1. Run spring boot as a standalone application (non-web)
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<project xmlns="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0 http://maven.apache.org/xsd/maven-4.0.0.xsd">
<modelVersion>4.0.0</modelVersion>
<groupId>com.study</groupId>
<artifactId>SpringBootTest</artifactId>
<version>0.0.1-SNAPSHOT</version>
<packaging>jar</packaging>
<name>SpringBootTest</name>
<description></description>
<parent>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-parent</artifactId>
<version>2.0.1.RELEASE</version>
<relativePath /> <!-- lookup parent from repository -->
</parent>
<properties>
<project.build.sourceEncoding>UTF-8</project.build.sourceEncoding>
<project.reporting.outputEncoding>UTF-8</project.reporting.outputEncoding>
<java.version>1.8</java.version>
</properties>
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter</artifactId>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
<build>
<plugins>
<plugin>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-maven-plugin</artifactId>
</plugin>
</plugins>
</build>
</project>
package com.commandline.runner; import org.springframework.boot.CommandLineRunner; import org.springframework.boot.SpringApplication; import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.SpringBootApplication; @SpringBootApplication public class Application implements CommandLineRunner { public static void main(String[] args) { SpringApplication app = new SpringApplication(Application.class); app.run(args); } @Override public void run(String... args) throws Exception { System.out.println("Hello World"); } }
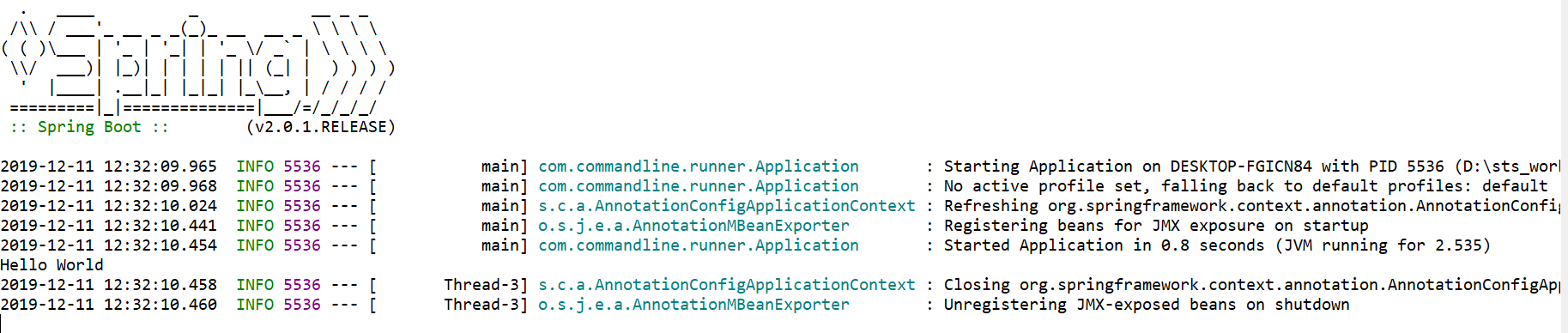
2. Use CommandLineRunner 启动系统任务
有一些特殊的任务需要在系统启动时执行,例如配置文件加载、数据库初始化等操作。
Spring Boot 项目会在启动时遍历素有CommandLineRunner的实现类并调用其中的 run 方法,如果有多个CommandLineRunner的实现类,那么可以使用@Order对这些实现类的调用顺序进行排序。
如下有2个实现CommandLineRunner 的类,并用 @Order 定义调用顺序。
<project xmlns="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xsi:schemaLocation="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0 http://maven.apache.org/xsd/maven-4.0.0.xsd"> <modelVersion>4.0.0</modelVersion> <parent> <groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId> <artifactId>spring-boot-starter-parent</artifactId> <version>2.0.1.RELEASE</version> <relativePath /> </parent> <groupId>com.study</groupId> <artifactId>SpringBootTest-1</artifactId> <version>0.0.1-SNAPSHOT</version> <name>RequestBodyTest</name> <description>Demo project for Spring Boot</description> <properties> <java.version>1.8</java.version> </properties> <dependencies> <dependency> <groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId> <artifactId>spring-boot-starter-web</artifactId> </dependency> </dependencies> <build> <plugins> <plugin> <groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId> <artifactId>spring-boot-maven-plugin</artifactId> </plugin> </plugins> </build> </project>
import java.util.Arrays; import org.springframework.boot.CommandLineRunner; import org.springframework.core.annotation.Order; import org.springframework.stereotype.Component; @Component @Order(1) public class MyCommandLineRunner1 implements CommandLineRunner { @Override public void run(String... args) throws Exception { System.out.println("Runner1>>>" + Arrays.toString(args)); } }
package com.commandline.runner; import java.util.Arrays; import org.springframework.boot.CommandLineRunner; import org.springframework.core.annotation.Order; import org.springframework.stereotype.Component; @Component @Order(2) public class MyCommandLineRunner2 implements CommandLineRunner { @Override public void run(String... args) throws Exception { System.out.println("Runner2>>>" + Arrays.toString(args)); } }
import org.springframework.boot.SpringApplication; import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.SpringBootApplication; @SpringBootApplication public class WebApplication { public static void main(String[] args) { SpringApplication.run(WebApplication.class, args); } }
配置参数
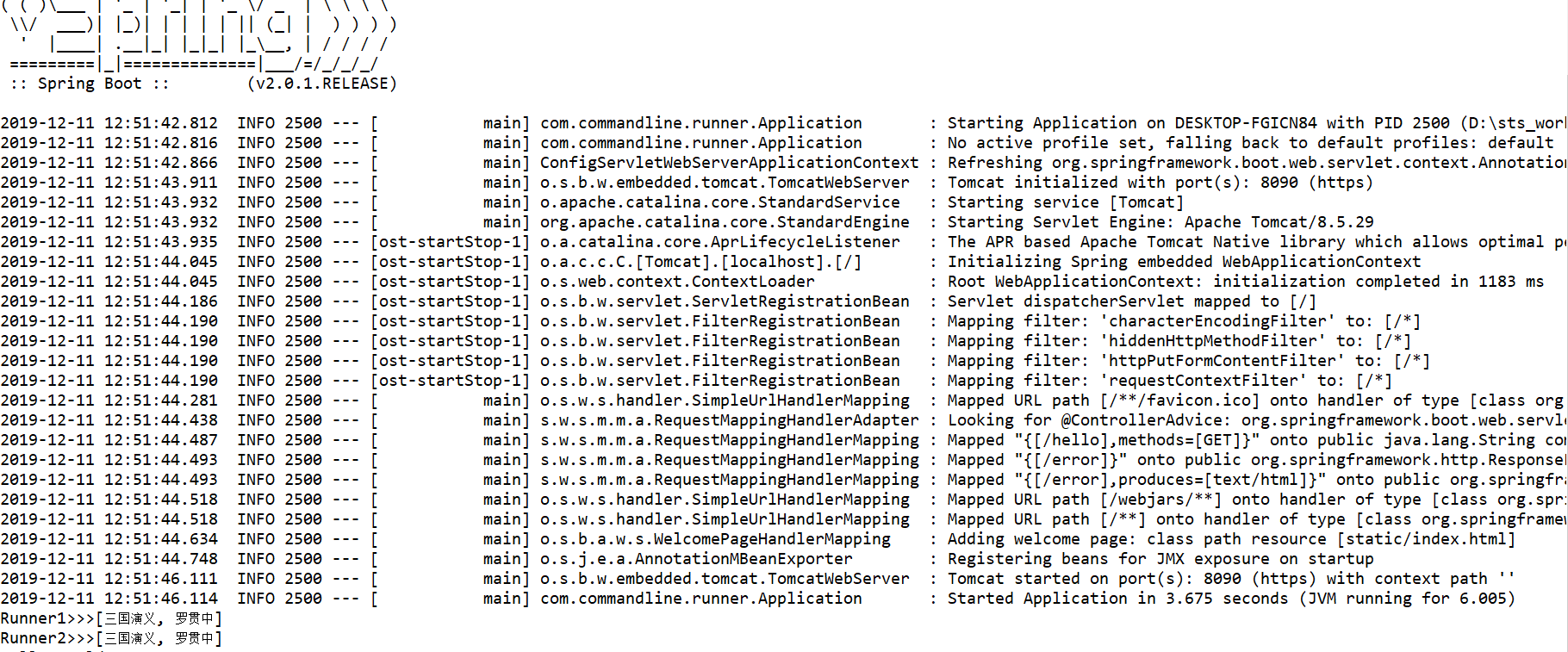
启动WebApplication, 可以看到,如下运行结果:
CommandLineRunner 实现类的 run 方法, 在SpringBoot Application 启动后被调用。
3. CommandLineRunner 和 ApplicationRunner 的区别
CommandLineRunner 和 ApplicationRunner 基本一致,差别主要体现在参数上:
CommandLineRunner: 参数为 String... args
ApplicationRunner: 参数为 ApplicationArguments
import org.springframework.boot.ApplicationArguments; import org.springframework.boot.ApplicationRunner; import org.springframework.stereotype.Component; import java.util.List; import java.util.Set; @Component public class MyApplicationRunner1 implements ApplicationRunner { @Override public void run(ApplicationArguments args) throws Exception { List<String> nonOptionArgs = args.getNonOptionArgs(); System.out.println("NonOptionArgs>>>" + nonOptionArgs); Set<String> optionNames = args.getOptionNames(); for (String optionName : optionNames) { System.out.println("key:" + optionName + ";value:" + args.getOptionValues(optionName)); } } }
将项目打包,并在命令行执行:

得到如下执行结果:
