T1 补票 Ticket
没什么好说的,不讲了
T2 删数字 Number
很后悔的是其实考场上不仅想出了正解的方程,甚至连优化都想到了,却因为码力不足只打了(O(n^2))暴力,甚至还因为细节挂成了(40 pts)
以后还是应该多写一下码农题
规定一下,下面的(j)没有特殊说明,取值范围默认在(1, i - 1)
考虑什么情况是合法的,首先最后对答案有贡献的元素组成的序列一定是严格上升的,即(a_i > a_j)
然后考虑还有没有别的限制呢
放一个图
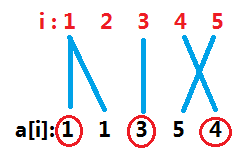
看到我们的对答案有贡献的序列和其对应的坐标的连边一定是一个越来越倾斜(并且逆时针旋转)的过程,思考一下为什么,发现如果不满足前面那个条件的话实际上是没法通过题目的变换方法得到最终对应的序列
举个例子
1 2 3 5 2
其中的3和5并不能同时对答案作出贡献
所以又有了一个限制条件(i - a[i] > = j - a[j])
看一下两个条件$$a_i > a_j$$ $$i - a[i] > = j - a[j]$$
发现是一个二维偏序
考虑一维一维的处理,先按第一个条件排一下序,然后在排序后的序列上处理后面那个条件,树状数组维护一下
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
#define N (100000 + 10)
#define lowbit(x) (x & (-x))
using namespace std;
inline int read() {
int cnt = 0, f = 1; char c = getchar();
while (!isdigit(c)) {if (c == '-') f = -f; c = getchar();}
while (isdigit(c)) {cnt = (cnt << 3) + (cnt << 1) + (c ^ 48); c = getchar();}
return cnt * f;
}
int n, tot, w, ans, gmax, BIT[N];
void modify(int x, int g) {
for (; x <= gmax; x += lowbit(x)) BIT[x] = max(BIT[x], g);
}
int query(int x) {
int ans = 0;
for (; x; x -= lowbit(x)) ans = max(ans, BIT[x]);
return ans;
}
struct node {
int d, s; //d: i - a[i].s, s: from input
}a[N];
bool cmp(node a, node b) {
return a.d == b.d ? a.s < b.s : a.d < b.d;
}
int main() {
n = read();
for (register int i = 1; i <= n; ++i) {
w = read();
if (w > i) continue;
a[++tot].s = w, a[tot].d = i - w;
gmax = max(gmax, w);
}
sort (a + 1, a + tot + 1, cmp);
for (register int i = 1; i <= tot; ++i) {
int d = query(a[i].s - 1) + 1;
modify(a[i].s, d);
ans = max(ans, d);
} printf("%d
", ans);
return 0;
}
T3 滑冰 Shortest
感觉题解很好理解,但就是想不到
先说一下算法流程
分别按(x)排一个序,(y)排一个序,然后相邻的连上边,跑最短路即可
说一下为什么是正确的
首先(min(|x[i] - x[j]|, |y[i] - y[j]|))这个条件是完全不用考虑的,因为最短路本身就是找(min)的过程,就算两条边都连上也可以得到正确答案
考虑(O(n^2))暴力,即每个点往其他所有点连边,然后这样显然跑不动
怎么优化呢
上面那个算法很巧妙的一点是,因为我们排过序了,所以两个点之间的连边一定已经是不可以分拆的最小单位了,并且用这些最小单位边一定可以组成其他的边,相当于去除了暴力连边中的重复信息,于是复杂度优化为(O(nlog(n)))
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
#define N (1001000 + 10)
using namespace std;
inline int read() {
int cnt = 0, f = 1; char c = getchar();
while (!isdigit(c)) {if (c == '-') f = -f; c = getchar();}
while (isdigit(c)) {cnt = (cnt << 3) + (cnt << 1) + (c ^ 48); c = getchar();}
return cnt * f;
}
int n, z;
struct node {
int x, y;
int pos;
}a[N];
bool cmp(node a, node b) {
return a.x == b.x ? a.y < b.y : a.x < b.x;
}
bool cmp2(node a, node b) {
return a.y == b.y ? a.x < b.x : a.y < b.y;
}
int first[N], nxt[N << 1], to[N << 1], w[N << 1], tot;
long long d[N];
bool vis[N];
void add(int x, int y, int z) {nxt[++tot] = first[x], first[x] = tot, to[tot] = y, w[tot] = z;}
priority_queue < pair<int, int> > q;
void dijkstra() {
memset(d, 0x3f, sizeof d);
memset(vis, 0, sizeof vis);
d[1] = 0;
q.push(make_pair(-d[1], 1));
while (!q.empty()) {
int x = q.top().second; q.pop();
if (vis[x]) continue;
vis[x] = 1;
for (register int i = first[x]; i; i = nxt[i]) {
int v = to[i], z = w[i];
if (d[v] > d[x] + z) {
d[v] = d[x] + z;
q.push(make_pair(-d[v], v));
}
}
}
}
int main() {
// freopen("shortest.in", "r", stdin);
// freopen("shortest.out", "w", stdout);
n = read();
for (register int i = 1; i <= n; ++i) a[i].x = read(), a[i].y = read(), a[i].pos = i;
sort (a + 1, a + n + 1, cmp);
for (register int i = 1; i < n; ++i) {
int z = a[i + 1].x - a[i].x;
add(a[i].pos, a[i + 1].pos, z), add(a[i + 1].pos, a[i].pos, z);
}
sort (a + 1, a + n + 1, cmp2);
for (register int i = 1; i < n; ++i) {
int z = a[i + 1].y - a[i].y;
// cout<<z<<endl;
add(a[i].pos, a[i + 1].pos, z), add(a[i + 1].pos, a[i].pos, z);
}
dijkstra();
printf("%lld", d[n]);
return 0;
}