一、redis介绍
redis是一个key-value存储系统。和Memcached类似,它支持存储的value类型相对更多,包括string(字符串)、list(链表)、set(集合)、zset(sorted set --有序集合)和hash(哈希类型)。与memcached一样,为了保证效率,数据都是缓存在内存中。区别的是redis会周期性的把更新的数据写入磁盘或者把修改操作写入追加的记录文件,并且在此基础上实现master-slave(主从)同步。
Redis是一个高性能的key-value数据库。redis的出现,很大程度补偿了memcached这类key/value存储的不足,在部分场合可以对关系数据库起到很好的补充作用。它提供了Java,C/C++,C#,PHP,JavaScript,Perl,Object-C,Python,Ruby等客户端,使用很方便。
如果简单地比较Redis与Memcached的区别,基本上有以下3点:
1、Redis不仅仅支持简单的k/v类型的数据,同时还提供list,set,zset,hash等数据结构的存储。
2、Redis支持数据的备份,即master-slave模式的数据备份。
3、Redis支持数据的持久化,可以将内存中的数据保持在磁盘中,重启的时候可以再次加载进行使用。
在Redis中,并不是所有的数据都一直存储在内存中的。这是和Memcached相比一个最大的区别。Redis只会缓存所有的key的信息,如果Redis发现内存的使用量超过了某一个阀值,将触发swap的操作,Redis根据“swappability = age*log(size_in_memory)”计算出哪些key对应的value需要swap到磁盘。然后再将这些key对应的value持久化到磁盘中,同时在内存中清除。这种特性使得Redis可以保持超过其机器本身内存大小的数据。当然,机器本身的内存必须要能够保持所有的key,因为这些数据是不会进行swap操作的。
当从Redis中读取数据的时候,如果读取的key对应的value不在内存中,那么Redis就需要从swap文件中加载相应数据,然后再返回给请求方。
memcached和redis的比较
1、网络IO模型
Memcached是多线程,非阻塞IO复用的网络模型,分为监听主线程和worker子线程,监听线程监听网络连接,接受请求后,将连接描述字pipe 传递给worker线程,进行读写IO, 网络层使用libevent封装的事件库,多线程模型可以发挥多核作用。
Redis使用单线程的IO复用模型,自己封装了一个简单的AeEvent事件处理框架,主要实现了epoll、kqueue和select,对于单纯只有IO操作来说,单线程可以将速度优势发挥到最大,但是Redis也提供了一些简单的计算功能,比如排序、聚合等,对于这些操作,单线程模型实际会严重影响整体吞吐量,CPU计算过程中,整个IO调度都是被阻塞住的。
2、内存管理方面
Memcached使用预分配的内存池的方式,使用slab和大小不同的chunk来管理内存,value根据大小选择合适的chunk存储。Redis使用现场申请内存的方式来存储数据。
3、存储方式及其它方面
Memcached基本只支持简单的key-value存储,不支持持久化和复制等功能,Redis除key/value之外,还支持list,set,sortedset,hash等众多数据结构
二、如何保持session会话
目前,为了使web能适应大规模的访问,需要实现应用的集群部署。集群最有效的方案就是负载均衡,而实现负载均衡用户每一个请求都有可能被分配到不固定的服务器上,这样我们首先要解决session的统一来保证无论用户的请求被转发到哪个服务器上都能保证用户的正常使用,即需要实现session的共享机制。
在集群系统下实现session统一的有如下几种方案:
1、请求精确定位:sessionsticky,例如基于访问ip的hash策略,即当前用户的请求都集中定位到一台服务器中,这样单台服务器保存了用户的session登录信息,如果宕机,则等同于单点部署,会丢失,会话不复制。
2、session复制共享:sessionreplication,如tomcat自带session共享,主要是指集群环境下,多台应用服务器之间同步session,使session保持一致,对外透明。 如果其中一台服务器发生故障,根据负载均衡的原理,调度器会遍历寻找可用节点,分发请求,由于session已同步,故能保证用户的session信息不会丢失,会话复制,。
此方案的不足之处:
必须在同一种中间件之间完成(如:tomcat-tomcat之间).
session复制带来的性能损失会快速增加.特别是当session中保存了较大的对象,而且对象变化较快时, 性能下降更加显著,会消耗系统性能。这种特性使得web应用的水平扩展受到了限制。
Session内容通过广播同步给成员,会造成网络流量瓶颈,即便是内网瓶颈。在大并发下表现并不好
3、基于cache DB缓存的session共享
基于memcache/redis缓存的 session 共享
即使用cacheDB存取session信息,应用服务器接受新请求将session信息保存在cache DB中,当应用服务器发生故障时,调度器会遍历寻找可用节点,分发请求,当应用服务器发现session不在本机内存时,则去cache DB中查找,如果找到则复制到本机,这样实现session共享和高可用。
三、nginx+tomcat+redis实现负载均衡、session共享
1、实验环境
|
主机 |
操作系统 |
IP地址 |
|
Nginx |
Centos7.2 |
192.168.31.141 |
|
Tomcat-1 |
192.168.31.83 |
|
|
Tomcat-2 |
192.168.31.250 |
|
|
Mysql |
192.168.31.225 |
|
|
Redis |
192.168.31.106 |
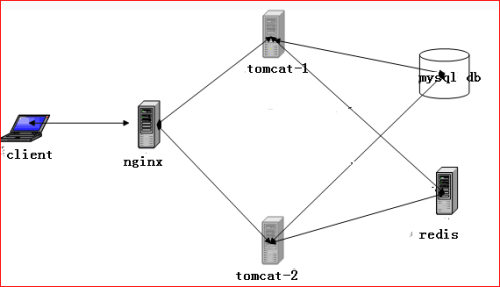
2、实验拓扑
在这个图中,nginx做为反向代理,实现静动分离,将客户动态请求根据权重随机分配给两台tomcat服务器,redis做为两台tomcat的共享session数据服务器,mysql做为两台tomcat的后端数据库。
3、nginx安装配置
使用Nginx作为Tomcat的负载平衡器,Tomcat的会话Session数据存储在Redis,能够实现零宕机的7x24效果。因为将会话存储在Redis中,因此Nginx就不必配置成stick粘贴某个Tomcat方式,这样才能真正实现后台多个Tomcat负载平衡。
安装nginx:
安装zlib-devel、pcre-devel等依赖包
|
1
|
[root@www ~]# yum -y install gccgcc-c++ make libtoolzlibzlib-develpcrepcre-developensslopenssl-devel |
注:
结合proxy和upstream模块实现后端web负载均衡
结合nginx默认自带的ngx_http_proxy_module模块 和ngx_http_upstream_module模块实现后端服务器的健康检查
创建nginx程序用户
|
1
|
[root@www ~]# useradd -s /sbin/nologin www |
编译安装nginx
[root@www ~]# tar zxf nginx-1.10.2.tar.gz
|
1
2
3
4
|
[root@www ~]# cd nginx-1.10.2/[root@www nginx-1.10.2]# ./configure --prefix=/usr/local/nginx1.10 --user=www --group=www --with-http_stub_status_module --with-http_realip_module --with-http_ssl_module--with-http_gzip_static_module --with-pcre --with-http_flv_module[root@www nginx-1.10.2]# make&& make install |
优化nginx程序的执行路径
|
1
2
3
4
|
[root@www nginx-1.10.2]# ln -s /usr/local/nginx1.10/sbin/nginx /usr/local/sbin/[root@www nginx-1.10.2]# nginx -tnginx: the configuration file /usr/local/nginx1.10/conf/nginx.conf syntax is oknginx: configuration file /usr/local/nginx1.10/conf/nginx.conf test is successful |
编写nginx服务脚本:脚本内容如下:
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
|
[root@www ~]# cat /etc/init.d/nginx#!/bin/bash# nginx Startup script for the Nginx HTTP Server# chkconfig: - 85 15# pidfile: /usr/local/nginx1.10/logs/nginx.pid# config: /usr/local/nginx1.10/conf/nginx.confnginxd=/usr/local/nginx1.10/sbin/nginxnginx_config=/usr/local/nginx1.10/conf/nginx.confnginx_pid=/usr/local/nginx1.10/logs/nginx.pidRETVAL=0prog="nginx"# Source function library.. /etc/rc.d/init.d/functions# Start nginx daemons functions.start() {if [ -f $nginx_pid ] ; thenecho "nginx already running...."exit 1fiecho -n "Starting $prog: " $nginxd -c ${nginx_config} RETVAL=$?[ $RETVAL = 0 ] && touch /var/lock/subsys/nginx}# Stop nginx daemons functions.stop() {echo -n "Stopping $prog: " $nginxd -s stop RETVAL=$?[ $RETVAL = 0 ] &&rm -f /var/lock/subsys/nginx}# reloadnginx service functions.reload() {echo -n "Reloading $prog: " $nginxd -s reload}# statusngnx service functionsstatus() {if [ -f $nginx_pid ] ; thenecho "$prog is running"elseecho "$prog is stop"fi}case "$1" instart)start ;;stop)stop ;;reload)reload ;;restart)stopstart ;;status)status ;;*)echo "Usage: $prog {start|stop|restart|reload|status}"exit 1 ;;esac[root@www ~]# chmod +x /etc/init.d/nginx[root@www ~]# chkconfig --add nginx[root@www ~]# chkconfignginx on[root@www ~]# systemctl daemon-reload |
配置nginx反向代理:反向代理+负载均衡+健康探测,nginx.conf文件内容:
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
|
[root@www ~]# cat /usr/local/nginx1.10/conf/nginx.confuser wwwwww;worker_processes 4;worker_cpu_affinity 0001 0010 0100 1000;error_log logs/error.log;#error_log logs/error.log notice;#error_log logs/error.log info;worker_rlimit_nofile 10240;pid logs/nginx.pid;events {useepoll;worker_connections 4096;}http {includemime.types;default_type application/octet-stream;log_format main '$remote_addr - $remote_user [$time_local] "$request" ' '$status $body_bytes_sent "$http_referer" ' '"$http_user_agent" "$http_x_forwarded_for"';access_log logs/access.log main;server_tokens off;sendfile on;tcp_nopush on; #keepalive_timeout 0;keepalive_timeout 65; #Compression Settingsgzip on;gzip_comp_level 6;gzip_http_version 1.1;gzip_proxied any;gzip_min_length 1k;gzip_buffers 16 8k;gzip_types text/plain text/css text/javascript application/json application/javascript application/x-javascript application/xml;gzip_vary on; #end gzip # http_proxy Settingsclient_max_body_size 10m;client_body_buffer_size 128k;proxy_connect_timeout 75;proxy_send_timeout 75;proxy_read_timeout 75;proxy_buffer_size 4k;proxy_buffers 4 32k;proxy_busy_buffers_size 64k;proxy_temp_file_write_size 64k; #load balance Settingsupstreambackend_tomcat {server 192.168.31.83:8080 weight=1 max_fails=2 fail_timeout=10s;server 192.168.31.250:8080 weight=1 max_fails=2 fail_timeout=10s; } #virtual host Settingsserver {listen 80;server_name www.benet.com;charset utf-8;location / {root html;index index.jsp index.html index.htm; }location ~* .(jsp|do)$ {proxy_pass http://backend_tomcat;proxy_redirect off;proxy_set_header Host $host;proxy_set_header X-Real-IP $remote_addr;proxy_set_header X-Forwarded-For $proxy_add_x_forwarded_for;proxy_next_upstream error timeout invalid_header http_500 http_502 http_503 http_504; }location /nginx_status {stub_status on;access_log off;allow 192.168.31.0/24;deny all; } }} |
重启nginx服务,使修改生效
|
1
|
[root@www ~]# service nginx restart |
配置防火墙规测
|
1
2
3
4
|
[root@www ~]# firewall-cmd --permanent --add-port=80/tcpsuccess[root@www ~]# firewall-cmd --reload success |
4、安装部署tomcat应用程序服务器
在tomcat-1和tomcat-2节点上安装JDK
在安装tomcat之前必须先安装JDK,JDK的全称是java development kit,是sun公司免费提供的java语言的软件开发工具包,其中包含java虚拟机(JVM),编写好的java源程序经过编译可形成java字节码,只要安装了JDK,就可以利用JVM解释这些字节码文件,从而保证了java的跨平台性。
安装JDK,配置java环境:
将jdk-7u65-linux-x64.gz解压
|
1
|
[root@tomcat-1 ~]# tar zxf jdk-7u65-linux-x64.gz |
将解压的jdk1.7.0_65目录移致动到/usr/local/下并重命名为java
|
1
|
[root@tomcat-1 ~]# mv jdk1.7.0_65/ /usr/local/java |
在/etc/profile文件中添加内容如下:
|
1
2
|
export JAVA_HOME=/usr/local/javaexport PATH=$JAVA_HOME/bin:$PATH |
通过source命令执行profile文件,使其生效。
|
1
2
3
|
[root@tomcat-1 ~]# source /etc/profile[root@tomcat-1 ~]# echo $PATH/usr/local/java/bin:/usr/local/sbin:/usr/local/bin:/usr/sbin:/usr/bin:/root/bin |
按照相同方法在tomcat-2也安装JDK
分别在在tomcat-1和tomcat-2节点运行java -version命令查看java版本是否和之前安装的一致。
|
1
2
3
4
|
[root@tomcat-1 ~]# java -versionjava version "1.7.0_65"Java(TM) SE Runtime Environment (build 1.7.0_65-b17)Java HotSpot(TM) 64-Bit Server VM (build 24.65-b04, mixed mode) |
至此java环境已经配置完成
在tomcat-1和tomcat-2节点安装配置tomcat
解压apache-tomcat-7.0.54.tar.gz包
|
1
|
[root@tomcat-1 ~]# tar zxf apache-tomcat-7.0.54.tar.gz |
将解压生成的文件夹移动到/usr/local/下,并改名为tomcat7
|
1
|
[root@tomcat-1 ~]# mv apache-tomcat-7.0.54 /usr/local/tomcat7 |
配置tomcat环境变量
/etc/profile文件内容如下:
|
1
2
3
|
export JAVA_HOME=/usr/local/javaexport CATALINA_HOME=/usr/local/tomcat7export PATH=$JAVA_HOME/bin:$CATALINA_HOME/bin:$PATH |
通过source命令执行profile文件,使其生效。
|
1
2
3
|
[root@tomcat-1 ~]# source /etc/profile[root@tomcat-1 ~]# echo $PATH/usr/local/java/bin:/usr/local/tomcat7/bin:/usr/local/java/bin:/usr/local/sbin:/usr/local/bin:/usr/sbin:/usr/bin:/root/bin |
查看tomcat的版本信息
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
|
[root@tomcat-1 ~]# catalina.sh versionUsing CATALINA_BASE: /usr/local/tomcat7Using CATALINA_HOME: /usr/local/tomcat7Using CATALINA_TMPDIR: /usr/local/tomcat7/tempUsing JRE_HOME: /usr/local/javaUsing CLASSPATH: /usr/local/tomcat7/bin/bootstrap.jar:/usr/local/tomcat7/bin/tomcat-juli.jarServer version: Apache Tomcat/7.0.54Server built: May 19 2014 10:26:15Server number: 7.0.54.0OS Name: LinuxOS Version: 3.10.0-327.el7.x86_64Architecture: amd64JVM Version: 1.7.0_65-b17JVM Vendor: Oracle Corporation启动tomcat[root@tomcat-1 ~]# /usr/local/tomcat7/bin/startup.sh Using CATALINA_BASE: /usr/local/tomcat7Using CATALINA_HOME: /usr/local/tomcat7Using CATALINA_TMPDIR: /usr/local/tomcat7/tempUsing JRE_HOME: /usr/local/javaUsing CLASSPATH: /usr/local/tomcat7/bin/bootstrap.jar:/usr/local/tomcat7/bin/tomcat-juli.jarTomcat started. |
Tomcat默认运行在8080端口,运行netstat命令查看8080端口监听的信息
|
1
2
3
|
[root@tomcat-1 ~]# netstat -anpt | grep javatcp6 0 0 :::8009 :::* LISTEN 42330/java tcp6 0 0 :::8080 :::* LISTEN 42330/java |
防火墙规则配置:
|
1
2
3
4
|
[root@tomcat-1 ~]# firewall-cmd --permanent --add-port=8080/tcpsuccess[root@tomcat-1 ~]# firewall-cmd --reloadsuccess |
按照相同方法在tomcat-2也安装
打开浏览器分别对tomcat-1和tomcat-2访问测试
如果想关闭tomcat则运行/usr/local/tomcat7/bin/shutdown.sh命令
好了,大家可以看到访成功。说明我们的tomcat安装完成,下面我们来修改配置文件
|
1
2
|
[root@tomcat-1 ~]# vim /usr/local/tomcat7/conf/server.xml |
设置默认虚拟主机,并增加jvmRoute
|
1
|
<Engine name="Catalina" defaultHost="localhost" jvmRoute="tomcat-1"> |
修改默认虚拟主机,并将网站文件路径指向/web/webapp1,在host段增加context段
|
1
2
3
4
|
<Host name="localhost" appBase="webapps"unpackWARs="true" autoDeploy="true"><Context docBase="/web/webapp1" path="" reloadable="true"/></Host> |
增加文档目录与测试文件
|
1
2
3
|
[root@tomcat-1 ~]# mkdir -p /web/webapp1[root@tomcat-1 ~]# cd /web/webapp1/[root@ tomcat-1 webapp1]# viindex.jsp |
index.jsp内容如下:
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
|
<%@page language="java" import="java.util.*" pageEncoding="UTF-8"%><html><head><title>tomcat-1</title></head><body><h1><font color="red">Session serviced by tomcat</font></h1><table aligh="center" border="1"><tr><td>Session ID</td><td><%=session.getId() %></td><% session.setAttribute("abc","abc");%></tr><tr><td>Created on</td><td><%= session.getCreationTime() %></td></tr></table></body><html> |
停止tomcat运行,检查配置文件并启动tomcat
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
|
[root@tomcat-1 ~]# shutdown.sh[root@tomcat-1 ~]# netstat -anpt | grep java[root@tomcat-1 ~]# catalina.shconfigtestUsing CATALINA_BASE: /usr/local/tomcat7Using CATALINA_HOME: /usr/local/tomcat7Using CATALINA_TMPDIR: /usr/local/tomcat7/tempUsing JRE_HOME: /usr/local/javaUsing CLASSPATH: /usr/local/tomcat7/bin/bootstrap.jar:/usr/local/tomcat7/bin/tomcat-juli.jarNov 16, 2016 1:04:05 AM org.apache.catalina.core.AprLifecycleListenerinitINFO: The APR based Apache Tomcat Native library which allows optimal performance in production environments was not found on the java.library.path: /usr/java/packages/lib/amd64:/usr/lib64:/lib64:/lib:/usr/libNov 16, 2016 1:04:05 AM org.apache.coyote.AbstractProtocolinitINFO: Initializing ProtocolHandler ["http-bio-8080"]Nov 16, 2016 1:04:05 AM org.apache.coyote.AbstractProtocolinitINFO: Initializing ProtocolHandler ["ajp-bio-8009"]Nov 16, 2016 1:04:05 AM org.apache.catalina.startup.Catalina loadINFO: Initialization processed in 534 ms[root@tomcat-1 ~]# startup.sh Using CATALINA_BASE: /usr/local/tomcat7Using CATALINA_HOME: /usr/local/tomcat7Using CATALINA_TMPDIR: /usr/local/tomcat7/tempUsing JRE_HOME: /usr/local/javaUsing CLASSPATH: /usr/local/tomcat7/bin/bootstrap.jar:/usr/local/tomcat7/bin/tomcat-juli.jarTomcat started.[root@tomcat-1 ~]# netstat -anpt | grep javatcp6 0 0 :::8009 :::* LISTEN 8180/java tcp6 0 0 :::8080 :::* LISTEN 8180/java |
Tomcat-2节点与tomcat-1节点配置基本类似,只是jvmRoute不同,另外为了区分由哪个节点提供访问,测试页标题也不同(生产环境两个tomcat服务器提供的网页内容是相同的)。其他的配置都相同。
用浏览器访问nginx主机,验证负载均衡
第一次访问的结果
第二次访问的结果
验证健康检查的方法可以关掉一台tomcat主机,用客户端浏览器测试访问。
从上面的结果能看出两次访问,nginx把访问请求分别分发给了后端的tomcat-1和tomcat-2,客户端的访问请求实现了负载均衡,但sessionid并一样。所以,到这里我们准备工作就全部完成了,下面我们来配置tomcat通过redis实现会话保持。
5、安装redis
下载redis源码,并进行相关操作,如下:
|
1
2
|
wget http://download.redis.io/releases/redis-3.2.3.tar.gz |
解压安装redis
|
1
|
[root@redis ~]# tar zxf redis-3.2.3.tar.gz |
解压完毕后,现在开始安装,如下:
|
1
2
|
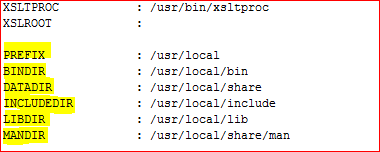
[root@redis ~]# cd redis-3.2.3/[root@redis redis-3.2.3]# make&& make install |
通过上图,我们可以很容易的看出,redis安装到/usr/local,/usr/local/bin,/usr/local/share,/usr/local/include,/usr/local/lib,/usr/local/share/man目录下。
然后再切换到utils目录下,执行redis初始化脚本install_server.sh,如下:
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
|
[root@redis redis-3.2.3]# cdutils/[root@redisutils]# ./install_server.shWelcome to the redis service installerThis script will help you easily set up a running redis server Please select the redis port for this instance: [6379] Selecting default: 6379Please select the redisconfig file name [/etc/redis/6379.conf] Selected default - /etc/redis/6379.confPlease select the redis log file name [/var/log/redis_6379.log]Selected default - /var/log/redis_6379.logPlease select the data directory for this instance [/var/lib/redis/6379] Selected default - /var/lib/redis/6379Please select the redis executable path [/usr/local/bin/redis-server] Selected config:Port : 6379Config file : /etc/redis/6379.confLog file : /var/log/redis_6379.logData dir : /var/lib/redis/6379Executable : /usr/local/bin/redis-serverCliExecutable : /usr/local/bin/redis-cliIs this ok? Then press ENTER to go on or Ctrl-C to abort.Copied /tmp/6379.conf => /etc/init.d/redis_6379Installing service...Successfully added to chkconfig!Successfully added to runlevels 345!Starting Redis server...Installation successful! |
通过上面的安装过程,我们可以看出redis初始化后redis配置文件为/etc/redis/6379.conf,日志文件为/var/log/redis_6379.log,数据文件dump.rdb存放到/var/lib/redis/6379目录下,启动脚本为/etc/init.d/redis_6379。
现在我们要使用systemd,所以在 /etc/systems/system 下创建一个单位文件名字为 redis_6379.service。
|
1
|
[root@redisutils]# vi /etc/systemd/system/redis_6379.service |
内容如下:
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
|
[Unit]Description=Redis on port 6379[Service]Type=forkingExecStart=/etc/init.d/redis_6379 startExecStop=/etc/init.d/redis_6379 stop[Install]WantedBy=multi-user.target |
注:这里Type=forking是后台运行的形式
启动redis
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
|
[root@redisutils]# systemctl daemon-reload [root@redisutils]# systemctl enable redis_6379.service[root@redisutils]# systemctl start redis_6379.service[root@redisutils]# systemctl status redis_6379.service ● redis_6379.service - Redis on port 6379 Loaded: loaded (/etc/systemd/system/redis_6379.service; enabled; vendor preset: disabled) Active: active (running) since Wed 2016-11-16 21:07:26 CST; 4min 25s ago Process: 7732 ExecStart=/etc/init.d/redis_6379 start (code=exited, status=0/SUCCESS) Main PID: 7734 (redis-server)CGroup: /system.slice/redis_6379.service└─7734 /usr/local/bin/redis-server 127.0.0.1:6379 Nov 16 21:07:26 redissystemd[1]: Starting Redis on port 6379...Nov 16 21:07:26 redis redis_6379[7732]: Starting Redis server...Nov 16 21:07:26 redissystemd[1]: Started Redis on port 6379.[root@redisutils]# netstat -anpt | grep 6379tcp 0 0 127.0.0.1:6379 0.0.0.0:* LISTEN 7734/redis-server 1 |
从显示结果可以看到redis默认监听的是127.0.0.1的6379端口
防火墙规则设置
|
1
2
3
4
|
[root@redisutils]# firewall-cmd --permanent --add-port=6379/tcpsuccess[root@redisutils]# firewall-cmd --reload success |
现在来查看redis版本使用redis-cli –version命令,如下
|
1
2
|
[root@redisutils]# redis-cli --versionredis-cli 3.2.3 |
通过显示结果,我们可以看到redis版本是3.2.3。
到此源码方式安装redis就介绍完毕。
redis安装完毕之后,我们再来配置redis
设置redis监听的地址,添加监听redis主机的ip
考虑到安全性,我们需要启用redis的密码验证功能requirepass参数
最终redis配置文件如下:
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
|
[root@redis ~]# grep -Ev '^#|^$' /etc/redis/6379.conf bind 127.0.0.1 192.168.31.106protected-mode yesport 6379tcp-backlog 511timeout 0tcp-keepalive 300daemonize yessupervised nopidfile /var/run/redis_6379.pidloglevel noticelogfile /var/log/redis_6379.logdatabases 16save 900 1save 300 10save 60 10000stop-writes-on-bgsave-error yesrdbcompression yesrdbchecksum yesdbfilenamedump.rdbdir /var/lib/redis/6379slave-serve-stale-data yesslave-read-only yesrepl-diskless-sync norepl-diskless-sync-delay 5repl-disable-tcp-nodelay noslave-priority 100requirepass pwd@123appendonly noappendfilename "appendonly.aof"appendfsynceverysecno-appendfsync-on-rewrite noauto-aof-rewrite-percentage 100auto-aof-rewrite-min-size 64mbaof-load-truncated yeslua-time-limit 5000slowlog-log-slower-than 10000slowlog-max-len 128latency-monitor-threshold 0notify-keyspace-events ""hash-max-ziplist-entries 512hash-max-ziplist-value 64list-max-ziplist-size -2list-compress-depth 0set-max-intset-entries 512zset-max-ziplist-entries 128zset-max-ziplist-value 64hll-sparse-max-bytes 3000activerehashing yesclient-output-buffer-limit normal 0 0 0client-output-buffer-limit slave 256mb 64mb 60client-output-buffer-limitpubsub 32mb 8mb 60hz 10aof-rewrite-incremental-fsync yes |
重新启动redis服务
|
1
2
3
|
[root@redis ~]# systemctl restart redis_6379.service[root@redis ~]# netstat -anpt | grep redistcp 0 0 192.168.31.106:6379 0.0.0.0:* LISTEN 8418/redis-server 1 |
redis配置文件配置完毕后,我们来启动redis并进行简单的操作。如下:
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
|
[root@redis ~]# redis-cli -h 192.168.31.106 -p 6379 -a pwd@123192.168.31.106:6379> keys *(empty list or set)192.168.31.106:6379> set name lisiOK192.168.31.106:6379> get name"lisi"192.168.31.106:6379> |
说明:
关于redis-cli -h 192.168.31.106 -p 6379 -a pwd@123的参数解释
这条命令是说要连接redis服务器,IP是192.168.31.106,端口是6379,密码是pwd@123。
keys *是查看redis所有的键值对。
set namelisi添加一个键值name,内容为lisi。
get name查看name这个键值的内容。
redis的命令使用暂时我们就介绍这么多
6、配置tomcat session redis同步
下载tomcat-redis-session-manager相应的jar包,主要有三个:
|
1
2
3
|
tomcat-redis-session-manage-tomcat7.jarjedis-2.5.2.jarcommons-pool2-2.2.jar |
下载完成后拷贝到$TOMCAT_HOME/lib中
|
1
|
[root@tomcat-1 ~]# cp tomcat-redis-session-manage-tomcat7.jar jedis-2.5.2.jar commons-pool2-2.2.jar /usr/local/tomcat7/lib/ |
修改tomcat的context.xml:
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
|
[root@tomcat-1 ~]# cat /usr/local/tomcat7/conf/context.xml <?xml version='1.0' encoding='utf-8'?><!-- Licensed to the Apache Software Foundation (ASF) under one or morecontributor license agreements. See the NOTICE file distributed withthis work for additional information regarding copyright ownership. The ASF licenses this file to You under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License"); you may not use this file except in compliance withthe License. You may obtain a copy of the License at http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0 Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, softwaredistributed under the License is distributed on an "AS IS" BASIS, WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied. See the License for the specific language governing permissions andlimitations under the License.--><!-- The contents of this file will be loaded for each web application --><Context><!-- Default set of monitored resources --><WatchedResource>WEB-INF/web.xml</WatchedResource><!-- Uncomment this to disable session persistence across Tomcat restarts --><!--<Manager pathname="" /> --><!-- Uncomment this to enable Comet connection tacking (provides eventson session expiration as well as webapp lifecycle) --><!--<Valve className="org.apache.catalina.valves.CometConnectionManagerValve" /> --><Valve className="com.orangefunction.tomcat.redissessions.RedisSessionHandlerValve" /><Manager className="com.orangefunction.tomcat.redissessions.RedisSessionManager"host="192.168.31.106"password="pwd@123"port="6379"database="0"maxInactiveInterval="60" /></Context> |
重启tomcat服务
说明:
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
|
maxInactiveInterval="60":session的失效时间[root@tomcat-1 ~]# shutdown.sh Using CATALINA_BASE: /usr/local/tomcat7Using CATALINA_HOME: /usr/local/tomcat7Using CATALINA_TMPDIR: /usr/local/tomcat7/tempUsing JRE_HOME: /usr/local/javaUsing CLASSPATH: /usr/local/tomcat7/bin/bootstrap.jar:/usr/local/tomcat7/bin/tomcat-juli.jar[root@tomcat-1 ~]# startup.sh Using CATALINA_BASE: /usr/local/tomcat7Using CATALINA_HOME: /usr/local/tomcat7Using CATALINA_TMPDIR: /usr/local/tomcat7/tempUsing JRE_HOME: /usr/local/javaUsing CLASSPATH: /usr/local/tomcat7/bin/bootstrap.jar:/usr/local/tomcat7/bin/tomcat-juli.jarTomcat started. |
tomcat-2执行和tomcat-1相同的操作
通过浏览器访问http://192.168.31.141/index.jsp测试页
刷新页面
可以看出,分别访问了不同的tomcat,但是得到的session却是相同的,说明达到了集群的目的。
注:从Tomcat6开始默认开启了Session持久化设置,测试时可以关闭本地Session持久化,其实也很简单,在Tomcat的conf目录下的context.xml文件中,取消注释下面那段配置即可:
修改前:
|
1
2
3
4
|
<!-- Uncomment this to disable session persistence across Tomcat restarts --><!--<Manager pathname="" />--> |
修改后:
|
1
2
|
<!-- Uncomment this to disable session persistence across Tomcat restarts --><Manager pathname="" /> |
重启tomcat服务
查看redis:
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
|
[root@redis ~]# redis-cli -h 192.168.31.106 -p 6379 -a pwd@123192.168.31.106:6379> keys *1) "6C3F950BE6413AD2E0EF00F930881224.tomcat-1.tomcat-1"2) "name"3) "7A6D5D4C5B1EA52C4E9EED1C5523FEB5.tomcat-2.tomcat-2"4) "32C35EEA064884F065E93CB00C690662.tomcat-1.tomcat-1" |
7、tomcat连接数据库
192.168.31.225作为mysql数据库服务器
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
|
[root@db ~]# mysql -uroot -p123.abcmysql> grant all on *.* to javauser@'192.168.31.%' identified by 'javapasswd';Query OK, 0 rows affected, 1 warning (0.02 sec) mysql> create database javatest;Query OK, 1 row affected (0.01 sec) mysql> use javatest;Database changed mysql> create table testdata(id int not null auto_increment primary key,foo varchar(25),bar int);Query OK, 0 rows affected (0.02 sec) |
插入些数据
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
|
mysql> insert into testdata(foo,bar) values ('hello','123456'),('ok','654321');Query OK, 2 rows affected (0.04 sec)Records: 2 Duplicates: 0 Warnings: 0mysql> select * from testdata;+----+-------+--------+| id | foo | bar |+----+-------+--------+| 1 | hello | 123456 || 2 | ok | 654321 |+----+-------+--------+2 rows in set (0.00 sec) |
mysql防火墙配置
配置tomcat服务器连接mysql数据库
下载mysql-connector-java-5.1.22-bin.jar并复制到$CATALINA_HOME/lib目录下
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
|
[root@tomcat-1 ~]# cp mysql-connector-java-5.1.22-bin.jar /usr/local/tomcat7/lib/[root@tomcat-1 ~]# ls /usr/local/tomcat7/lib/mysql-connector-java-5.1.22-bin.jar /usr/local/tomcat7/lib/mysql-connector-java-5.1.22-bin.jar context configurationconfigure the JNDI datasource in tomcat by adding a declaration for your resource to yourcontext[root@tomcat-1 ~]# vi /usr/local/tomcat7/conf/context.xml在<Context>中添加如下内容:<Resource name="jdbc/TestDB" auth="Container" type="javax.sql.DataSource"maxActive="100" maxIdle="30" maxWait="10000"username="javauser" password="javapass" driverClassName="com.mysql.jdbc.Driver"url="jdbc:mysql://192.168.31.225:3306/javatest"/> |
保存修改并退出
|
1
2
3
|
web.xml configuration[root@tomcat-1 ~]# mkdir /web/webapp1/WEB-INF[root@tomcat-1 ~]# vi /web/webapp1/WEB-INF/web.xml |
添加内容如下:
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
|
<web-app xmlns="http://java.sun.com/xml/ns/j2ee"xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"xsi:schemaLocation="http://java.sun.com/xml/ns/j2eehttp://java.sun.com/xml/ns/j2ee/web-app_2_4.xsd"version="2.4"><description>MySQL Test App</description><resource-ref><description>DB Connection</description><res-ref-name>jdbc/TestDB</res-ref-name><res-type>javax.sql.DataSource</res-type><res-auth>Container</res-auth></resource-ref></web-app> |
保存修改并退出,重启tomcat服务
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
|
[root@tomcat-1 ~]# shutdown.sh Using CATALINA_BASE: /usr/local/tomcat7Using CATALINA_HOME: /usr/local/tomcat7Using CATALINA_TMPDIR: /usr/local/tomcat7/tempUsing JRE_HOME: /usr/local/javaUsing CLASSPATH: /usr/local/tomcat7/bin/bootstrap.jar:/usr/local/tomcat7/bin/tomcat-juli.jar[root@tomcat-1 ~]# startup.sh Using CATALINA_BASE: /usr/local/tomcat7Using CATALINA_HOME: /usr/local/tomcat7Using CATALINA_TMPDIR: /usr/local/tomcat7/tempUsing JRE_HOME: /usr/local/javaUsing CLASSPATH: /usr/local/tomcat7/bin/bootstrap.jar:/usr/local/tomcat7/bin/tomcat-juli.jarTomcat started.tomcat-2进行和tomcat-1相同的操用Test codeNow create a simple test.jsp page,内容如下:[root@tomcat-2 ~]# vi /web/webapp1/test.jsp[root@tomcat-2 webapp1]# cattest.jsp<%@ page language="java" import="java.sql.*" pageEncoding="GB2312"%><html><head><title>MySQL</title></head><body>connect MySQL<br><%String driverClass="com.mysql.jdbc.Driver";String url="jdbc:mysql://192.168.31.225:3306/javatest";String username = "javauser"; String password = "javapasswd"; Class.forName(driverClass); Connection conn=DriverManager.getConnection(url, username, password); Statement stmt=conn.createStatement();ResultSetrs = stmt.executeQuery("select * from testdata"); while(rs.next()){out.println("<br>foo:"+rs.getString(2)+"bar:"+rs.getString(3));}rs.close();stmt.close();conn.close();%></body></html> |
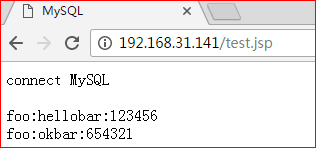
通过浏览器访问http://192.168.31.141/test.jsp测试页
注:
以上配置可以参考tomcat docs
![XZGG`3(]IJ7)PARZMSUO4FH.png wKiom1jXUdKjKxhMAAASRhD8deE337.png-wh_50](https://s5.51cto.com/wyfs02/M02/8F/33/wKiom1jXUdKjKxhMAAASRhD8deE337.png-wh_500x0-wm_3-wmp_4-s_2989605117.png)
![4BJLA`2CNU)YY~9]SU}UQKQ.png wKioL1jXUd7gVRnoAAASX8f_EkE880.png-wh_50](https://s3.51cto.com/wyfs02/M02/8F/31/wKioL1jXUd7gVRnoAAASX8f_EkE880.png-wh_500x0-wm_3-wmp_4-s_3447034394.png)
![]$_~FS2`(2RA1%X0{YVNS77.png wKiom1jXUgnD8_q-AAALkOr0KKQ166.png-wh_50](https://s4.51cto.com/wyfs02/M01/8F/33/wKiom1jXUgnD8_q-AAALkOr0KKQ166.png-wh_500x0-wm_3-wmp_4-s_96000611.png)
![OKLX%HF4B]9X{]{3%(7]4S8.png wKiom1jXUoOD5GjCAAAn_mMzZ5E351.png-wh_50](https://s2.51cto.com/wyfs02/M00/8F/33/wKiom1jXUoOD5GjCAAAn_mMzZ5E351.png-wh_500x0-wm_3-wmp_4-s_433742508.png)
![}JLU]RKBB3WPX9`H~XZF})J.png wKioL1jXUo-zQJfHAAAnXzLwnbU700.png-wh_50](https://s5.51cto.com/wyfs02/M00/8F/31/wKioL1jXUo-zQJfHAAAnXzLwnbU700.png-wh_500x0-wm_3-wmp_4-s_1514498012.png)