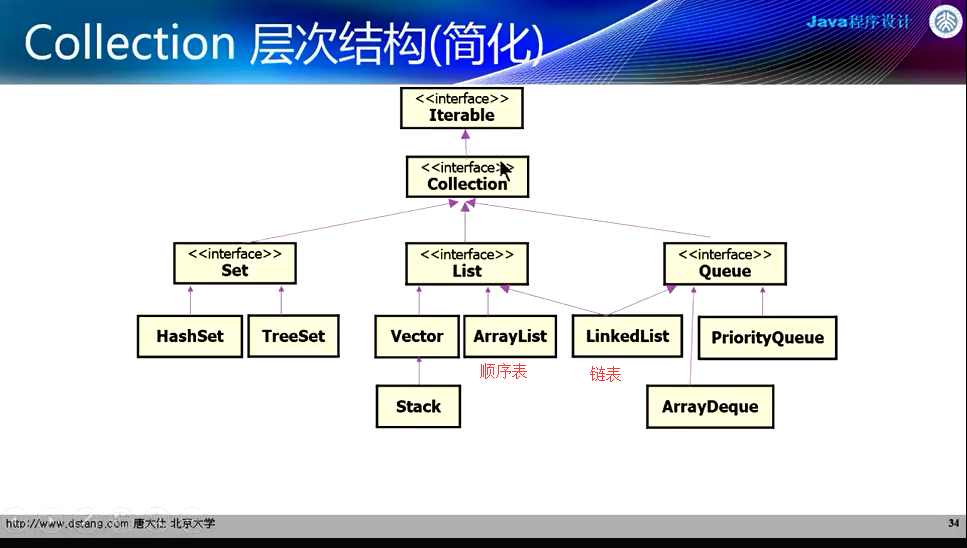
1、Collection接口有两个子接口:
List:保存元素顺序的线性表,允许有重复元素。
Set:不记录元素的保存顺序,不允许有重复元素。数学中的集合
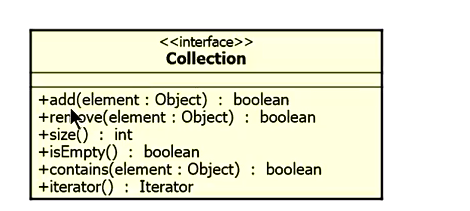
Collection接口中的方法如下:
Collection层次结构:
List:

import java.util.*; class TestList{ public static void main(String[] args){ List<Photo> album=new LinkedList<>();//<>就是泛型编程的意思,将自定义的类对象存储在 album.add(new Photo("one",new Date(),"NanChang")); album.add(new Photo("two",new Date(),"ZhengZhou")); album.add(new Photo("three",new Date(),"NanJing")); album.add(new Photo("four",new Date(),"ShangQiu")); for (Photo photo:album) { System.out.println(photo.toString()); } } } class Photo{ String title; Date date; String memo; Photo(String title,Date date,String memo){ this.title=title; this.date=date; this.memo=memo; } @Override public String toString(){ return title+"("+date+")"+memo;
} }
数组等传统的数据类型是将int、char等基本数据类型顺序存储在一起,而list的作用就是能够将程序员自定义类对象顺序存储在一起。
Stack:

import java.util.*; public class TestStack { static String[] months = { "January", "February", "March", "April", "May", "June", "July", "August", "September", "October", "November", "December" }; public static void main(String[] args) { Stack<String> stk = new Stack<>();//将String类型对象作为元素存储到Stack中 for(int i = 0; i < months.length; i++) stk.push(months[i] + " "); System.out.println("stk = " + stk); System.out.println("popping elements:"); while(!stk.empty()) System.out.println(stk.pop()); } }
队列:
