首先按照上一篇文章的介绍,启动并连接数据库
然后我们开始学习如何使用MongoDB数据库:
1、创建数据库
第一步,在cmd窗口执行:
use dbname
dbname是你打算要创建的数据库名称
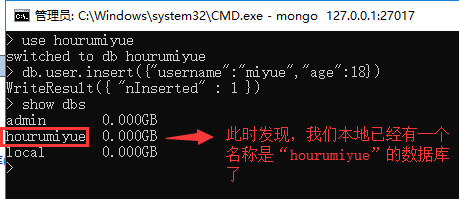
执行完上一步,我们并没有真正的创建数据库,我们如果想要dbname数据库真正的创建,我们需要先创建一个表(集合),但是MongoDB也没有创建表的命令,
那么我们如果想创建表,我们需要直接向表里插入一条数据:
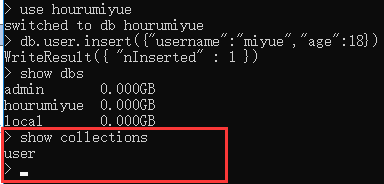
此时我们可以通过命令查看本地所有的数据库:
显示当前的所有数据集合(mysql 中叫表)
show collections
2、删除数据库,删除表:
删除数据库,删除当前所在的数据库
db.dropDatabase();
删除集合,删除指定的集合 删除表
删除集合 db.COLLECTION_NAME.drop()
db.user.drop()
3、向某个表插入数据:
db.表名.insert({"name":"zhangsan"});
注意,在插入数据的时候字段数可以不保持统一
例如:
db.user.insert({"name":"zhangsan"});
db.user.insert({"name":"lisi","age":20});
4、查找数据
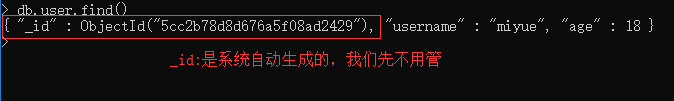
1、查询所有记录
db.userInfo.find();
相当于:select* from userInfo;
2、查询去掉后的当前聚集集合中的某列的重复数据
db.userInfo.distinct("name");
会过滤掉 name 中的相同数据
相当于:select distict name from userInfo;
3、查询 age = 22 的记录
db.userInfo.find({"age": 22});
相当于: select * from userInfo where age = 22;
4、查询 age > 22 的记录
db.userInfo.find({age: {$gt: 22}});
相当于:select * from userInfo where age >22;
5、查询 age < 22 的记录
db.userInfo.find({age: {$lt: 22}});
相当于:select * from userInfo where age <22;
6、查询 age >= 25 的记录
db.userInfo.find({age: {$gte: 25}});
相当于:select * from userInfo where age >= 25;
7、查询 age <= 25 的记录
db.userInfo.find({age: {$lte: 25}});
8、查询 age >= 23 并且 age <= 26 注意书写格式
db.userInfo.find({age: {$gte: 23, $lte: 26}});
9、查询 name 中包含 mongo 的数据 模糊查询用于搜索
db.userInfo.find({name: /mongo/});
//相当于%%
select * from userInfo where name like ‘%mongo%’;
10、查询 name 中以 mongo 开头的
db.userInfo.find({name: /^mongo/});
select * from userInfo where name like ‘mongo%’;
11、查询指定列 name、age 数据
db.userInfo.find({}, {name: 1, age: 1});
相当于:select name, age from userInfo;
当然 name 也可以用 true 或 false,当用 ture 的情况下河 name:1 效果一样,如果用 false 就
是排除 name,显示 name 以外的列信息。
12、查询指定列 name、age 数据, age > 25
db.userInfo.find({age: {$gt: 25}}, {name: 1, age: 1});
相当于:select name, age from userInfo where age >25;
13、按照年龄排序 1 升序 -1 降序
升序:db.userInfo.find().sort({age: 1});
降序:db.userInfo.find().sort({age: -1});
14、查询 name = zhangsan, age = 22 的数据
db.userInfo.find({name: 'zhangsan', age: 22});
相当于:select * from userInfo where name = ‘zhangsan’ and age = ‘22’;
15、查询前 5 条数据
db.userInfo.find().limit(5);
相当于:selecttop 5 * from userInfo;
16、查询 10 条以后的数据
db.userInfo.find().skip(10);
相当于:select * from userInfo where id not in (
selecttop 10 * from userInfo
);
17、分页查询
db.userInfo.find().limit(10).skip(500);
可用于分页,limit 是 pageSize,skip (50*10)是第几页*pageSize,查出来的是501-510之间的数据
18、or 与 查询
db.userInfo.find({$or: [{age: 22}, {age: 25}]});
相当于:select * from userInfo where age = 22 or age = 25;
19、findOne 查询第一条数据
db.userInfo.findOne();
相当于:selecttop 1 * from userInfo;
db.userInfo.find().limit(1);
20、查询某个结果集的记录条数 统计数量
db.userInfo.find({age: {$gte: 25}}).count();
相当于:select count(*) from userInfo where age >= 20;
如果要返回限制之后的记录数量,要使用 count(true)或者 count(非 0)
db.users.find().skip(10).limit(5).count(true);
5、修改数据
查找名字叫做小明的,把年龄更改为 16 岁:
db.student.update({"name":"小明"},{$set:{"age":16}});
查找数学成绩是 70,把年龄更改为 33 岁:
db.student.update({"score.shuxue":70},{$set:{"age":33}});
更改所有匹配项目:"
By default, the update() method updates a single document. To update multiple documents, use
the multi option in the update() method.
默认情况下,update()方法更新单个文档。若要更新多个文档,请使用
update()方法中的multi选项。
db.student.update({"sex":"男"},{$set:{"age":33}},{multi: true});
如果不使用$set 关键字了:完整替换, 注意:下面这句sql的意思就是把name=小明的数据的数据内容填充为:{"name":"大明","age":16}
db.student.update({"name":"小明"},{"name":"大明","age":16});
db.users.update({name: 'Lisi'}, {$inc: {age: 50}}, false, true);
相当于:update users set age = age + 50 where name = ‘Lisi’;
db.users.update({name: 'Lisi'}, {$inc: {age: 50}, $set: {name: 'hoho'}}, false, true);
相当于:update users set age = age + 50, name = ‘hoho’ where name = ‘Lisi’;
6、删除数据
db.collectionsNames.remove( { "borough": "Manhattan" } )
db.users.remove({age: 132,“username”:“zhagsan”});
By default, the remove() method removes all documents that match the remove condition. Use
the justOne option to limit the remove operation to only one of the matching documents.
默认情况下,remove()方法删除所有匹配remove条件的文档。使用
justOne选项将删除操作限制为只有一个匹配的文档。
db.restaurants.remove( { "borough": "Queens" }, { justOne: true } )
