java -version :jdk 1.8.0_191
构造
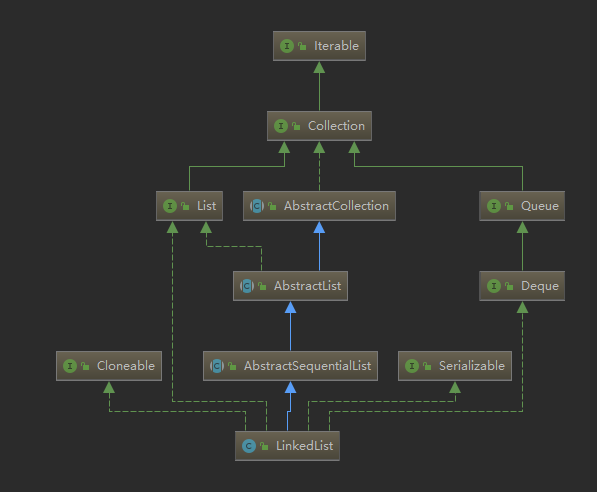
类内参数,方法
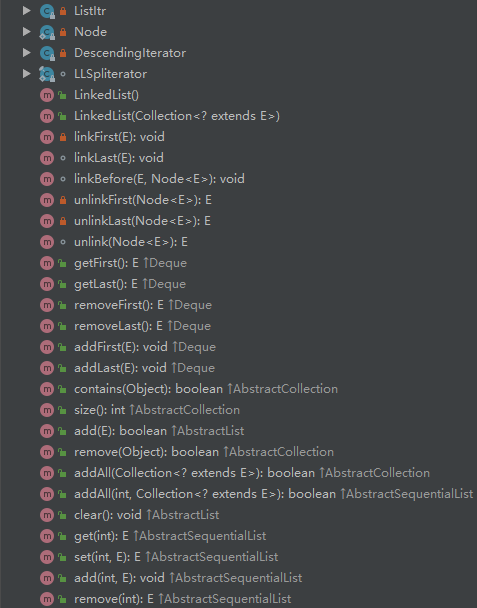
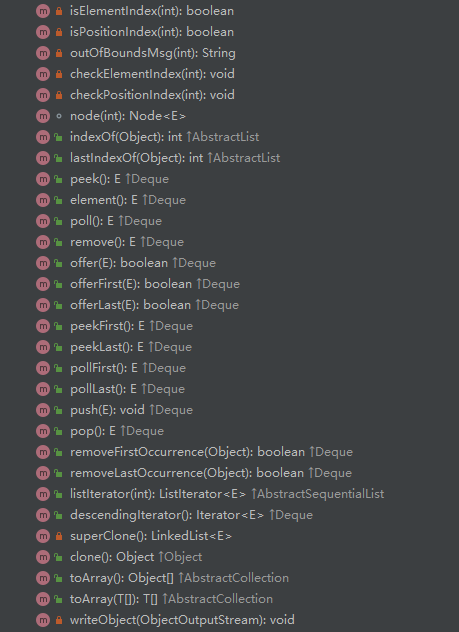
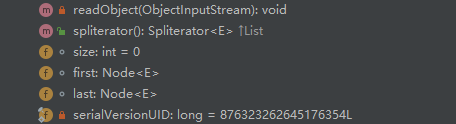
实现
基于双向链表实现。
插入时间复杂度 O(1)
查找时间复杂度 O(n)
删除时间复杂度 O(1)
修改时间复杂度 O(n)
链表不存在扩容的问题。
静态参数
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
/**
* Pointer to first node.
* Invariant: (first == null && last == null) ||
* (first.prev == null && first.item != null)
*/
transient Node<E> first;
链表的第一个,不能被序列化
/**
* Pointer to last node.
* Invariant: (first == null && last == null) ||
* (last.next == null && last.item != null)
*/
transient Node<E> last;
链表的最后一个,不能被序列化
节点参数
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
private static class Node<E> {
//数据
E item;
//下一个节点
Node<E> next;
//上一个节点
Node<E> prev;
Node(Node<E> prev, E element, Node<E> next) {
this.item = element;
this.next = next;
this.prev = prev;
}
}
add方法
public boolean add(E e)
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
/**
* Appends the specified element to the end of this list.
*
* <p>This method is equivalent to {@link #addLast}.
*
* @param e element to be appended to this list
* @return {@code true} (as specified by {@link Collection#add})
*/
public boolean add(E e) {
//插入到链表的尾端
linkLast(e);
return true;
}
/**
* Links e as last element.
*/
void linkLast(E e) {
final Node<E> l = last;
final Node<E> newNode = new Node<>(l, e, null);
last = newNode;
if (l == null)
first = newNode;
else
l.next = newNode;
size++;
modCount++;
}
public void add(int index, E element)
将 e 添加到指定位置
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
/**
* Inserts the specified element at the specified position in this list.
* Shifts the element currently at that position (if any) and any
* subsequent elements to the right (adds one to their indices).
*
* @param index index at which the specified element is to be inserted
* @param element element to be inserted
* @throws IndexOutOfBoundsException {@inheritDoc}
*/
public void add(int index, E element) {
//先判断是否会越界
checkPositionIndex(index);
//刚好是最后一个
if (index == size)
linkLast(element);
else
linkBefore(element, node(index));
}
get方法
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
/**
* Returns the element at the specified position in this list.
*
* @param index index of the element to return
* @return the element at the specified position in this list
* @throws IndexOutOfBoundsException {@inheritDoc}
*/
public E get(int index) {
checkElementIndex(index);
return node(index).item;
}
for 循环遍历下标,找到对应的节点,根据下标的大小判断是从头遍历还是从尾部遍历
/**
* Returns the (non-null) Node at the specified element index.
*/
Node<E> node(int index) {
// assert isEle 大专栏 理解 LinkedListmentIndex(index);
从头遍历
if (index < (size >> 1)) {
Node<E> x = first;
for (int i = 0; i < index; i++)
x = x.next;
return x;
} else {
从尾部遍历
Node<E> x = last;
for (int i = size - 1; i > index; i--)
x = x.prev;
return x;
}
}
remove方法
循环遍历找到对应的节点,然后将上一个节点的next指向该节点的下一个节点。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
/**
* Removes the first occurrence of the specified element from this list,
* if it is present. If this list does not contain the element, it is
* unchanged. More formally, removes the element with the lowest index
* {@code i} such that
* <tt>(o==null ? get(i)==null : o.equals(get(i)))</tt>
* (if such an element exists). Returns {@code true} if this list
* contained the specified element (or equivalently, if this list
* changed as a result of the call).
*
* @param o element to be removed from this list, if present
* @return {@code true} if this list contained the specified element
*/
public boolean remove(Object o) {
if (o == null) {
for (Node<E> x = first; x != null; x = x.next) {
if (x.item == null) {
unlink(x);
return true;
}
}
} else {
for (Node<E> x = first; x != null; x = x.next) {
if (o.equals(x.item)) {
unlink(x);
return true;
}
}
}
return false;
}
序列化
LinkedList 和 ArrayList 一样,不能通过一般方式的序列化
序列化writeObject(java.io.ObjectOutputStream s)
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
/**
* Saves the state of this {@code LinkedList} instance to a stream
* (that is, serializes it).
*
* @serialData The size of the list (the number of elements it
* contains) is emitted (int), followed by all of its
* elements (each an Object) in the proper order.
*/
private void writeObject(java.io.ObjectOutputStream s)
throws java.io.IOException {
// Write out any hidden serialization magic
s.defaultWriteObject();
// Write out size
s.writeInt(size);
// Write out all elements in the proper order.
for (Node<E> x = first; x != null; x = x.next)
s.writeObject(x.item);
}
反序列化readObject(java.io.ObjectInputStream s)
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
/**
* Reconstitutes this {@code LinkedList} instance from a stream
* (that is, deserializes it).
*/
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
private void readObject(java.io.ObjectInputStream s)
throws java.io.IOException, ClassNotFoundException {
// Read in any hidden serialization magic
s.defaultReadObject();
// Read in size
int size = s.readInt();
// Read in all elements in the proper order.
for (int i = 0; i < size; i++)
linkLast((E)s.readObject());
}
其他
LinkedList 和 ArrayList 一样,都不是线程安全的数据结构。