表1 foreign key 表2
则表1的多条记录对应表2的一条记录,即多对一
利用foreign key的原理我们可以制作两张表的多对多,一对一关系
多对多:
表1的多条记录可以对应表2的一条记录
表2的多条记录也可以对应表1的一条记录
一对一:
表1的一条记录唯一对应表2的一条记录,反之亦然
分析时,我们先从按照上面的基本原理去套,然后再翻译成真实的意义,就很好理解了
1、先确立关系
2、找到多的一方,吧关联字段写在多的一方
一、多对一或者一对多(左边表的多条记录对应右边表的唯一一条记录)
需要注意的:1.先建被关联的表,保证被关联表的字段必须唯一。
2.在创建关联表,关联字段一定保证是要有重复的。
其实上一篇博客已经举了一个多对一关系的小例子了,那我们在用另一个小例子来回顾一下。
这是一个书和出版社的一个例子,书要关联出版社(多个书可以是一个出版社,一个出版社也可以有好多书)。
谁关联谁就是谁要按照谁的标准。
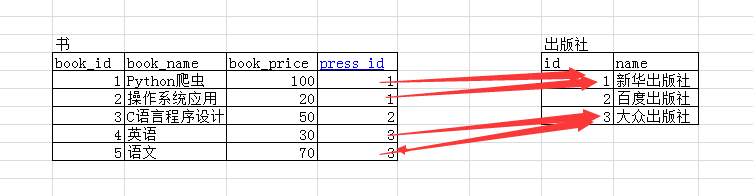
书要关联出版社 被关联的表 create table press( id int primary key auto_increment, name char(20) ); 关联的表 create table book( book_id int primary key auto_increment, book_name varchar(20), book_price int, press_id int, constraint Fk_pressid_id foreign key(press_id) references press(id) on delete cascade on update cascade );插记录
insert into press(name) values('新华出版社'),
('海燕出版社'),
('摆渡出版社'),
('大众出版社');
insert into book(book_name,book_price,press_id) values('Python爬虫',100,1),
('Linux',80,1),
('操作系统',70,2),
('数学',50,2),
('英语',103,3),
('网页设计',22,3);
运行结果截图:

二、一对一
例子一:用户和管理员(只有管理员才可以登录,一个管理员对应一个用户)
管理员关联用户
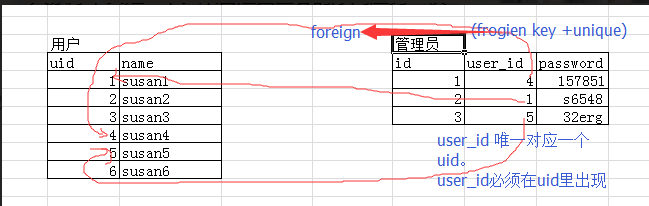
===========例子一:用户表和管理员表========= 先建被关联的表 create table user( id int primary key auto_increment, #主键自增 name char(10) ); 在建关联表 create table admin( id int primary key auto_increment, user_id int unique, password varchar(16), foreign key(user_id) references user(id) on delete cascade on update cascade ); insert into user(name) values('susan1'), ('susan2'), ('susan3'), ('susan4'), ('susan5'), ('susan6'); insert into admin(user_id,password) values(4,'sds156'), (2,'531561'), (6,'f3swe');
运行结果截图:

例子二:学生表和客户表
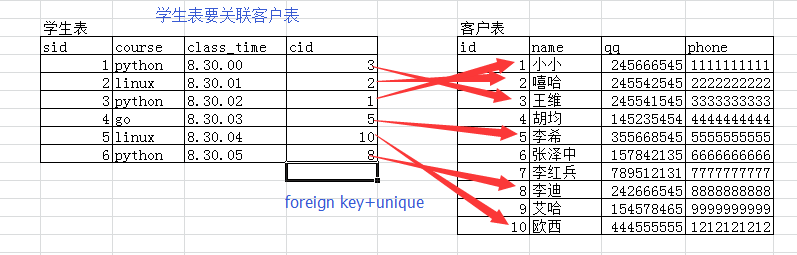
========例子二:学生表和客户表========= create table customer( id int primary key auto_increment, name varchar(10), qq int unique, phone int unique ); create table student1( sid int primary key auto_increment, course char(20), class_time time, cid int unique, foreign key(cid) references customer(id) on delete cascade on update cascade ); insert into customer(name,qq,phone) values('小小',13564521,11111111), ('嘻哈',14758254,22222222), ('王维',44545522,33333333), ('胡军',545875212,4444444), ('李希',145578543,5555555), ('李迪',754254653,8888888), ('艾哈',74545145,8712547), ('啧啧',11147752,7777777); insert into student1(course,class_time,cid) values('python','08:30:00',3), ('python','08:30:00',4), ('linux','08:30:00',1), ('linux','08:30:00',7);
运行结果截图:

三、多对多(多条记录对应多条记录)
书和作者(我们可以再创建一张表,用来存book和author两张表的关系)
要把book_id和author_id设置成联合唯一
联合唯一:unique(book_id,author_id)
联合主键:alter table t1 add primary key(id,avg)
多对多:一个作者可以写多本书,一本书也可以有多个作者,双向的一对多,即多对多 关联方式:foreign key+一张新的表
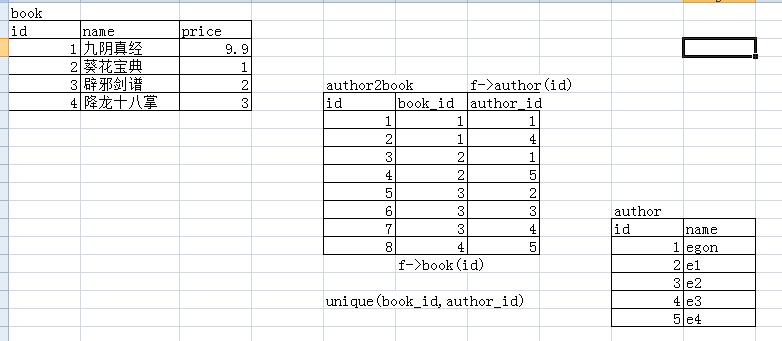


========书和作者,另外在建一张表来存书和作者的关系 #被关联的 create table book1( id int primary key auto_increment, name varchar(10), price float(3,2) ); #========被关联的 create table author( id int primary key auto_increment, name char(5) ); #========关联的 create table author2book( id int primary key auto_increment, book_id int not null, author_id int not null, unique(book_id,author_id), foreign key(book_id) references book1(id) on delete cascade on update cascade, foreign key(author_id) references author(id) on delete cascade on update cascade ); #========插入记录 insert into book1(name,price) values('九阳神功',9.9), ('葵花宝典',9.5), ('辟邪剑谱',5), ('降龙十巴掌',7.3); insert into author(name) values('egon'),('e1'),('e2'),('e3'),('e4'); insert into author2book(book_id,author_id) values(1,1), (1,4), (2,1), (2,5), (3,2), (3,3), (3,4), (4,5);
多对多关系举例
用户表,用户组,主机表
-- 用户组 create table user ( id int primary key auto_increment, username varchar(20) not null, password varchar(50) not null ); insert into user(username,password) values('egon','123'), ('root',147), ('alex',123), ('haiyan',123), ('yan',123);-- 用户组表
create table usergroup(
id int primary key auto_increment,
groupname varchar(20) not null unique
);
insert into usergroup(groupname) values('IT'),
('Sale'),
('Finance'),
('boss');-- 建立user和usergroup的关系表
create table user2usergroup(
id int not NULL UNIQUE auto_increment,
user_id int not null,
group_id int not NULL,
PRIMARY KEY(user_id,group_id),
foreign key(user_id) references user(id)
ON DELETE CASCADE
on UPDATE CASCADE ,
foreign key(group_id) references usergroup(id)
ON DELETE CASCADE
on UPDATE CASCADE
);
insert into user2usergroup(user_id,group_id) values(1,1),
(1,2),
(1,3),
(1,4),
(2,3),
(2,4),
(3,4);
-- 主机表 CREATE TABLE host( id int primary key auto_increment, ip CHAR(15) not NULL UNIQUE DEFAULT '127.0.0.1' ); insert into host(ip) values('172.16.45.2'), ('172.16.31.10'), ('172.16.45.3'), ('172.16.31.11'), ('172.10.45.3'), ('172.10.45.4'), ('172.10.45.5'), ('192.168.1.20'), ('192.168.1.21'), ('192.168.1.22'), ('192.168.2.23'), ('192.168.2.223'), ('192.168.2.24'), ('192.168.3.22'), ('192.168.3.23'), ('192.168.3.24');-- 业务线表
create table business(
id int primary key auto_increment,
business varchar(20) not null unique
);
insert into business(business) values
('轻松贷'),
('随便花'),
('大富翁'),
('穷一生');-- 建立host和business关系表
CREATE TABLE host2business(
id int not null unique auto_increment,
host_id int not null ,
business_id int not NULL ,
PRIMARY KEY(host_id,business_id),
foreign key(host_id) references host(id),
FOREIGN KEY(business_id) REFERENCES business(id)
);insert into host2business(host_id,business_id) values
(1,1),
(1,2),
(1,3),
(2,2),
(2,3),
(3,4);
-- 建立user和host的关系 create table user2host( id int not null unique auto_increment, user_id int not null, host_id int not null, primary key(user_id,host_id), foreign key(user_id) references user(id), foreign key(host_id) references host(id) );insert into user2host(user_id,host_id) values(1,1),
(1,2),
(1,3),
(1,4),
(1,5),
(1,6),
(1,7),
(1,8),
(1,9),
(1,10),
(1,11),
(1,12),
(1,13),
(1,14),
(1,15),
(1,16),
(2,2),
(2,3),
(2,4),
(2,5),
(3,10),
(3,11),
(3,12);
练习

