一:单向链表基本介绍
链表是一种数据结构,和数组同级。比如,Java中我们使用的ArrayList,其实现原理是数组。而LinkedList的实现原理就是链表了。链表在进行循环遍历时效率不高,但是插入和删除时优势明显。下面对单向链表做一个介绍。
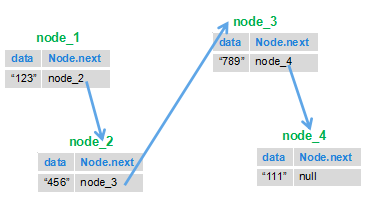
单向链表是一种线性表,实际上是由节点(Node)组成的,一个链表拥有不定数量的节点。其数据在内存中存储是不连续的,它存储的数据分散在内存中,每个结点只能也只有它能知道下一个结点的存储位置。由N各节点(Node)组成单向链表,每一个Node记录本Node的数据及下一个Node。向外暴露的只有一个头节点(Head),我们对链表的所有操作,都是直接或者间接地通过其头节点来进行的。 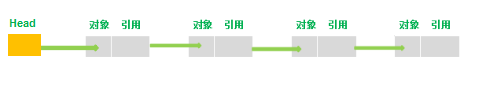
上图中最左边的节点即为头结点(Head),但是添加节点的顺序是从右向左的,添加的新节点会被作为新节点。最先添加的节点对下一节点的引用可以为空。引用是引用下一个节点而非下一个节点的对象。因为有着不断的引用,所以头节点就可以操作所有节点了。
下图描述了单向链表存储情况。存储是分散的,每一个节点只要记录下一节点,就把所有数据串了起来,形成了一个单向链表。 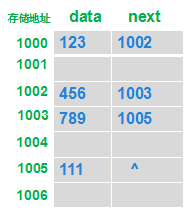
节点(Node)是由一个需要储存的对象及对下一个节点的引用组成的。也就是说,节点拥有两个成员:储存的对象、对下一个节点的引用。下面图是具体的说明:
二、单项链表的实现
/** * @author Administrator */ public class MyLink { Node head = null; // 头节点 /** * 链表中的节点,data代表节点的值,next是指向下一个节点的引用 * * @author zjn * */ class Node { Node next = null;// 节点的引用,指向下一个节点 int data;// 节点的对象,即内容 public Node(int data) { this.data = data; } } /** * 向链表中插入数据 * * @param d */ public void addNode(int d) { Node newNode = new Node(d);// 实例化一个节点 if (head == null) { head = newNode; return; } Node tmp = head; while (tmp.next != null) { tmp = tmp.next; } tmp.next = newNode; } /** * * @param index:删除第index个节点 * @return */ public boolean deleteNode(int index) { if (index < 1 || index > length()) { return false; } if (index == 1) { head = head.next; return true; } int i = 1; Node preNode = head; Node curNode = preNode.next; while (curNode != null) { if (i == index) { preNode.next = curNode.next; return true; } preNode = curNode; curNode = curNode.next; i++; } return false; } /** * * @return 返回节点长度 */ public int length() { int length = 0; Node tmp = head; while (tmp != null) { length++; tmp = tmp.next; } return length; } /** * 在不知道头指针的情况下删除指定节点 * * @param n * @return */ public boolean deleteNode11(Node n) { if (n == null || n.next == null) { return false; } int tmp = n.data; n.data = n.next.data; n.next.data = tmp; n.next = n.next.next; System.out.println("删除成功!"); return true; } public void printList() { Node tmp = head; while (tmp != null) { System.out.println(tmp.data); tmp = tmp.next; } } public static void main(String[] args) { MyLink list = new MyLink(); list.addNode(5); list.addNode(3); list.addNode(1); list.addNode(2); list.addNode(55); list.addNode(36); System.out.println("linkLength:" + list.length()); System.out.println("head.data:" + list.head.data); list.printList(); list.deleteNode(4); System.out.println("After deleteNode(4):"); list.printList(); } }
三、链表相关的常用操作实现方法
1. 链表反转
/** * 链表反转 * * @param head * @return */ public Node ReverseIteratively(Node head) { Node pReversedHead = head; Node pNode = head; Node pPrev = null; while (pNode != null) { Node pNext = pNode.next; if (pNext == null) { pReversedHead = pNode; } pNode.next = pPrev; pPrev = pNode; pNode = pNext; } this.head = pReversedHead; return this.head; }
2. 查找单链表的中间节点
采用快慢指针的方式查找单链表的中间节点,快指针一次走两步,慢指针一次走一步,当快指针走完时,慢指针刚好到达中间节点。
/** * 查找单链表的中间节点 * * @param head * @return */ public Node SearchMid(Node head) { Node p = this.head, q = this.head; while (p != null && p.next != null && p.next.next != null) { p = p.next.next; q = q.next; } System.out.println("Mid:" + q.data); return q; }
3. 查找倒数第k个元素
采用两个指针P1,P2,P1先前移K步,然后P1、P2同时移动,当p1移动到尾部时,P2所指位置的元素即倒数第k个元素 。
/** * 查找倒数 第k个元素 * * @param head * @param k * @return */ public Node findElem(Node head, int k) { if (k < 1 || k > this.length()) { return null; } Node p1 = head; Node p2 = head; for (int i = 0; i < k; i++)// 前移k步 p1 = p1.next; while (p1 != null) { p1 = p1.next; p2 = p2.next; } return p2; }
4. 对链表进行排序
/** * 排序 * * @return */ public Node orderList() { Node nextNode = null; int tmp = 0; Node curNode = head; while (curNode.next != null) { nextNode = curNode.next; while (nextNode != null) { if (curNode.data > nextNode.data) { tmp = curNode.data; curNode.data = nextNode.data; nextNode.data = tmp; } nextNode = nextNode.next; } curNode = curNode.next; } return head; }
5. 删除链表中的重复节点
/** * 删除重复节点 */ public void deleteDuplecate(Node head) { Node p = head; while (p != null) { Node q = p; while (q.next != null) { if (p.data == q.next.data) { q.next = q.next.next; } else q = q.next; } p = p.next; } }
6. 从尾到头输出单链表,采用递归方式实现
/** * 从尾到头输出单链表,采用递归方式实现 * * @param pListHead */ public void printListReversely(Node pListHead) { if (pListHead != null) { printListReversely(pListHead.next); System.out.println("printListReversely:" + pListHead.data); } }
7. 判断链表是否有环,有环情况下找出环的入口节点
/** * 判断链表是否有环,单向链表有环时,尾节点相同 * * @param head * @return */ public boolean IsLoop(Node head) { Node fast = head, slow = head; if (fast == null) { return false; } while (fast != null && fast.next != null) { fast = fast.next.next; slow = slow.next; if (fast == slow) { System.out.println("该链表有环"); return true; } } return !(fast == null || fast.next == null); } /** * 找出链表环的入口 * * @param head * @return */ public Node FindLoopPort(Node head) { Node fast = head, slow = head; while (fast != null && fast.next != null) { slow = slow.next; fast = fast.next.next; if (slow == fast) break; } if (fast == null || fast.next == null) return null; slow = head; while (slow != fast) { slow = slow.next; fast = fast.next; } return slow; }
转载自:https://blog.csdn.net/jianyuerensheng/article/details/51200274