地形在三维中的地位是毋庸置疑的,最近在看《Focus On 3D Terrain Programming》这本书,做一下简单的笔记.
本书的第二章主要解决了三个问题:
- 什么是高度图?怎么创建高度图?如何载入高度图?
- 如何使用直接的方法渲染地形?(how to render terrain using a brute force algorithm?)
- 如何使用fault formation与mid displacement算法动态生成高度图,然后生成地形。
高度图就是一个灰度图片,每一个像素代表了一个高度。通常情况下黑色的像素点代表了地形低洼的地带,白色的像素点代表了地形高的像素点。读入高度图后可以通过OpenGL直接将绘制出来。
地形生成算法(Fractal Terrain Generation):
1:Fault Formation
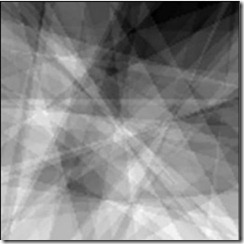
此算法的主要思想:对于想要生成的m*n维高度图,在此高度图上随机取一条直线,直线将高度图一份为二,然后在其中的一边(被直线分成的两部分中的一部分)加上一个随机的高度。此算法过程中,每次迭代都需要一个平滑滤波对其进行做一定的修改,不然得出的高度图会非常的尖锐。如图所示:
在生成fault formation的时候,进行改变的一边是用过向量的叉乘得来的,在确定直线的两点A(iRandX1, iRandX1)、B(iRandX2, iRandX2)。通过这两点可以确定直线的方向向量,然后再在高度图上另取一点C(x, z),此时通过向量AC叉乘向量AB,通过叉乘法则(右手法则)就可以确定直线的一边,然后对其进行变换。变换代码如下:
1: for(i = 0; i < m_iSize * m_iSize; i++)2: fTempBuffer[i] = 0;3:4: for(iCurrentIteration = 0; iCurrentIteration < iIterations; iCurrentIteration++)5: {6: // calculate the height range (linear interpolation from iMaxDelta to iMinDelta7: // for this fault-pass8: iHeight = iMaxDelta - ((iMaxDelta - iMinDelta) * iCurrentIteration) / iIterations;9:10: // pick two points at random from the entire height map11: iRandX1 = rand() % m_iSize;12: iRandZ1 = rand() % m_iSize;13:14: // check to make sure that the points are not the same15: do16: {17: iRandX2 = rand() % m_iSize;18: iRandZ2 = rand() % m_iSize;19: }while(iRandX1 == iRandX2 && iRandZ2 == iRandZ1);20:21: // iDirX1, iDirZ1 is a vector going the same direction as the line22: iDirX1 = iRandX2 - iRandX1;23: iDirZ1 = iRandZ2 - iRandZ1;24:25: for(z = 0; z < m_iSize; z++)26: {27: for(x = 0; x < m_iSize; x++)28: {29: // iDirX2, iDirZ2 is a vector from iRandX1, iRandZ1 to the current point30: iDirX2 = x - iRandX1;31: iDirZ2 = z - iRandZ1;32:33: // if the result of(iDirX2 * iDirZ1 - iDirX1 * iDirZ2) is "up"34: // then raise this point by iHeight35: if(iDirX2 * iDirZ1 - iDirX1 * iDirZ2 > 0)36: fTempBuffer[(z*m_iSize) + x] += (float)iHeight;37:38: }39: }
经过这些变换之后,得到的高度图并不能得到非常平滑的地形,因此需要一个滤波变换(erosion filter)本文中使用的是FIR滤波器,在对高度图进行处理的时候分别从左到右、从右到左、从上到下、从下到上进行处理。最后得出高度图,如图所示:
2:Midpoint Displacement(plasma fractal/diamond-square)
优点:对于fault formation来说生成小地形(小的山丘等)完全可以胜任,但是如果地形如果有很多山脉,fault DIsplacement就有点儿不行了,此时就需要使用midpoint displacement算法了。
缺点:只能生成一个正方形的高度图,并且维度为2的n次方。
中点偏移算法(我自己翻译的,如有不对还望告知)算法思想非常简单,对于一维的(一条直线)而言取其中点,然后对重点进行一定范围的位移,这个范围是[-fHeight/2, fHeight/2],其中fHeight=length。经过一次迭代后,此时变换的高度要乘以一个缩放系数,2-Roughness,其中Roughness是地形的粗糙度。这样变换是为了能够在接下来的迭代过程中能够得到非常好的地形。
对于二维情况,中点是由其上下左右四个点共同决定的,废话少说,代码说明问题:
1:2: // being the displacement process3: while(iRectSize > 0)4: {5: for(i = 0; i < m_iSize; i += iRectSize)6: {7: for(j = 0; j < m_iSize; j += iRectSize)8: {9: ni = (i + iRectSize) % m_iSize;10: nj = (j + iRectSize) % m_iSize;11:12: mi = (i + iRectSize / 2 );13: mj = ( j + iRectSize / 2);14:15: fTempBuffer[mi + mj * m_iSize] = (float)((fTempBuffer[i + j*m_iSize] + fTempBuffer[ni + j*m_iSize]16: + fTempBuffer[i + nj*m_iSize] + fTempBuffer[ni + nj*m_iSize]) / 4 + RangedRandom( -fHeight/2, fHeight/2 ));17: }18: }19:20:21: for(i = 0; i < m_iSize; i += iRectSize)22: {23: for(j = 0; j < m_iSize; j += iRectSize)24: {25: ni = (i + iRectSize) % m_iSize;26: nj = (j + iRectSize) % m_iSize;27:28: mi = (i + iRectSize / 2);29: mj = (j + iRectSize / 2);30:31: pmi = (i - iRectSize / 2 + m_iSize) % m_iSize;32: pmj = (j - iRectSize / 2 + m_iSize) % m_iSize;33:34: //Calculate the square value for the top side of the rectangle35: fTempBuffer[mi+j*m_iSize]= ( float )( ( fTempBuffer[i+j*m_iSize] +36: fTempBuffer[ni+j*m_iSize] +37: fTempBuffer[mi+pmj*m_iSize] +38: fTempBuffer[mi+mj*m_iSize] )/4+39: RangedRandom( -fHeight/2, fHeight/2 ) );40:41: //Calculate the square value for the left side of the rectangle42: fTempBuffer[i+mj*m_iSize]= ( float )( ( fTempBuffer[i+j*m_iSize] +43: fTempBuffer[i+nj*m_iSize] +44: fTempBuffer[pmi+mj*m_iSize] +45: fTempBuffer[mi+mj*m_iSize] )/4+46: RangedRandom( -fHeight/2, fHeight/2 ) );47: }48: }49:50: // reduce the rectangle size by two prepare for the next51: // displacement stage52: iRectSize /= 2;53:54: // reduce the height by height reducer55: fHeight *= fHeightReducer;56: }57:58: // normalize the terrain for our purposes59: NormalizeTerrain(fTempBuffer);60:61: // transfer the terrain into our class's unsigned char height buffer62: for(z = 0; z < m_iSize; z++)63: {64: for(x = 0; x < m_iSize; x ++)65: SetHeightAtPoint((unsigned char) fTempBuffer[(z * m_iSize) + x], x, z);66: }运行结果如下:
两种方法,各有所长。
![$Q}])JX7_OCZU6}VGNCQRSB $Q}])JX7_OCZU6}VGNCQRSB](https://images.cnblogs.com/cnblogs_com/cg_ghost/201204/201204052247437023.jpg)
![O]H_%L7WQU[UY639}5_JR6O O]H_%L7WQU[UY639}5_JR6O](https://images.cnblogs.com/cnblogs_com/cg_ghost/201204/201204052248068201.jpg)