Swing 使用 JTable详解
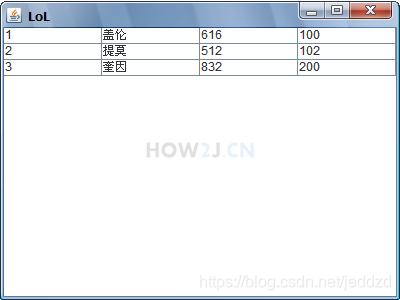
示例 1 : 基本表格
显示一个Table需要两组数据
- 一维数组: String[]columnNames 表示表格的标题
- 二维数组: String[][] heros 表格中的内容
默认情况下,表格的标题是不会显示出来了,除非使用了JScrollPane
package gui;
import java.awt.BorderLayout;
import javax.swing.JFrame;
import javax.swing.JTable;
public class TestGUI {
public static void main(String[] args) {
JFrame f = new JFrame("LoL");
f.setSize(400, 300);
f.setLocation(200, 200);
f.setLayout(new BorderLayout());
// 表格上的title
String[] columnNames = new String[] { "id", "name", "hp", "damage" };
// 表格中的内容,是一个二维数组
String[][] heros = new String[][] { { "1", "盖伦", "616", "100" },
{ "2", "提莫", "512", "102" }, { "3", "奎因", "832", "200" } };
JTable t = new JTable(heros, columnNames);
f.add(t, BorderLayout.CENTER);
f.setDefaultCloseOperation(JFrame.EXIT_ON_CLOSE);
f.setVisible(true);
}
}
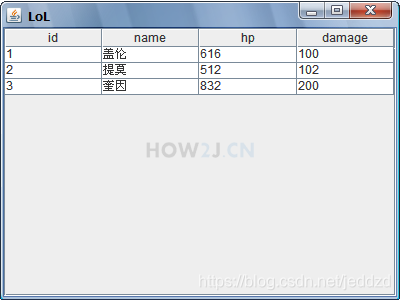
示例 2 : JScrollPane
JScrollPane: 带滚动条的Panel
把table放进去就可以看到table的title
同样的把textarea放进去,并且textarea内容够长的话,就会看到滚动条
package gui;
import java.awt.BorderLayout;
import javax.swing.JFrame;
import javax.swing.JScrollPane;
import javax.swing.JTable;
public class TestGUI {
public static void main(String[] args) {
JFrame f = new JFrame("LoL");
f.setSize(400, 300);
f.setLocation(200, 200);
f.setLayout(new BorderLayout());
String[] columnNames = new String[] { "id", "name", "hp", "damage" };
String[][] heros = new String[][] { { "1", "盖伦", "616", "100" },
{ "2", "提莫", "512", "102" }, { "3", "奎因", "832", "200" } };
JTable t = new JTable(heros, columnNames);
// 根据t创建 JScrollPane
JScrollPane sp = new JScrollPane(t);
//或则创建一个空的JScrollPane,再通过setViewportView把table放在JScrollPane中
// JScrollPane sp = new JScrollPane(t);
// sp.setViewportView(t);
// 把sp而非JTable加入到JFrame上,
f.add(sp, BorderLayout.CENTER);
f.setDefaultCloseOperation(JFrame.EXIT_ON_CLOSE);
f.setVisible(true);
}
}
示例 3 : 列宽
设置列宽度
package gui;
import java.awt.BorderLayout;
import javax.swing.JFrame;
import javax.swing.JScrollPane;
import javax.swing.JTable;
public class TestGUI {
public static void main(String[] args) {
JFrame f = new JFrame("LoL");
f.setSize(400, 300);
f.setLocation(200, 200);
f.setLayout(new BorderLayout());
String[] columnNames = new String[] { "id", "name", "hp", "damage" };
String[][] heros = new String[][] { { "1", "盖伦", "616", "100" },
{ "2", "提莫", "512", "102" }, { "3", "奎因", "832", "200" } };
JTable t = new JTable(heros, columnNames);
JScrollPane sp = new JScrollPane(t);
// 设置列宽度
t.getColumnModel().getColumn(0).setPreferredWidth(10);
f.add(sp, BorderLayout.CENTER);
f.setDefaultCloseOperation(JFrame.EXIT_ON_CLOSE);
f.setVisible(true);
}
}
示例 4 : TableModel
首先说下TableModel的设计思想,在Model这种思想的指导下,数据和显示分离开来了。 比如对于JTable而言,有数据部分,也有显示部分(比如列宽等信息)。 数据部分,专门做一个类,叫做TableModel,就用于存放要显示的数据。
使用TableModel的方式存放Table需要显示的数据
HeroTableModel 继承AbstractTableModel ,进而实现了接口TableModel
在HeroTableModel 中提供一个table显示需要的所有信息
- getRowCount 返回一共有多少行
- getColumnCount 返回一共有多少列
- getColumnName 每一列的名字
- isCellEditable 单元格是否可以修改
- getValueAt 每一个单元格里的值
当图形界面需要渲染第一个单元格的数据的时候,就会调用方法TabelModel的getValueAt(0,0) ,把返回值拿到并显示
package gui;
import javax.swing.table.AbstractTableModel;
public class HeroTableModel extends AbstractTableModel {
String[] columnNames = new String[] { "id", "name", "hp", "damage" };
String[][] heros = new String[][] { { "1", "盖伦", "616", "100" },
{ "2", "提莫", "512", "102" }, { "3", "奎因", "832", "200" } };
// 返回一共有多少行
public int getRowCount() {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
return heros.length;
}
// 返回一共有多少列
public int getColumnCount() {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
return columnNames.length;
}
// 获取每一列的名称
public String getColumnName(int columnIndex) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
return columnNames[columnIndex];
}
// 单元格是否可以修改
public boolean isCellEditable(int rowIndex, int columnIndex) {
return false;
}
// 每一个单元格里的值
public Object getValueAt(int rowIndex, int columnIndex) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
return heros[rowIndex][columnIndex];
}
}
.
package gui;
import java.awt.BorderLayout;
import javax.swing.JFrame;
import javax.swing.JScrollPane;
import javax.swing.JTable;
public class TestGUI {
public static void main(String[] args) {
JFrame f = new JFrame("LoL");
f.setSize(400, 300);
f.setLocation(200, 200);
f.setLayout(new BorderLayout());
//创建一个TableModel
HeroTableModel htm= new HeroTableModel();
//根据 TableModel来创建 Table
JTable t = new JTable(htm);
JScrollPane sp = new JScrollPane(t);
f.add(sp, BorderLayout.CENTER);
f.setDefaultCloseOperation(JFrame.EXIT_ON_CLOSE);
f.setVisible(true);
}
}
示例 5 : 进一步理解TableModel
在使用TableModel之前,是使用
String[] columnNames =。。。
String[][] heros = 。。。
JTable t = new JTable(heros, columnNames);
这样的风格创建一个JTable的
所以实际上调用的是如下的构造方法:
JTable(Object[][] rowData, Object[] columnNames)
如图所示,在JTable的的源代码中,它就会根据rowData和columnNames去创建一个TableModel对象

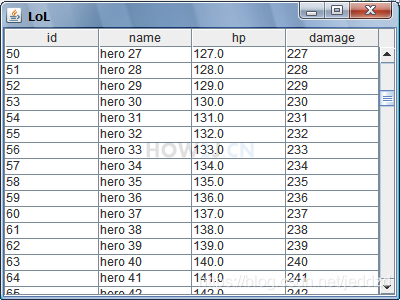
示例 6 : TableModel 与DAO结合
通过TableModel与DAO结合显示数据库中Hero信息。
DAO使用HeroDAO
在TableModel中,使用从DAO返回的List作为TableModel的数据
只需要修改HeroTableModel,无需修改TestGUI。 这正好演绎了Model设计思想中的数据分离的好处,当只需要数据发生变化的时候,修改Model即可,界面GUI部分,不需要做任何改动
package gui;
import java.util.List;
import javax.swing.table.AbstractTableModel;
import jdbc.HeroDAO;
import charactor.Hero;
public class HeroTableModel extends AbstractTableModel {
String[] columnNames = new String[] { "id", "name", "hp", "damage" };
// 使用从DAO返回的List作为TableModel的数据
public List<Hero> heros = new HeroDAO().list();
// heros.size返回一共有多少行
public int getRowCount() {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
return heros.size();
}
public int getColumnCount() {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
return columnNames.length;
}
public String getColumnName(int columnIndex) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
return columnNames[columnIndex];
}
public boolean isCellEditable(int rowIndex, int columnIndex) {
return false;
}
// 先通过heros.get(rowIndex)获取行对应的Hero对象
// 然后根据columnIndex返回对应的属性
public Object getValueAt(int rowIndex, int columnIndex) {
Hero h = heros.get(rowIndex);
if (0 == columnIndex)
return h.id;
if (1 == columnIndex)
return h.name;
if (2 == columnIndex)
return h.hp;
if (3 == columnIndex)
return h.damage;
return null;
}
}
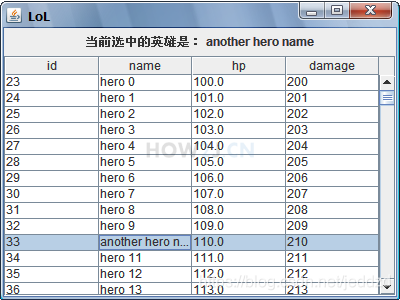
示例 7 : TableSelectionModel
通过table可以获取一个 TableSelectionModel,专门用于监听jtable选中项的变化
package gui;
import java.awt.BorderLayout;
import javax.swing.JFrame;
import javax.swing.JLabel;
import javax.swing.JPanel;
import javax.swing.JScrollPane;
import javax.swing.JTable;
import javax.swing.event.ListSelectionEvent;
import javax.swing.event.ListSelectionListener;
import charactor.Hero;
public class TestGUI {
public static void main(String[] args) {
JFrame f = new JFrame("LoL");
f.setSize(400, 300);
f.setLocation(200, 200);
f.setLayout(new BorderLayout());
final HeroTableModel htm = new HeroTableModel();
final JTable t = new JTable(htm);
// 准备一个Panel上面放一个Label用于显示哪条被选中了
JPanel p = new JPanel();
final JLabel l = new JLabel("暂时未选中条目");
p.add(l);
JScrollPane sp = new JScrollPane(t);
// 使用selection监听器来监听table的哪个条目被选中
t.getSelectionModel().addListSelectionListener(
new ListSelectionListener() {
// 当选择了某一行的时候触发该事件
public void valueChanged(ListSelectionEvent e) {
// 获取哪一行被选中了
int row = t.getSelectedRow();
// 根据选中的行,到HeroTableModel中获取对应的对象
Hero h = htm.heros.get(row);
// 更新标签内容
l.setText("当前选中的英雄是: " + h.name);
}
});
f.add(p, BorderLayout.NORTH);
f.add(sp, BorderLayout.CENTER);
f.setDefaultCloseOperation(JFrame.EXIT_ON_CLOSE);
f.setVisible(true);
}
}
示例 8 : 更新Table
以新增数据到数据库中,然后更新Table为例

package gui;
import java.awt.BorderLayout;
import java.awt.Dimension;
import java.awt.event.ActionEvent;
import java.awt.event.ActionListener;
import javax.swing.JButton;
import javax.swing.JFrame;
import javax.swing.JLabel;
import javax.swing.JPanel;
import javax.swing.JScrollPane;
import javax.swing.JTable;
import javax.swing.JTextField;
import jdbc.HeroDAO;
import charactor.Hero;
public class TestGUI {
public static void main(String[] args) {
JFrame f = new JFrame("LoL");
f.setSize(400, 300);
f.setLocation(200, 200);
f.setLayout(new BorderLayout());
final HeroTableModel htm = new HeroTableModel();
final JTable t = new JTable(htm);
// 增加 一个 panel用于放置名称,血量输入框和增加 按钮
JPanel p = new JPanel();
final JLabel lName = new JLabel("名称");
final JTextField tfName = new JTextField("");
final JLabel lHp = new JLabel("血量");
final JTextField tfHp = new JTextField("");
JButton bAdd = new JButton("增加");
tfName.setPreferredSize(new Dimension(80, 30));
tfHp.setPreferredSize(new Dimension(80, 30));
p.add(lName);
p.add(tfName);
p.add(lHp);
p.add(tfHp);
p.add(bAdd);
// 为增加按钮添加监听
bAdd.addActionListener(new ActionListener() {
@Override
public void actionPerformed(ActionEvent e) {
HeroDAO dao = new HeroDAO();
// 根据输入框数据创建一个Hero对象
Hero h = new Hero();
h.name = tfName.getText();
h.hp = Integer.parseInt(tfHp.getText());
// 通过dao把该对象加入到数据库
dao.add(h);
// 通过dao更新tablemodel中的数据
htm.heros = dao.list();
// 调用JTable的updateUI,刷新界面。
// 刷新界面的时候,会到tablemodel中去取最新的数据
// 就能看到新加进去的数据了
t.updateUI();
}
});
JScrollPane sp = new JScrollPane(t);
f.add(p, BorderLayout.NORTH);
f.add(sp, BorderLayout.CENTER);
f.setDefaultCloseOperation(JFrame.EXIT_ON_CLOSE);
f.setVisible(true);
}
}
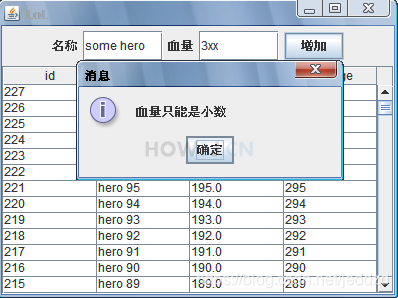
示例 9 : 输入项验证
如果用户输入的名称为空,或者血量不是小数,在提交数据的时候都会报错。
“感觉上” 界面就卡住了。 这是不友好的人机交互行为。
所以需要加上输入项的验证,如果输入的数据不合格,应该弹出对话框提示用户具体原因。
package gui;
import java.awt.BorderLayout;
import java.awt.Dimension;
import java.awt.event.ActionEvent;
import java.awt.event.ActionListener;
import javax.swing.JButton;
import javax.swing.JFrame;
import javax.swing.JLabel;
import javax.swing.JOptionPane;
import javax.swing.JPanel;
import javax.swing.JScrollPane;
import javax.swing.JTable;
import javax.swing.JTextField;
import jdbc.HeroDAO;
import charactor.Hero;
public class TestGUI {
public static void main(String[] args) {
final JFrame f = new JFrame("LoL");
f.setSize(400, 300);
f.setLocation(200, 200);
f.setLayout(new BorderLayout());
final HeroTableModel htm = new HeroTableModel();
final JTable t = new JTable(htm);
JPanel p = new JPanel();
final JLabel lName = new JLabel("名称");
final JTextField tfName = new JTextField("");
final JLabel lHp = new JLabel("血量");
final JTextField tfHp = new JTextField("");
JButton bAdd = new JButton("增加");
tfName.setPreferredSize(new Dimension(80, 30));
tfHp.setPreferredSize(new Dimension(80, 30));
p.add(lName);
p.add(tfName);
p.add(lHp);
p.add(tfHp);
p.add(bAdd);
bAdd.addActionListener(new ActionListener() {
@Override
public void actionPerformed(ActionEvent e) {
HeroDAO dao = new HeroDAO();
Hero h = new Hero();
String name = tfName.getText();
// 通过name长度判断 名称是否为空
if (name.length() == 0) {
// 弹出对话框提示用户
JOptionPane.showMessageDialog(f, "名称不能为空");
// 名称输入框获取焦点
tfName.grabFocus();
return;
}
String hp = tfHp.getText().trim();
try {
// 把hp转换为浮点型,如果出现异常NumberFormatException表示不是浮点型格式
Float.parseFloat(hp);
} catch (NumberFormatException e1) {
JOptionPane.showMessageDialog(f, "血量只能是小数 ");
tfHp.grabFocus();
return;
}
h.name = name;
h.hp = Float.parseFloat(hp);
dao.add(h);
htm.heros = dao.list();
t.updateUI();
}
});
JScrollPane sp = new JScrollPane(t);
f.add(p, BorderLayout.NORTH);
f.add(sp, BorderLayout.CENTER);
f.setDefaultCloseOperation(JFrame.EXIT_ON_CLOSE);
f.setVisible(true);
}
}
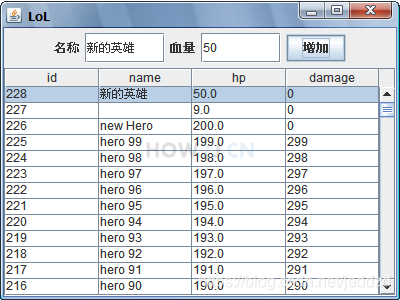
示例 10 : 选中指定行
- table初始化后,应该默认选中第一行
- 增加数据后,也应该选中新增的这一条
package gui;
import java.awt.BorderLayout;
import java.awt.Dimension;
import java.awt.event.ActionEvent;
import java.awt.event.ActionListener;
import javax.swing.JButton;
import javax.swing.JFrame;
import javax.swing.JLabel;
import javax.swing.JOptionPane;
import javax.swing.JPanel;
import javax.swing.JScrollPane;
import javax.swing.JTable;
import javax.swing.JTextField;
import javax.swing.ListSelectionModel;
import jdbc.HeroDAO;
import charactor.Hero;
public class TestGUI {
public static void main(String[] args) {
final JFrame f = new JFrame("LoL");
f.setSize(400, 300);
f.setLocation(200, 200);
f.setLayout(new BorderLayout());
final HeroTableModel htm = new HeroTableModel();
final JTable t = new JTable(htm);
// 设置选择模式为 只能选中一行
t.setSelectionMode(ListSelectionModel.SINGLE_SELECTION);
// 选中第一行 (基本0)
t.getSelectionModel().setSelectionInterval(0, 0);
JPanel p = new JPanel();
final JLabel lName = new JLabel("名称");
final JTextField tfName = new JTextField("");
final JLabel lHp = new JLabel("血量");
final JTextField tfHp = new JTextField("");
JButton bAdd = new JButton("增加");
tfName.setPreferredSize(new Dimension(80, 30));
tfHp.setPreferredSize(new Dimension(80, 30));
p.add(lName);
p.add(tfName);
p.add(lHp);
p.add(tfHp);
p.add(bAdd);
bAdd.addActionListener(new ActionListener() {
@Override
public void actionPerformed(ActionEvent e) {
HeroDAO dao = new HeroDAO();
Hero h = new Hero();
String name = tfName.getText();
if (name.length() == 0) {
JOptionPane.showMessageDialog(f, "名称不能为空");
tfName.grabFocus();
return;
}
String hp = tfHp.getText().trim();
try {
Float.parseFloat(hp);
} catch (NumberFormatException e1) {
JOptionPane.showMessageDialog(f, "血量只能是小数 ");
tfHp.grabFocus();
return;
}
h.name = name;
h.hp = Float.parseFloat(hp);
dao.add(h);
htm.heros = dao.list();
t.updateUI();
// 选中 第一行 ,因为 DAO是按照 ID倒排序查询,所以第一行就是新加入的数据
t.getSelectionModel().setSelectionInterval(0, 0);
}
});
JScrollPane sp = new JScrollPane(t);
f.add(p, BorderLayout.NORTH);
f.add(sp, BorderLayout.CENTER);
f.setDefaultCloseOperation(JFrame.EXIT_ON_CLOSE);
f.setVisible(true);
}
}
更多内容,点击了解: Swing 使用 JTable详解