1. 线性表的顺序表示和代码实现
package lineTable;
/**
* @author wcc
* @description 线性表的顺序表示和实现
*/
public class SequenceList<T> {
private int length;//元素
private final int defaultInitSize = 10;//元素
private T[] array;//数据对象,一系列T类型元素的集合,使用SequenceList<T>这种ADT抽象数据类型来进行操作
public SequenceList() {
length = 0;
array = (T[]) new Object[defaultInitSize];
}
public SequenceList(int size) {
this.length = 0;
this.array = (T[]) new Object[size];
}
//position为1添加为第一个元素,头元素,在指定位置处添加元素
public void add(T element, int position) {
//保证程序的健壮性
if (position < 1 || (position > (length + 1))) {
System.out.println("添加元素位置不合理");
System.exit(1);
}
//如果数组已经存满,需要进行扩容,默认扩容两倍
if (length == array.length) {
T[] newArr = (T[]) new Object[length * 2];
for (int i = 0; i < length; i++) {
newArr[i] = array[i];
}
array = newArr;
}
//插入在中间某个位置时,需要将此位置后的每一个元素向后移动一位,这里从最后一位开始向后移动一位,直到移动到position-1处
for (int i = length; i > position - 1; i--) {
array[i] = array[i - 1];
}
array[position - 1] = element;
length++;
}
//删除指定位置的元素,position为1,删除第一个元素,头元素
public void delete(int position) {
//首先进行position的校验
if (position < 1 || position > length) {
System.out.println("此位置不存在数据元素,不能删除");
System.exit(1);
}
//删除元素肯定不涉及扩容哈,比增加简单些,同时删除元素是该元素之后的所有元素向前移动一位,
// 从钙元素开始递增,这里并没有进行删除元素的保存返回,需要的话改下即可
for (int i = position - 1; i < length - 1; i++) {
array[i] = array[i + 1];
}
length--;
}
//在线性表中查找某个元素的位置
public int find(T obj) {
for (int i = 0; i < length; i++) {
if (array[i].equals(obj)) {
return i + 1;
}
}
return -1;//返回-1表示没有查询到此元素
}
//其它方法由于都简单一些就不写了先
public void show() {
for (int i = 0; i < length; i++) {
System.out.print(array[i] + ".");
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
SequenceList<Integer> t = new SequenceList<>();
t.add(1, 1);
t.add(2, 1);
t.add(3, 1);
t.add(4, 1);
t.add(5, 1);
t.add(6, 1);
t.add(7, 1);
t.add(8, 1);
t.add(9, 1);
t.add(10, 1);
t.add(11, 1);
t.add(12, 1);
t.show();
System.out.println();
t.delete(1);
t.show();
System.out.println("t.find(3) = " + t.find(3));
}
}
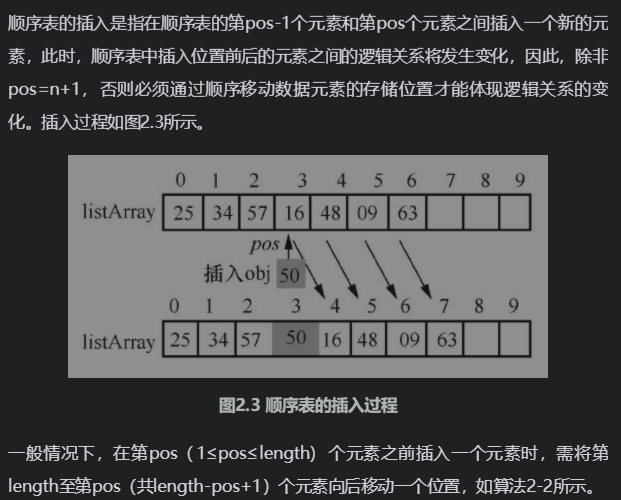
2.插入逻辑:
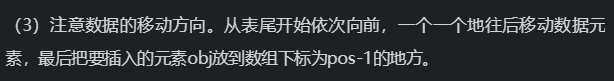
3.删除逻辑: