单表查询语法:
SELECT 字段1,字段2... FROM 表名
WHERE 条件
GROUP BY field
HAVING 筛选
ORDER BY field
LIMIT 限制条数
关键字的执行顺序:
这个是非常重要的,不了解以后会有很多坑。
1.form 找到表:from 2.where 拿着where指定的约束条件,去文件/表中取出一条条记录 3.group by 将取出的一条条记录进行分组group by,如果没有group by,则整体作为一组 4.having 将分组的结果进行having过滤 5.select 执行select 6.distinct 去重 7.order by 将结果按条件排序:order by 8.limit 限制结果的显示条数
准备数据源
建立一个名为student的学生表,下面是他们的字段名及字段类型表。
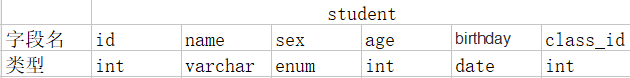

create table student( id int not null unique auto_increment, name varchar(20) not null, sex enum('male','female') not null default 'male', age int(3) unsigned not null default 28, birthday date not null, class_id int );
效果图:


insert into student(name,sex,age,birthday,class_id) values ('成龙','male',48,'20101111',1), ('歪歪','female',48,'20150311',2), ('丫丫','female',38,'20101101',2), ('丁丁','female',18,'20110312',2), ('星星','female',18,'20160513',2), ('格格','female',28,'20170127',2), ('张野','male',28,'20160311',3), ('程咬金','male',18,'19970312',3), ('程咬银','female',18,'20130311',3), ('程咬铜','male',18,'20150411',3), ('程咬铁','female',18,'20140512',3);
效果图:
普通查询
# 简单查询 select * from student; # 查询表中所有记录 select name, age from student; # 查询表中的name和age字段 # 去重查询 select distinct age from student; # 去重查询表中所有人的年龄 # 查询加四则运算 select name, age-1 from student; # 这样查询出来的为两个字段,字段名分别为name和age-1,age-1字段中值为原始年龄-1 select name, age-1 as 年龄减一 from student; # 查询同上,默认的age-1字段名改成了年龄减一。 # 定义显示格式 # ----------concat()函数用于连接字符串 select concat("姓名:",name," 年龄",age+1)as 显示 from student; # ----------concat_ws()第一个参数为分隔符 select concat_ws("__",name, age) as 显示 from student; # ----------结合case语句 select ( case when name="成龙" then name when name = "丫丫" then concat(name,"_美女") else concat(name,"_凡人") end )as new_name from student;
where约束查询
where语句中可以使用:
- 比较运算符:>,<,>=,<=,<>,!=
- between 80 and 100,值在80到100之间
- is null,判断某个字段是否为NUll不能用等号,要用is。空字符串并不是null。
- in(10,20,30),值是10或者20或者30
- like "张%",模糊查询,找"张"开头的。
- %:表示任意0个或多个字符。可匹配任意类型和长度的字符
- _:表示任意单个字符
- [ ]:表示括号内所列字符中的一个(类似正则表达式)。
- [^ ]:表示不在括号所列之内的单个字符。
# 单条件查询 select name from student where age>20; # 多条件查询 select name from student where age>20 and sex="male"; # 关键字between .. and .. select name from student where age between 20 and 40; # 关键字is null select class_id from student where class_id is null; select class_id from student where class_id is not null; # 关键字in select name from student where age in (18, 20, 38); select name from student where age not in (18, 20, 38); # 模糊查询 select * from student where name like "成%";
group by 分组查询
首先要明确一点,分组是在where之后进行的。
分组是按照某个相同的字段进行归类。比如:班级,性别。
注意:
当我们进行分组之后,只能查询分组字段,想要获取组内其他相关信息,需要借助函数。
# 当我们进行分组之后,只能查询分组字段,想要获取组内其他相关信息,需要借助函数。 # GROUP BY关键字和GROUP_CONCAT()函数一起使用 select class_id, group_concat(name)as 组内名字 from student group by class_id; # GROUP BY与聚合函数一起使用 select class_id, group_concat(name)as 组内名字, count(*)as 组人数 from student group by class_id;
常用的聚合函数:
COUNT(),MAX(),MIN(), AVG(),SUM()
having过滤
#!!!执行优先级从高到低:where > group by > having #1. Where 发生在分组group by之前,因而Where中可以有任意字段,但是绝对不能使用聚合函数。 #2. Having发生在分组group by之后,因而Having中可以使用分组的字段,无法直接取到其他字段,可以使用聚合函数
order by 排序
# 按单列排序 select * from student order by age; # 默认升序 select * from student order by age ASC; # 升序排列 select * from student order by age DESC; # 降序排列 # 按多列排序 先按照age升序排序,如果年纪相同,则按照名字降序排序 select * from student order by age, name desc;
注:因为ordery by 在分组之后,所以也可以用分组的聚合函数。
limit限制查询的记录数
select * from student LIMIT 3; #默认初始位置为0 select * from student LIMIT 0,5; #从第0开始,即先查询出第一条,然后包含这一条在内往后查5条 select * from student LIMIT 5,5; #从第5开始,即先查询出第6条,然后包含这一条在内往后查5条
使用正则表达式查询
select * from student regexp "^成";
