简介
在单链表中,我们只能向一个方向(向后)访问结点:即从索引小的到索引大的方向,而不能逆向访问,例如通过第3个结点的指针,无法直接得到第2个结点的地址。这是因为单链表的每一个结点只保存了下一个结点的地址。
而双向链表中,结点有2个指针域:prior 和 next。next同样保存下一个结点的指针,而结点新增的成员prior则用来保存前一个结点的地址。
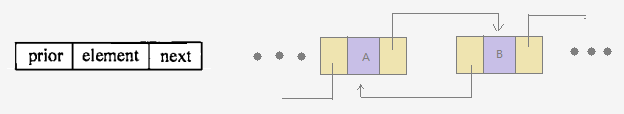
因此,双向链表在访问元素操作上比单链表快。为什么?例如,链表总长度为100,在单链表中,要访问索引为第98的结点(倒数第二个),我们必须从索引为0的结点开始向后迭代寻。而在双向链表中,我们先通过逻辑判断:索引为98的结点,是更靠近首结点(索引为0),还是更靠近尾结点(索引为99)?这里当然是更靠近尾结点,则从尾结点开始向前迭代。
对于双向链表,他的缺点也很明显:
1、比单链表更占空间,因为每个结点多了一个指针域。
2、操作复杂。
但这不影响它的使用,从实际应用的角度看,他的优点大于他的缺点。例如在Java集合框架中,LinkedList就是一个双向链表。
结点的定义
struct DLNode //双向链表的结点定义 { int element; //数据域 DLNode* prior //指针域:保存前一个结点的指针 DLNode* next; //指针域:保存后一个结点的指针 ListNode(int e=0,DLNode* pri=0,DLNode* nxt = 0):element(e),prior(pri),next(nxt) { } };
代码实现
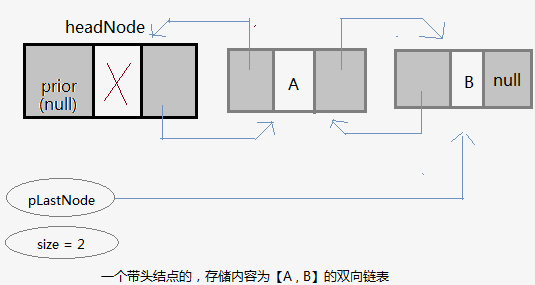
初始化状态
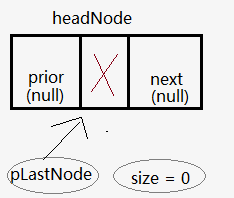
#include<iostream> #include<cstdlib> #include<stdexcept> using namespace std; struct DLNode //双向链表的结点定义 { int element; //数据域 DLNode* prior; //指针域:保存前一个结点的指针 DLNode* next; //指针域:保存后一个结点的指针 DLNode(int e=0,DLNode* pri=0,DLNode* nxt = 0):element(e),prior(pri),next(nxt) { } }; class DLinkList { private: DLNode headNode; //头结点 DLNode * pLastNode; //尾结点指针 int size; //长度 //获取双向链表中,索引为index 的结点的地址。 //如果不存在此结点,则返回NULL DLNode* _getNodeAt(int index) const { DLNode*p; int i; if(index < 0 || index >=size ) return 0; //返回NULL if( index < size /2) //从前向后寻找更快到达 { for(i=0,p=headNode.next ; i<index ;i++,p=p->next){ // NOOP } return p; } else { //从后向前 寻找更快到达 for(i=size-1,p = pLastNode; i>index ;i--,p=p->prior){ // NOOP } return p; } } public: DLinkList():headNode(),pLastNode(&headNode),size(0) { /* * * ************************* * * * * * * * prior * x * next * * * (NULL) * *(NULL) * * ************************* * / headNode * / * / * / * pLastNode = &headNode * * size = 0 * ********/ } ~DLinkList() { clear(); } //追加一个元素到表末尾 void append(int e) { DLNode * new_node = new DLNode(e,pLastNode,0); //新结点向前连接 pLastNode->next = new_node; //最后一个结点向后连接新的尾结点 pLastNode = new_node; //更新最后一个结点指针 size++; } bool insert(int index,int e) { DLNode*new_node; DLNode*p = _getNodeAt(index-1); //获取待插入位置的前一个结点地址 if(p==0) return false; new_node = new DLNode(e,p,p->next); if(p->next ==0) pLastNode = new_node; //如果新结点是插入为最后一个结点,则更新pLastNode的值 else p->next->prior = new_node; p->next = new_node; size++; return true; } bool remove(int index) { DLNode*del_node; DLNode*p = _getNodeAt(index-1); //获取待删除结点的前一个结点地址 if(p==0 || p->next ==0) return false; del_node = p->next; p->next = p->next->next; if(p->next->next == 0){ //说明被删除的是最后一个结点 pLastNode = p; }else{ p->next->next->prior = p; } delete del_node; size--; return true; } size_t length ()const { return size; } bool isEmpty()const { return size == 0; } int indexOf(int e) const { DLNode *p = headNode.next; int i=0; while(p!=0){ if(p->element == e) return i; i++; p=p->next; } return -1; } /* * 功能:删除所有的数据结点,清空表 */ void clear() { DLNode*p = headNode.next; DLNode*t; while(p!=0){ t = p; p=p->next; delete t; } //回归初始状态 headNode.next = 0; pLastNode = &headNode; size = 0; } void show()const { DLNode*p = headNode.next; cout<<'['; while(p!=0) { if(p!=headNode.next) cout<<','; cout<<p->element; p = p->next; } cout<<']'; } int operator[](int index) const { DLNode*p = _getNodeAt(index); if(p==0) throw std::out_of_range(0); return p->element; } int& operator[](int index) { DLNode*p = _getNodeAt(index); if(p==0) throw std::out_of_range(0); return p->element; } }; int main() { DLinkList list; for(int i=0;i<10;++i) list.append(i); list.show(); cout<<' '; list.remove(3); list.remove(3); list[0] = 101; list.show(); cout<<' '; return 0; }
总结
单链表 vs 双向链表:双向链表由于结点多了一个指针域,因此空间占用量比单链表高,但是结点的访问时间却可以加快了,因为我们可以选择最近的迭代查找方向,从尾结点向前,或者从头结点向后。这是一个用空间换时间的例子。实际开发中,双向链表更加通用,强大。
DLNode* _getNodeAt(int index) const { DLNode*p; int i; if(index < 0 || index >=size ) return 0; //索引不合法,返回NULL if( index < size /2) //从前向后寻找更快到达 { for(i=0,p=headNode.next ; i<index ;i++,p=p->next){ // NOOP } return p; } else { //从后向前 寻找更快到达 for(i=size-1,p = pLastNode; i>index ;i--,p=p->prior){ // NOOP } return p; } }