结论:蒸馏是个好方法。
模型压缩/蒸馏在论文《Model Compression》及《Distilling the Knowledge in a Neural Network》提及,下面介绍后者及使用keras测试mnist数据集。
蒸馏:使用小模型模拟大模型的泛性。
通常,我们训练mnist时,target是分类标签,在蒸馏模型时,使用的是教师模型的输出概率分布作为“soft target”。也即损失为学生网络与教师网络输出的交叉熵(这里采用DistilBert论文中的策略,此论文不同)。
当训练好教师网络后,我们可以不再需要分类标签,只需要比较2个网络的输出概率分布。当然可以在损失里再加上学生网络的分类损失,论文也提到可以进一步优化。
如图,将softmax公式稍微变换一下,目的是使得输出更小,softmax后就更为平滑。
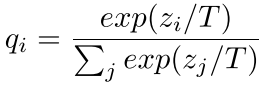
论文的损失定义

本文代码使用的损失为p和q的交叉熵
代码测试部分
1,教师网络,测试精度99.46%,已经相当好了,可训练参数858,618。
# 教师网络 inputs=Input((28,28,1)) x=Conv2D(64,3)(inputs) x=BatchNormalization(center=True,scale=False)(x) x=Activation('relu')(x) x=Conv2D(64,3,strides=2)(x) x=BatchNormalization(center=True,scale=False)(x) x=Activation('relu')(x) x=Conv2D(128,5)(x) x=BatchNormalization(center=True,scale=False)(x) x=Activation('relu')(x) x=Conv2D(128,5)(x) x=BatchNormalization(center=True,scale=False)(x) x=Activation('relu')(x) x=Flatten()(x) x=Dense(100)(x) x=BatchNormalization(center=True,scale=False)(x) x=Activation('relu')(x) x=Dropout(0.3)(x) x=Dense(10,activation='softmax')(x) model=Model(inputs,x) model.compile(optimizer=optimizers.SGD(momentum=0.8,nesterov=True),loss=categorical_crossentropy,metrics=['accuracy']) model.summary() model.fit(X_train,y_train,batch_size=128,epochs=30,validation_split=0.2,verbose=2) # 重新编译后,完整数据集训练18轮,原始16轮后开始过拟合,训练集变大后不易过拟合,这里增加2轮 model.fit(X_train,y_train,batch_size=128,epochs=18,verbose=2) model.evaluate(X_test,y_test)# 99.46%
2,学生网络,测试精度99.24%,可训练参数164,650,不到原来的1/5。
# 定义温度 tempetature=3 # 学生网络 inputs=Input((28,28,1)) x=Conv2D(16,3)(inputs) x=BatchNormalization(center=True,scale=False)(x) x=Activation('relu')(x) x=Conv2D(16,3)(x) x=BatchNormalization(center=True,scale=False)(x) x=Activation('relu')(x) x=Conv2D(32,5)(x) x=BatchNormalization(center=True,scale=False)(x) x=Activation('relu')(x) x=Conv2D(32,5,strides=2)(x) x=BatchNormalization(center=True,scale=False)(x) x=Activation('relu')(x) x=Flatten()(x) x=Dense(60)(x) x=BatchNormalization(center=True,scale=False)(x) x=Activation('relu')(x) x=Dropout(0.3)(x) x=Dense(10,activation='softmax')(x) x=Lambda(lambda t:t/tempetature)(x)# softmax后除以温度,使得更平滑 student=Model(inputs,x) student.compile(optimizer=optimizers.SGD(momentum=0.9,nesterov=True),loss=categorical_crossentropy,metrics=['accuracy']) # 使用老师和学生概率分布结果的软交叉熵,即除以温度后的交叉熵 student.fit(X_train,model.predict(X_train)/tempetature,batch_size=128,epochs=30,verbose=2)
最后测试一下
student.evaluate(X_test,y_test/tempetature)# 99.24%
3,继续减少参数,去除Dropout和BN,前期卷积使用步长,精度98.80%。参数72,334,大约原来的1/12。
# 定义温度 tempetature=3 # 学生网络 inputs=Input((28,28,1)) x=Conv2D(16,3,activation='relu')(inputs) # x=BatchNormalization(center=True,scale=False)(x) # x=Activation('relu')(x) x=Conv2D(16,3,strides=2,activation='relu')(x) # x=BatchNormalization(center=True,scale=False)(x) # x=Activation('relu')(x) x=Conv2D(32,5,activation='relu')(x) # x=BatchNormalization(center=True,scale=False)(x) # x=Activation('relu')(x) x=Conv2D(32,5,activation='relu')(x) # x=BatchNormalization(center=True,scale=False)(x) # x=Activation('relu')(x) x=Flatten()(x) x=Dense(60,activation='relu')(x) # x=BatchNormalization(center=True,scale=False)(x) # x=Activation('relu')(x) # x=Dropout(0.3)(x) x=Dense(10,activation='softmax')(x) x=Lambda(lambda t:t/tempetature)(x)# softmax后除以温度,使得更平滑 student=Model(inputs,x) student.compile(optimizer=optimizers.SGD(momentum=0.9,nesterov=True),loss=categorical_crossentropy,metrics=['accuracy']) student.fit(X_train,model.predict(X_train)/tempetature,batch_size=128,epochs=30,verbose=2) student.evaluate(X_test,y_test/tempetature)# 98.80%
4,在3的基础上,loss部分加上学生网络与分类标签的损失,测试精度98.79%。基本没变化,此时这个损失倒不太重要了。
# 冻结老师网络 model.trainable=False # 定义温度 temperature=3 # 自定义loss,加上学生网络与真实标签的损失,这个损失计算应使学生网络温度为1,即这个损失不用除以温度 class Calculate_loss(Layer): def __init__(self,T,label_loss_weight,**kwargs): ''' T: temperature for soft-target label_loss_weight: weight for loss between student-net and labels, could be small because the other loss is more important ''' self.T=T self.label_loss_weight=label_loss_weight super(Calculate_loss,self).__init__(**kwargs) def call(self,inputs): student_output=inputs[0] teacher_output=inputs[1] labels=inputs[2] loss_1=categorical_crossentropy(teacher_output/self.T,student_output/self.T) loss_2=self.label_loss_weight*categorical_crossentropy(labels,student_output) self.add_loss(loss_1+loss_2,inputs=inputs) return labels # 将标签转化为tensor输入 y_inputs=Input((10,))# 类似placeholder作用 y=Lambda(lambda t:t)(y_inputs) # 学生网络 inputs=Input((28,28,1)) x=Conv2D(16,3,activation='relu')(inputs) x=Conv2D(16,3,strides=2,activation='relu')(x) x=Conv2D(32,5,activation='relu')(x) x=Conv2D(32,5,activation='relu')(x) x=Flatten()(x) x=Dense(60,activation='relu')(x) x=Dense(10,activation='softmax')(x) x=Calculate_loss(T=temperature,label_loss_weight=0.1)([x,model(inputs),y]) student=Model([inputs,y_inputs],x) student.compile(optimizer=optimizers.SGD(momentum=0.9,nesterov=True),loss=None) student.summary() student.fit(x=[X_train,y_train],y=None,batch_size=128,epochs=30,verbose=2)
提取出预测模型,标签one-hot化了,重新加载一下
softmax_layer=student.layers[-4] predict_model=Model(inputs,softmax_layer.output) res=predict_model.predict(X_test) import numpy as np result=[np.argmax(a) for a in res] (x_train,y_train),(x_test,y_test)=mnist.load_data() from sklearn.metrics import accuracy_score accuracy_score(y_test,result)# 98.79%
5,作为对比,相同网络不使用蒸馏,测试精度98.4%
# 对应上面,不使用蒸馏,精度为98.4% inputs=Input((28,28,1)) x=Conv2D(16,3,activation='relu')(inputs) x=Conv2D(16,3,strides=2,activation='relu')(x) x=Conv2D(32,5,activation='relu')(x) x=Conv2D(32,5,activation='relu')(x) x=Flatten()(x) x=Dense(60,activation='relu')(x) x=Dense(10,activation='softmax')(x) student=Model(inputs,x) student.compile(optimizer=optimizers.SGD(momentum=0.9,nesterov=True),loss=categorical_crossentropy,metrics=['accuracy']) student.summary() # student.fit(X_train,y_train,validation_split=0.2,batch_size=128,epochs=30,verbose=2) student.fit(X_train,y_train,batch_size=128,epochs=10,verbose=2) student.evaluate(X_test,y_test)