1、二叉树的建立
首先,定义数组存储树的data,然后使用list集合将所有的二叉树结点都包含进去,最后给每个父亲结点赋予左右孩子。
需要注意的是:最后一个父亲结点需要单独处理
1 public static TreeNode root; 2 //建立二叉树内部类 3 class TreeNode{ 4 public Object data; //携带变量 5 public TreeNode lchild,rchild; //左右孩子 6 public TreeNode() { 7 data = null; 8 lchild = null; 9 rchild = null; 10 } 11 public TreeNode(Object data) { 12 this.data = data; 13 } 14 public void setLeft(TreeNode left) 15 { 16 this.lchild = left; 17 } 18 public void setRight(TreeNode right) 19 { 20 this.rchild = right; 21 } 22 } 23 //建立二叉树,通过List作为中间过渡量 24 public void CreatBinTree(int []datas,List<TreeNode> nodelist) { 25 for(int i=0;i<datas.length;i++) 26 { 27 TreeNode aNode = new TreeNode(datas[i]); 28 nodelist.add(aNode); 29 } 30 //给所有父亲结点设定子节点 31 for(int index = 0;index<nodelist.size()/2-1;index++) 32 { 33 //在起始结点为0时,为N的父亲结点他的左孩子为2*N+1,右孩子为2*N+2 34 nodelist.get(index).lchild = nodelist.get(2*index+1); 35 nodelist.get(index).rchild = nodelist.get(2*index+2); 36 } 37 //单独处理最后一个父亲结点 38 int index = nodelist.size()/2-1; 39 nodelist.get(index).lchild = nodelist.get(2*index+1); 40 if(nodelist.size()%2==1) 41 nodelist.get(index).rchild = nodelist.get(2*index+2); 42 }
2、先序遍历
2.1 递归方法
//先序遍历,递归操作 public void PreOrder(TreeNode root) { if(root == null) return ; System.out.print(root.data+" "); PreOrder(root.lchild); PreOrder(root.rchild); }
2.2 非递归操作,使用栈(两种方法)
本人认为第一种方法相对容易理解,较为简单
方法一:
思想:
(1)若栈非空或者结点非空,则进入循环
(2)若结点非空,读取该节点,并将结点压入栈中,结点向左孩子移动,移到最左孩子
(3)若栈非空,取出栈顶元素,此时父节点已读,所以移向右孩子
****************核心为:边读取左结点变将其压入栈中,左孩子对下一级来说上也代表父亲结点,所以之后可以直接读取右孩子。*******************
/* * 方法一:先序遍历,使用栈操作,相对较简单 * 思想: * (1)若栈非空或者结点非空,则进入循环 * (2)若结点非空,读取该节点,并将结点压入栈中,结点向左孩子移动,移到最左孩子 * (3)若栈非空,取出栈顶元素,此时父节点已读,所以移向右孩子 * 核心为:边读取左结点变将其压入栈中,左孩子对下一级来说上也代表父亲结点,所以之后可以直接读取右孩子。 */ public void preOrder1() { Stack<TreeNode> stack = new Stack<>(); TreeNode node = root; while(!stack.isEmpty()||node!=null) { while(node!=null) { System.out.print(node.data+" "); //访问该节点 stack.push(node); node = node.lchild; } if(!stack.isEmpty()) { node = stack.pop(); node = node.rchild; } } }
方法二:
思想:
(1)首先将根节点入栈
(2)判断非空,将结点从栈中取出并访问
(3)依次访问栈中的左孩子,并将右孩子放入栈中,结点不断往左孩子移动
(4)重复步骤(2)(3),直到栈为空
/* * 方法二:先序遍历,使用栈操作,相对较麻烦 * 思想: * (1)首先将根节点入栈 * (2)判断非空,将结点从栈中取出并访问 * (3)依次访问栈中的左孩子,并将右孩子放入栈中,结点不断往左孩子移动 * (4)重复步骤(2)(3),直到栈为空 */ public void preOrder2() throws Exception { TreeNode pNode = root; if(pNode!=null) //首先判断根结点是否为空 { Stack<TreeNode> astack = new Stack<>(); //构造栈操作 astack.push(pNode); //将根节点压入栈中 while(!astack.isEmpty()) //循环操作直到栈中没有结点存在,即最右结点访问完毕 { pNode = astack.pop(); //首先将结点从栈中取出 System.out.print(pNode.data+" "); //访问该节点 while(pNode!=null) //若该结点不为空 { if(pNode.lchild!=null) //访问左子树 System.out.print(pNode.lchild.data+" "); if(pNode.rchild!=null) //将右子树压入栈中 astack.push(pNode.rchild); pNode = pNode.lchild; //进入到下一个左子树中 } } } }
3、中序遍历
3.1 递归操作
//中序遍历,递归操作 public void inOrder(TreeNode root) { if(root==null) return ; inOrder(root.lchild); System.out.print(root.data+" "); inOrder(root.rchild); }
3.2 非递归操作,栈
思想:
* (1)若栈非空或者结点非空,则进入循环
* (2)若结点非空,则将结点压入栈中,结点向左孩子移动,一直到最左边
* (3)若栈非空,则取出栈顶元素,并读取访问数据,而后结点向右孩子移动
/* * 中序遍历,使用栈操作 * 思想: * (1)若栈非空或者结点非空,则进入循环 * (2)若结点非空,则将结点压入栈中,结点向左孩子移动,一直到最左边 * (3)若栈非空,则取出栈顶元素,并读取访问数据,而后结点向右孩子移动 */ public void inOrder1() throws Exception { TreeNode node = root; Stack<TreeNode> stack = new Stack<>(); while(node!=null||!stack.isEmpty()) { while(node!=null) { stack.push(node); node = node.lchild; } if(stack!=null) { node = stack.pop(); System.out.print(node.data+" "); node = node.rchild; } } }
4、后序遍历
4.1 递归操作
//后序遍历,递归操作 public void postOrder(TreeNode root) { if(root==null) return ; postOrder(root.lchild); postOrder(root.rchild); System.out.print(root.data+" "); }
4.2 非递归操作
前提:设置标志结点pre,指示是否访问过某结点
思想:
* (1)若栈非空或者结点非空,则进入循环
* (2)若结点非空,则将结点压入栈中,结点向左孩子移动,一直到最左边
* (3)若栈非空,首先取出栈顶元素的右孩子赋给tmp
1、若栈顶元素的右孩子为空或者等于pre(即已访问过),则弹出元素并访问,将该结点赋值给pre,并将当前结点赋值为null
2、否则的话将右孩子赋值给当前结点
/* * 后序遍历,栈操作 * 前提:设置标志结点pre,指示是否访问过某结点 * 思想: * (1)若栈非空或者结点非空,则进入循环 * (2)若结点非空,则将结点压入栈中,结点向左孩子移动,一直到最左边 * (3)若栈非空,首先取出栈顶元素的右孩子赋给tmp * 1、若栈顶元素的右孩子为空或者等于pre(即已访问过),则弹出元素并访问,将该结点赋值给pre,并将当前结点赋值为null * 2、否则的话将右孩子赋值给当前结点 */ public void postOrder1() { Stack<TreeNode> stack = new Stack<>(); TreeNode node = root,pre = root; while(!stack.isEmpty()||node!=null) { while(node!=null) { stack.push(node); node = node.lchild; } if(!stack.isEmpty()) { TreeNode tmp = stack.peek().rchild; if(tmp==null||tmp==pre) { node = stack.pop(); System.out.print(node.data+" "); pre = node; node = null; }else { node = tmp; } } } }
5、层次遍历(广度优先遍历)使用队列
思想:
* (1)读取根节点,并将其压入队列中
* (2)以队列的长度作为循环的判断条件,取出队收元素并访问,访问后将其弹出
* (3)判断是否有左右孩子,若有则加入队列中。
public void bfs() { Queue<TreeNode> queue = new LinkedList(); if(root==null) return ; queue.offer(root); while(queue.size()>0) { TreeNode node = queue.peek(); queue.poll(); System.out.print(node.data+" "); if(node.lchild!=null) { queue.offer(node.lchild); } if(node.rchild!=null) { queue.offer(node.rchild); } } }
6、深度优先遍历
此部分相对较难理解,自行琢磨
public void dfs(TreeNode node,List<List<Integer>> nList,List<Integer> list) { if(node==null) return ; if(node.lchild==null&node.rchild==null) { list.add((Integer) node.data); nList.add(new ArrayList<>(list)); list.remove(list.size()-1); } list.add((Integer) node.data); dfs(node.lchild, nList, list); dfs(node.rchild, nList, list); list.remove(list.size()-1); }
7、求树的深度
(1)若二叉树为空,则返回0
(2)若二叉树非空,求左子树的深度,求右子树的深度
(3)比较左右子树的深度,求最大值加1,即为二叉树的深度
//求二叉树的深度 public int Depth(TreeNode node) { if(node==null) return 0; else { int ldepth = Depth(node.lchild); System.out.println("node'data:"+node.data+"ldepth: "+ldepth); int rdepth = Depth(node.rchild); System.out.println("node'data:"+node.data+"rdepth: "+rdepth+" "); if(ldepth<rdepth) return rdepth+1; else return ldepth+1; } }
7、应用及全部代码展示
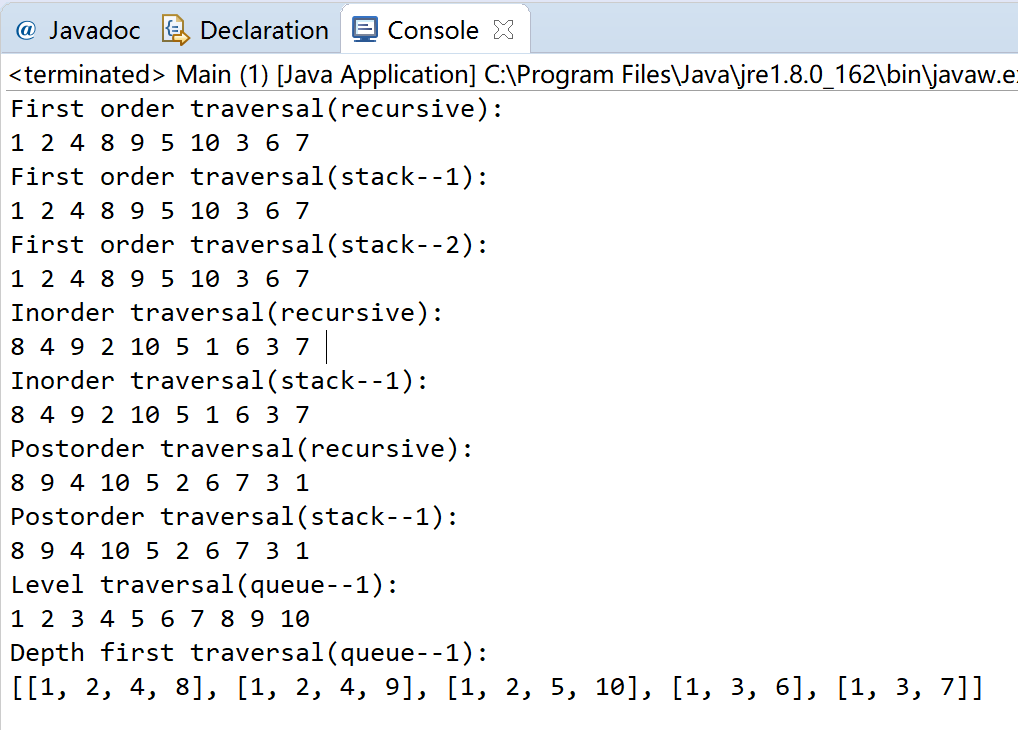
1 package Main; 2 3 import java.util.ArrayList; 4 import java.util.Collection; 5 import java.util.Iterator; 6 import java.util.LinkedList; 7 import java.util.List; 8 import java.util.Queue; 9 import java.util.Scanner; 10 import java.util.Stack; 11 12 import javax.naming.directory.SearchControls; 13 public class Main{ 14 public static TreeNode root; 15 //建立二叉树内部类 16 class TreeNode{ 17 public Object data; //携带变量 18 public TreeNode lchild,rchild; //左右孩子 19 public TreeNode() { 20 data = null; 21 lchild = null; 22 rchild = null; 23 } 24 public TreeNode(Object data) { 25 this.data = data; 26 } 27 public void setLeft(TreeNode left) 28 { 29 this.lchild = left; 30 } 31 public void setRight(TreeNode right) 32 { 33 this.rchild = right; 34 } 35 } 36 //建立二叉树,通过List作为中间过渡量 37 public void CreatBinTree(int []datas,List<TreeNode> nodelist) { 38 for(int i=0;i<datas.length;i++) 39 { 40 TreeNode aNode = new TreeNode(datas[i]); 41 nodelist.add(aNode); 42 } 43 //给所有父亲结点设定子节点 44 for(int index = 0;index<nodelist.size()/2-1;index++) 45 { 46 //在起始结点为0时,为N的父亲结点他的左孩子为2*N+1,右孩子为2*N+2 47 nodelist.get(index).lchild = nodelist.get(2*index+1); 48 nodelist.get(index).rchild = nodelist.get(2*index+2); 49 } 50 //单独处理最后一个父亲结点 51 int index = nodelist.size()/2-1; 52 nodelist.get(index).lchild = nodelist.get(2*index+1); 53 if(nodelist.size()%2==1) 54 nodelist.get(index).rchild = nodelist.get(2*index+2); 55 } 56 //先序遍历,递归操作 57 public void PreOrder(TreeNode root) 58 { 59 if(root == null) 60 return ; 61 System.out.print(root.data+" "); 62 PreOrder(root.lchild); 63 PreOrder(root.rchild); 64 } 65 /* 66 * 方法一:先序遍历,使用栈操作,相对较简单 67 * 思想: 68 * (1)若栈非空或者结点非空,则进入循环 69 * (2)若结点非空,读取该节点,并将结点压入栈中,结点向左孩子移动,移到最左孩子 70 * (3)若栈非空,取出栈顶元素,此时父节点已读,所以移向右孩子 71 * 核心为:边读取左结点变将其压入栈中,左孩子对下一级来说上也代表父亲结点,所以之后可以直接读取右孩子。 72 */ 73 public void preOrder1() 74 { 75 Stack<TreeNode> stack = new Stack<>(); 76 TreeNode node = root; 77 while(!stack.isEmpty()||node!=null) 78 { 79 while(node!=null) 80 { 81 System.out.print(node.data+" "); //访问该节点 82 stack.push(node); 83 node = node.lchild; 84 } 85 if(!stack.isEmpty()) 86 { 87 node = stack.pop(); 88 node = node.rchild; 89 } 90 } 91 } 92 /* 93 * 方法二:先序遍历,使用栈操作,相对较麻烦 94 * 思想: 95 * (1)首先将根节点入栈 96 * (2)判断非空,将结点从栈中取出并访问 97 * (3)依次访问栈中的左孩子,并将右孩子放入栈中,结点不断往左孩子移动 98 * (4)重复步骤(2)(3),直到栈为空 99 */ 100 public void preOrder2() throws Exception 101 { 102 TreeNode pNode = root; 103 if(pNode!=null) //首先判断根结点是否为空 104 { 105 Stack<TreeNode> astack = new Stack<>(); //构造栈操作 106 astack.push(pNode); //将根节点压入栈中 107 while(!astack.isEmpty()) //循环操作直到栈中没有结点存在,即最右结点访问完毕 108 { 109 pNode = astack.pop(); //首先将结点从栈中取出 110 System.out.print(pNode.data+" "); //访问该节点 111 while(pNode!=null) //若该结点不为空 112 { 113 if(pNode.lchild!=null) //访问左子树 114 System.out.print(pNode.lchild.data+" "); 115 if(pNode.rchild!=null) //将右子树压入栈中 116 astack.push(pNode.rchild); 117 pNode = pNode.lchild; //进入到下一个左子树中 118 } 119 } 120 121 } 122 } 123 //中序遍历,递归操作 124 public void inOrder(TreeNode root) 125 { 126 if(root==null) 127 return ; 128 inOrder(root.lchild); 129 System.out.print(root.data+" "); 130 inOrder(root.rchild); 131 } 132 /* 133 * 中序遍历,使用栈操作 134 * 思想: 135 * (1)若栈非空或者结点非空,则进入循环 136 * (2)若结点非空,则将结点压入栈中,结点向左孩子移动,一直到最左边 137 * (3)若栈非空,则取出栈顶元素,并读取访问数据,而后结点向右孩子移动 138 */ 139 public void inOrder1() throws Exception 140 { 141 TreeNode node = root; 142 Stack<TreeNode> stack = new Stack<>(); 143 while(node!=null||!stack.isEmpty()) 144 { 145 while(node!=null) 146 { 147 stack.push(node); 148 node = node.lchild; 149 } 150 if(stack!=null) 151 { 152 node = stack.pop(); 153 System.out.print(node.data+" "); 154 node = node.rchild; 155 } 156 } 157 } 158 //后序遍历,递归操作 159 public void postOrder(TreeNode root) 160 { 161 if(root==null) 162 return ; 163 postOrder(root.lchild); 164 postOrder(root.rchild); 165 System.out.print(root.data+" "); 166 } 167 /* 168 * 后序遍历,栈操作 169 * 前提:设置标志结点pre,指示是否访问过某结点 170 * 思想: 171 * (1)若栈非空或者结点非空,则进入循环 172 * (2)若结点非空,则将结点压入栈中,结点向左孩子移动,一直到最左边 173 * (3)若栈非空,首先取出栈顶元素的右孩子赋给tmp 174 * 1、若栈顶元素的右孩子为空或者等于pre(即已访问过),则弹出元素并访问,将该结点赋值给pre,并将当前结点赋值为null 175 * 2、否则的话将右孩子赋值给当前结点 176 */ 177 public void postOrder1() 178 { 179 Stack<TreeNode> stack = new Stack<>(); 180 TreeNode node = root,pre = root; 181 while(!stack.isEmpty()||node!=null) 182 { 183 while(node!=null) 184 { 185 stack.push(node); 186 node = node.lchild; 187 } 188 if(!stack.isEmpty()) 189 { 190 TreeNode tmp = stack.peek().rchild; 191 if(tmp==null||tmp==pre) 192 { 193 node = stack.pop(); 194 System.out.print(node.data+" "); 195 pre = node; 196 node = null; 197 }else { 198 node = tmp; 199 } 200 201 } 202 } 203 204 } 205 /*层次遍历,即广度优先遍历,从上到下遍历二叉树 206 * 思想: 207 * (1)读取根节点,并将其压入队列中 208 * (2)以队列的长度作为循环的判断条件,取出队收元素并访问,访问后将其弹出 209 * (3)判断是否有左右孩子,若有则加入队列中。 210 * */ 211 public void bfs() 212 { 213 Queue<TreeNode> queue = new LinkedList(); 214 if(root==null) 215 return ; 216 queue.offer(root); 217 while(queue.size()>0) { 218 TreeNode node = queue.peek(); 219 queue.poll(); 220 System.out.print(node.data+" "); 221 if(node.lchild!=null) 222 { 223 queue.offer(node.lchild); 224 } 225 if(node.rchild!=null) 226 { 227 queue.offer(node.rchild); 228 } 229 } 230 231 } 232 /* 233 * 深度优先遍历,从左到右遍历二叉树 234 * */ 235 public void dfs(TreeNode node,List<List<Integer>> nList,List<Integer> list) 236 { 237 if(node==null) 238 return ; 239 if(node.lchild==null&node.rchild==null) 240 { 241 list.add((Integer) node.data); 242 nList.add(new ArrayList<>(list)); 243 list.remove(list.size()-1); 244 } 245 list.add((Integer) node.data); 246 dfs(node.lchild, nList, list); 247 dfs(node.rchild, nList, list); 248 list.remove(list.size()-1); 249 } 250 //查找算法 251 public static TreeNode Searchparameter(TreeNode root,int x) 252 { 253 TreeNode node = root; 254 if(root==null) 255 return null; 256 else { 257 if(node.data.equals(x)) 258 return node; 259 else { 260 TreeNode aNode = Searchparameter(node.lchild, x); 261 if(aNode==null) 262 return Searchparameter(node.rchild, x); 263 else 264 return aNode; 265 } 266 } 267 } 268 //求二叉树的深度 269 public int Depth(TreeNode node) 270 { 271 if(node==null) 272 return 0; 273 else { 274 int ldepth = Depth(node.lchild); 275 int rdepth = Depth(node.rchild); 276 if(ldepth<rdepth) 277 return rdepth+1; 278 else 279 return ldepth+1; 280 } 281 } 282 public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception { 283 int datas[] = {1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9,10}; 284 List<TreeNode> nodelist = new LinkedList<>(); 285 Main aMain = new Main(); 286 aMain.CreatBinTree(datas,nodelist); 287 root = nodelist.get(0); 288 289 System.out.println("First order traversal(recursive):"); 290 aMain.PreOrder(root); 291 System.out.println(); 292 System.out.println("First order traversal(stack--1):"); 293 aMain.preOrder1(); 294 System.out.println(); 295 System.out.println("First order traversal(stack--2):"); 296 aMain.preOrder2(); 297 System.out.println(); 298 System.out.println("Inorder traversal(recursive):"); 299 aMain.inOrder(root); 300 System.out.println(); 301 System.out.println("Inorder traversal(stack--1):"); 302 aMain.inOrder1(); 303 System.out.println(); 304 System.out.println("Postorder traversal(recursive):"); 305 aMain.postOrder(root); 306 System.out.println(); 307 System.out.println("Postorder traversal(stack--1):"); 308 aMain.postOrder1(); 309 System.out.println(); 310 System.out.println("Level traversal(queue--1):"); 311 aMain.bfs(); 312 313 List<List<Integer>> rst = new ArrayList<>(); 314 List<Integer> list = new ArrayList<>(); 315 System.out.println(); 316 System.out.println("Depth first traversal(queue--1):"); 317 aMain.dfs(root,rst,list); 318 System.out.println(rst); 319 int x = 6; 320 TreeNode aNode = Searchparameter(root,x); 321 System.out.println(aNode.data); 322 323 int depth = aMain.Depth(root); 324 System.out.println("the depth of the tree is :"+depth); 325 } 326 327 328 }
结果展示: