,双线性插值,不是简单copy源像素的值,而是获取四个最邻
近目标像素的像素值乘以权重系数,简单的数学公式可以表示为:
D(x, y) = S(j, k) * a + S(j+1, k) *b + S(j+1,k+1) * c + S(j, K+1) * d 公式一
问题转化如何提取源像素的中四个临近点,根据临近点插值中从目标像素寻找最临近的源像
素点的方法:
Sx= Dx * (Sh/Dh) // row
Sy= Dy * (Sw/Dw) // column
公式的详细说明参见这里http://blog.csdn.net/jia20003/article/details/6907152
计算出来的值是浮点数坐标,分别取整数部分坐标为(j, k), 小数部分坐标为(t, u)
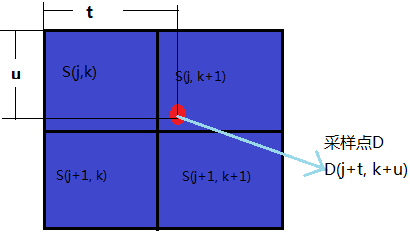
根据小数部分的(t,u)坐标,首先进行水平方向的权重计算得出
Q11 = S(j,k) * (1-t) + S(j, k+1) * t;
Q22 = S(j+1, k) * (1-t) + S(j+1,K+1) *t
利用Q11, Q22的值,进行垂直方向权重计算得出计算采样点值
D(x, y) = Q11*(1-u) + Q22 * u; 把Q11, Q22带入,最终有等式:
D(x, y) = S(j, k) *(1-t)*(1-u) + S(j, k+1)*t*(1-u) + S(j+1,k)*(1-t)*u + S(j+1,k+1)*t*u
从而得出四个对应的权重系数分别为:
a = (1-t)*(1-u)
b = (1-t)*u
c = t*u
d = t*(1-u)
带入公式一,即可得出目标像素的值。
二:双线性内插值算法优缺点
双线性内插值算法在图像的放缩处理中,具有抗锯齿功能, 是最简单和常见的图像放缩算法,但是双线性内插值算法没有考虑边缘和图像的梯度变化,相比之下双立方插值算法更好解决这些问题。
三:关键程序代码解析
根据目标像素坐标,计算采样点浮点数坐标的代码如下:
float rowRatio = ((float)srcH)/((float)destH);
float colRatio = ((float)srcW)/((float)destW);
double srcRow = ((float)row)*rowRatio;
double srcCol = ((float)col)*colRatio;
计算采样点的整数坐标和小数部分坐标代码如下:
double j = Math.floor(srcRow);
double t = srcRow – j
double k = Math.floor(srcCol);
double u = srcCol - k;
根据小数坐标(t,u)来计算四个相邻像素点权重系数代码如下:
double coffiecent1 = (1.0d-t)*(1.0d-u);
double coffiecent2 = (t)*(1.0d-u);
double coffiecent3 = t*u;
double coffiecent4 = (1.0d-t)*u;
处理边缘像素代码如下:
return x>max ? max : x<min? min : x;
四:程序运行效果如下

左边为源图像,右边为基于双线性内插值放大两倍以后的图像
五:双线性内插值JAVA算法代码
- public class BilineInterpolationScale implements ImageScale {
- public BilineInterpolationScale() {
- }
- /**
- *
- */
- @Override
- public int[] imgScale(int[] inPixelsData, int srcW, int srcH, int destW, int destH) {
- double[][][] input3DData = processOneToThreeDeminsion(inPixelsData, srcH, srcW);
- int[][][] outputThreeDeminsionData = new int[destH][destW][4];
- float rowRatio = ((float)srcH)/((float)destH);
- float colRatio = ((float)srcW)/((float)destW);
- for(int row=0; row<destH; row++) {
- // convert to three dimension data
- double srcRow = ((float)row)*rowRatio;
- double j = Math.floor(srcRow);
- double t = srcRow - j;
- for(int col=0; col<destW; col++) {
- double srcCol = ((float)col)*colRatio;
- double k = Math.floor(srcCol);
- double u = srcCol - k;
- double coffiecent1 = (1.0d-t)*(1.0d-u);
- double coffiecent2 = (t)*(1.0d-u);
- double coffiecent3 = t*u;
- double coffiecent4 = (1.0d-t)*u;
- outputThreeDeminsionData[row][col][0] = (int)(coffiecent1 * input3DData[getClip((int)j,srcH-1,0)][getClip((int)k,srcW-1, 0)][0] +
- coffiecent2 * input3DData[getClip((int)(j+1),srcH-1,0)][getClip((int)k,srcW-1,0)][0] +
- coffiecent3 * input3DData[getClip((int)(j+1),srcH-1,0)][getClip((int)(k+1),srcW-1,0)][0] +
- coffiecent4 * input3DData[getClip((int)j,srcH-1,0)][getClip((int)(k+1),srcW-1,0)][0]); // alpha
- outputThreeDeminsionData[row][col][1] = (int)(coffiecent1 * input3DData[getClip((int)j,srcH-1,0)][getClip((int)k,srcW-1, 0)][1] +
- coffiecent2 * input3DData[getClip((int)(j+1),srcH-1,0)][getClip((int)k,srcW-1,0)][1] +
- coffiecent3 * input3DData[getClip((int)(j+1),srcH-1,0)][getClip((int)(k+1),srcW-1,0)][1] +
- coffiecent4 * input3DData[getClip((int)j,srcH-1,0)][getClip((int)(k+1),srcW-1,0)][1]); // red
- outputThreeDeminsionData[row][col][2] = (int)(coffiecent1 * input3DData[getClip((int)j,srcH-1,0)][getClip((int)k,srcW-1, 0)][2] +
- coffiecent2 * input3DData[getClip((int)(j+1),srcH-1,0)][getClip((int)k,srcW-1,0)][2] +
- coffiecent3 * input3DData[getClip((int)(j+1),srcH-1,0)][getClip((int)(k+1),srcW-1,0)][2] +
- coffiecent4 * input3DData[getClip((int)j,srcH-1,0)][getClip((int)(k+1),srcW-1,0)][2]);// green
- outputThreeDeminsionData[row][col][3] = (int)(coffiecent1 * input3DData[getClip((int)j,srcH-1,0)][getClip((int)k,srcW-1, 0)][3] +
- coffiecent2 * input3DData[getClip((int)(j+1),srcH-1,0)][getClip((int)k,srcW-1,0)][3] +
- coffiecent3 * input3DData[getClip((int)(j+1),srcH-1,0)][getClip((int)(k+1),srcW-1,0)][3] +
- coffiecent4 * input3DData[getClip((int)j,srcH-1,0)][getClip((int)(k+1),srcW-1,0)][3]); // blue
- }
- }
- return convertToOneDim(outputThreeDeminsionData, destW, destH);
- }
- private int getClip(int x, int max, int min) {
- return x>max ? max : x<min? min : x;
- }
- /* <p> The purpose of this method is to convert the data in the 3D array of ints back into </p>
- * <p> the 1d array of type int. </p>
- *
- */
- public int[] convertToOneDim(int[][][] data, int imgCols, int imgRows) {
- // Create the 1D array of type int to be populated with pixel data
- int[] oneDPix = new int[imgCols * imgRows * 4];
- // Move the data into the 1D array. Note the
- // use of the bitwise OR operator and the
- // bitwise left-shift operators to put the
- // four 8-bit bytes into each int.
- for (int row = 0, cnt = 0; row < imgRows; row++) {
- for (int col = 0; col < imgCols; col++) {
- oneDPix[cnt] = ((data[row][col][0] << 24) & 0xFF000000)
- | ((data[row][col][1] << 16) & 0x00FF0000)
- | ((data[row][col][2] << 8) & 0x0000FF00)
- | ((data[row][col][3]) & 0x000000FF);
- cnt++;
- }// end for loop on col
- }// end for loop on row
- return oneDPix;
- }// end convertToOneDim
- private double [][][] processOneToThreeDeminsion(int[] oneDPix2, int imgRows, int imgCols) {
- double[][][] tempData = new double[imgRows][imgCols][4];
- for(int row=0; row<imgRows; row++) {
- // per row processing
- int[] aRow = new int[imgCols];
- for (int col = 0; col < imgCols; col++) {
- int element = row * imgCols + col;
- aRow[col] = oneDPix2[element];
- }
- // convert to three dimension data
- for(int col=0; col<imgCols; col++) {
- tempData[row][col][0] = (aRow[col] >> 24) & 0xFF; // alpha
- tempData[row][col][1] = (aRow[col] >> 16) & 0xFF; // red
- tempData[row][col][2] = (aRow[col] >> 8) & 0xFF; // green
- tempData[row][col][3] = (aRow[col]) & 0xFF; // blue
- }
- }
- return tempData;
- }
- }
版权声明:本文为博主原创文章,未经博主允许不得转载。