Background
Valhalla于2014年开始,项目的目标是提供一个flattened type,也叫inline class(代码里面用得多,关键字也叫这个), value type(编程语言共享的名字,比如很多语言都有继承这个概念,但是具体表现形式不一样),primitive class(口号是Codes like a class, works like an int,突出这些类的行为和primitive type类似)。什么是flatten呢,比如一个Point[]现在长这样:
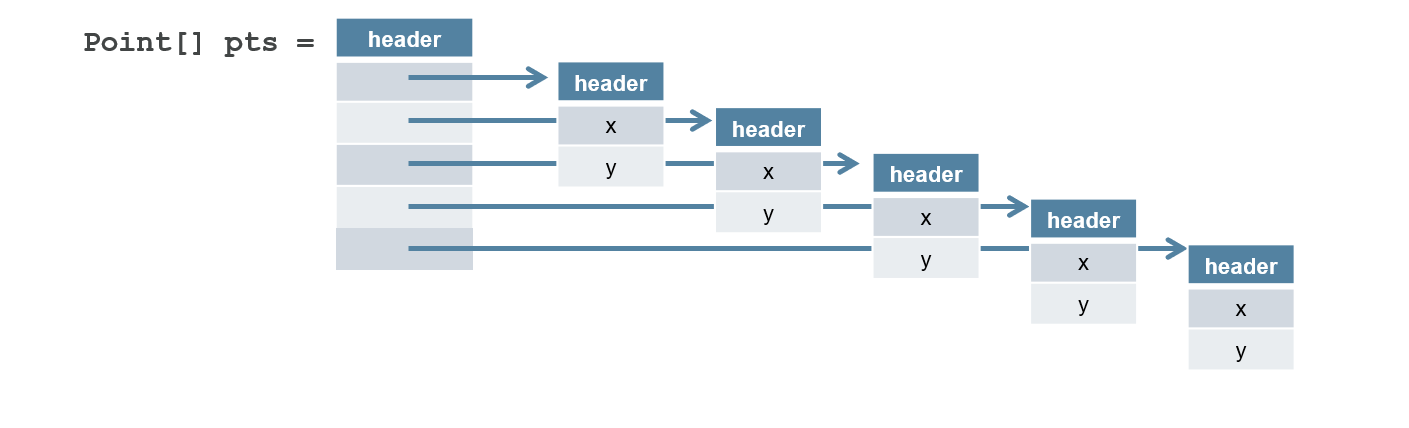
flatten之后

在JVM出现的20实际90年代,算术运算和内存内存读取的成本差距不大,但是现在有了memory cache,指令级并行,cache miss的成本相当于1000次算术运输了,以前对象的间接布局与现代的处理器不太匹配了。
Valhalla的keyword变化非常迅速,极其不稳定,目前已知已经变过:__ByValue, value, inline, primitive
//TODO: 如果Point{}里面有Object,他的header会去掉吗?Point会变成flatten吗?对Point[3].hashCode()怎么办?
新字节码
defaultvalue
public primitive class Point{
int x;
int y;
}
Point p = Point.default;
Point p2 = new Point(0,0);
Point.default对象其实是Point.class上隐含的一个字段".default"
class InstanceKlass: public Klass{
...
int default_value_offset() {
int offset = *((int*)adr_default_value_offset());
assert(offset != 0, "must not be called if not initialized");
return offset;
}
void set_default_value(oop val) {
java_mirror()->obj_field_put(default_value_offset(), val);
}
oop default_value() {
oop val = java_mirror()->obj_field_acquire(default_value_offset());
assert(oopDesc::is_oop(val), "Sanity check");
assert(val->is_inline_type(), "Sanity check");
assert(val->klass() == this, "sanity check");
return val;
}
};
withfield
对primitive的状态修改只能通过withfield字节码进行。
__WithField只能在inline类内部使用,而且修改的对象仅限于当前类,比如
public inline class Point {
public int x;
public int y;
public static Point makePoint(int x, int y) {
Point p = new Point(x, y);
p = __WithField(p.x,0);
return p;
}
Point() {
this.x = 100000303;
this.y = 202342423;
}
}
是可以的,但是其他地方就不行:
public inline class Test{
static Point p = Point.makePoint(17,5);
static void test1(Point px){
Point p = Point.default;
p = __WithField(p.x,4634); // 编译错误
b = x;
...
}
只是个人观察是这样,实际可能还有更通用更准确的定义。
Q-Type
对象布局
primitive类型的Line,里面包含两个primitive类型的Point
public primitive class Point {
public long x;
public long y;
....
}
public final primitive class Line {
public Point p1;
public Point p2;
....
}
用PrintInlineLayout可以输出它的layout
// -XX:-UseCompressedOops -XX:-UseCompressedClassPointer
Layout of class Line
Instance fields:
@0 16/- RESERVED
@16 "p1" QPoint; 16/8 INLINED
@32 "p2" QPoint; 16/8 INLINED
Static fields:
@0 192/- RESERVED
@192 ".default" Ljava/lang/Object; 8/8 REGULAR
Instance size = 48 bytes
First field offset = 16
Alignment = 8 bytes
Exact size = 32 bytes
//-XX:-UseCompressedOops -XX:+UseCompressedClassPointer
Layout of class Line
Instance fields:
@0 12/- RESERVED
@12 4/1 PADDING
@16 "p1" QPoint; 16/8 INLINED
@32 "p2" QPoint; 16/8 INLINED
Static fields:
@0 184/- RESERVED
@184 ".default" Ljava/lang/Object; 8/8 REGULAR
Instance size = 48 bytes
First field offset = 16
Alignment = 8 bytes
Exact size = 32 bytes
//-XX:+UseCompressedOops -XX:+UseCompressedClassPointer (default)
Layout of class Line
Instance fields:
@0 12/- RESERVED
@12 4/1 PADDING
@16 "p1" QPoint; 16/8 INLINED
@32 "p2" QPoint; 16/8 INLINED
Static fields:
@0 112/- RESERVED
@112 ".default" Ljava/lang/Object; 4/4 REGULAR
Instance size = 48 bytes
First field offset = 16
Alignment = 8 bytes
Exact size = 32 bytes
primtive type还有一个特性是它会对field进行排序,让内存占用最小,因为primitive type的设计意图就是让它能嵌入进其他容器里面,所以越小越好。考虑下面的类
public final primitive class Line {
public Point p1;
public char cc;
public Point p2;
...
}
vm会将cc放到最后面,而不是按照program order放中间:
Layout of class Line
Instance fields:
@0 12/- RESERVED
@12 4/1 PADDING
@16 "p1" QPoint; 16/8 INLINED
@32 "p2" QPoint; 16/8 INLINED
@48 "cc" C 2/2 REGULAR
Static fields:
@0 112/- RESERVED
@112 ".default" Ljava/lang/Object; 4/4 REGULAR
Instance size = 56 bytes
First field offset = 16
Alignment = 8 bytes
Exact size = 34 bytes
排序策略是:1. 先放到的primitive field 2.然后oop field 3.最后小的primitive field
Type.ref
XX.ref可以一句话概括为:nullable的primitive type
默认的值类型都是不能为null的,比如:
primitive class Point{
int x;
int y;
}
Point[] p = new Point[5]
p.x += p.y;
虽然只分配了p数组,里面没有new Point(),但是p.x还是能正常工作,因为vm会为他默认创建值,上面的代码相当于:
Point[] p = new Point[5]
for (int i=0;i<5;i++){
p = Point.default;
}
p.x += p.y;
但是有些场合要有可以为null的primitive type,比如用容器存放primitive type,这个时候就可以这样写:
List<Point.ref> p = new ArrayList<>();
p.add(null);
p.add(Point.default);
假如用户写了一个primitive类型的Point.java,javac会自动生成一个companion类,即Point$ref.class。这个类就是可null的。
Point p1 = null; // ERROR, javac错误,不兼容类型
Point.ref p2 = null; // OK
Identity Object
参见最初的提案http://cr.openjdk.java.net/~briangoetz/valhalla/sov/02-object-model.html
inline class的instance没有identity,也就是说,不能将inline instance用于一些identity-sensitive的操作(比如synchronization,exception)。为了避免混乱,也为了便于描述,valhalla引入了identity class的概念,identity class的instance就叫做identity object。
幼虫态
larval state
调用约定
InlineTypePassFieldsAsArgs
ScalarizeInlineTypes
UseArrayMarkWordCheck
ForceNonTearable
ProfileACmpTypes