一、什么是最长公共子序列
什么是最长公共子序列呢?举个简单的例子吧,一个数列S,若分别是两个或多个已知序列的子序列,且是所有符合条件序列中最长的,则S称为已知序列的最长公共子序列。
举例如下,如:有两个随机数列,1 2 3 4 5 6 和 3 4 5 8 9,则它们的最长公共子序列便是:3 4 5。
最长公共子串(Longest Common Substirng)和最长公共子序列(Longest Common Subsequence,LCS)的区别为:子串是串的一个连续的部分,子序列则是从不改变序列的顺序,而从序列中去掉任意的元素而获得新的序列;也就是说,子串中字符的位置必须是连续的,子序列则可以不必连续。
二、解决方案
<1> 枚举法
这种方法是最简单,也是最容易想到的,当然时间复杂度也是龟速的,我们可以分析一下,刚才也说过了cnblogs的子序列个数有27个 ,延伸一下:一个长度为N的字符串,其子序列有2N个,每个子序列要在第二个长度为N的字符串中去匹配,匹配一次需要O(N)的时间,总共也就是O(N*2N),可以看出,时间复杂度为指数级,恐怖的令人窒息。
<2> 动态规划
最长公共子序列的结构有如下表示:
设序列X=<x1, x2, …, xm>和Y=<y1, y2, …, yn>的一个最长公共子序列Z=<z1, z2, …, zk>,则:
1> 若 xm=yn,则 zk=xm=yn,且Zk-1是Xm-1和Yn-1的最长公共子序列;
2> 若 xm≠yn且 zk≠xm ,则 Z是 Xm-1和 Y的最长公共子序列;
3> 若 xm≠yn且 zk≠yn ,则 Z是 X和 Yn-1的最长公共子序列;
现有两个序列X={x1,x2,x3,...xi},Y={y1,y2,y3,....,yi},设一个C[i,j]: 保存Xi与Yj的LCS的长度,递推方程为:

代码:
//只能打印一个最长公共子序列 #include <iostream> using namespace std; const int X = 100, Y = 100; //串的最大长度 char result[X+1]; //用于保存结果 int count=0; //用于保存公共最长公共子串的个数 /*功能:计算最优值 *参数: * x:字符串x * y:字符串y * b:标志数组 * xlen:字符串x的长度 * ylen:字符串y的长度 *返回值:最长公共子序列的长度 * */ int Lcs_Length(string x, string y, int b[][Y+1],int xlen,int ylen) { int i = 0; int j = 0; int c[X+1][Y+1]; for (i = 0; i<=xlen; i++) { c[i][0]=0; } for (i = 0; i <= ylen; i++ ) { c[0][i]=0; } for (i = 1; i <= xlen; i++) { for (j = 1; j <= ylen; j++) { if (x[i - 1] == y[j - 1]) { c[i][j] = c[i-1][j-1]+1; b[i][j] = 1; } else if (c[i-1][j] > c[i][j-1]) { c[i][j] = c[i-1][j]; b[i][j] = 2; } else if(c[i-1][j] <= c[i][j-1]) { c[i][j] = c[i][j-1]; b[i][j] = 3; } } } return c[xlen][ylen]; } void Display_Lcs(int i, int j, string x, int b[][Y+1],int current_Len) { if (i ==0 || j==0) { return; } if(b[i][j]== 1) { current_Len--; result[current_Len]=x[i- 1]; Display_Lcs(i-1, j-1, x, b, current_Len); } else if(b[i][j] == 2) { Display_Lcs(i-1, j, x, b, current_Len); } else if(b[i][j]==3) { Display_Lcs(i, j-1, x, b, current_Len); } else
{ Display_Lcs(i-1,j,x,b, current_Len); } } int main(int argc, char* argv[]) { string x = "ABCBDAB"; string y = "BDCABA"; int xlen = x.length(); int ylen = y.length(); int b[X + 1][Y + 1]; int lcs_max_len = Lcs_Length( x, y, b, xlen,ylen ); cout << lcs_max_len << endl; Display_Lcs( xlen, ylen, x, b, lcs_max_len ); //打印结果如下所示 for(int i = 0; i < lcs_max_len; i++) { cout << result[i]; } cout << endl; return 0; }
运行结果如下:
4 BDAB
由于有时并不是只有一个最长公共子序列,所以,对上面的代码进行改进,增加一个数组保存结果等....代码如下所示。
//求取所有的最长公共子序列 #include <iostream> using namespace std; const int X = 100, Y = 100; //串的最大长度 char result[X+1]; //用于保存结果 int cnt = 0; //用于保存公共最长公共子串的个数 /*功能:计算最优值 *参数: * x:字符串x * y:字符串y * b:标志数组 * xlen:字符串x的长度 * ylen:字符串y的长度 *返回值:最长公共子序列的长度 * */ int Lcs_Length(string x, string y, int b[][Y+1],int xlen,int ylen) { int i = 0; int j = 0; int c[X+1][Y+1]; for (i = 0; i<=xlen; i++) { c[i][0]=0; } for (i = 0; i <= ylen; i++ ) { c[0][i]=0; } for (i = 1; i <= xlen; i++) { for (j = 1; j <= ylen; j++) { if (x[i - 1] == y[j - 1]) { c[i][j] = c[i-1][j-1]+1; b[i][j] = 1; } else if (c[i-1][j] > c[i][j-1]) { c[i][j] = c[i-1][j]; b[i][j] = 2; } else if(c[i-1][j] < c[i][j-1]) { c[i][j] = c[i][j-1]; b[i][j] = 3; } else { c[i][j] = c[i][j-1]; //或者c[i][j]=c[i-1][j]; b[i][j] = 4; } } } return c[xlen][ylen]; } /*功能:计算最长公共子序列 *参数: * xlen:字符串x的长度 * ylen:字符串y的长度 * x :字符串x * b:标志数组 * current_len:当前长度 * lcs_max_len:最长公共子序列长度 * */ void Display_Lcs(int i, int j, string x, int b[][Y+1],int current_len,int lcs_max_len) { if (i ==0 || j==0) { for(int s=0; s < lcs_max_len; s++) { cout << result[s]; } cout<<endl; cnt++; return; } if(b[i][j]== 1) { current_len--; result[current_len]=x[i- 1]; Display_Lcs(i-1, j-1, x, b,current_len,lcs_max_len); } else if(b[i][j] == 2) { Display_Lcs(i-1, j, x, b,current_len,lcs_max_len); } else if(b[i][j]==3) { Display_Lcs(i, j-1, x, b,current_len,lcs_max_len); } else { Display_Lcs(i,j-1,x,b,current_len,lcs_max_len); Display_Lcs(i-1,j,x,b,current_len,lcs_max_len); } } int main(int argc, char* argv[]) { string x = "ABCBDAB"; string y = "BDCABA"; int xlen = x.length(); int ylen = y.length(); int b[X + 1][Y + 1]; int lcs_max_len = Lcs_Length( x, y, b, xlen,ylen ); cout << lcs_max_len << endl; Display_Lcs( xlen, ylen, x, b, lcs_max_len, lcs_max_len ); cout << "共有:" << cnt << "种"; return 0; }
运行结果如下:
4 BDAB BCAB BCBA 共有: 3 种
/****************************************
update
****************************************/
示例:
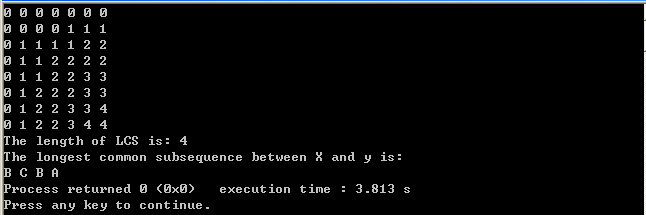
#include <iostream> using namespace std; #define X_LEN 7 #define Y_LEN 6 #define EQUAL 0 #define UP 1 #define LEVEL 2 void lcs_length(char* X,char* Y,int c[X_LEN+1][Y_LEN+1],int b[X_LEN+1][Y_LEN+1]); void print_lcs(int b[X_LEN+1][Y_LEN+1],char *X,int i,int j); int main() { char X[X_LEN+1] = {' ','A','B','C','B','D','A','B'}; char Y[Y_LEN+1] = {' ','B','D','C','A','B','A'}; int c[X_LEN+1][Y_LEN+1]={0}; int b[X_LEN+1][Y_LEN+1] = {0}; int i,j; lcs_length(X,Y,c,b); for(i=0;i<=X_LEN;i++) { for(j=0;j<=Y_LEN;j++) cout<<c[i][j]<<" "; cout<<endl; } cout<<"The length of LCS is: "<<c[X_LEN][Y_LEN]<<endl; cout<<"The longest common subsequence between X and y is: "<<endl; print_lcs(b,X,X_LEN,Y_LEN); return 0; } //采用动态规划方法自底向上的进行计算,寻找最优解 void lcs_length(char* X,char* Y,int c[X_LEN+1][Y_LEN+1],int b[X_LEN+1][Y_LEN+1]) { int i,j; //设置边界条件,即i=0或者j=0 for(i=0;i<X_LEN;i++) c[i][0] = 0; for(j=0;j<Y_LEN;j++) c[0][j] = 0; for(i=1;i<=X_LEN;i++) for(j=1;j<=Y_LEN;j++) { if(X[i] == Y[j]) //满足递归公式第二条 { c[i][j] = c[i-1][j-1]+1; b[i][j] = EQUAL ; } else if(c[i-1][j] >= c[i][j-1]) //递归公式第三条 { c[i][j] = c[i-1][j]; b[i][j] = UP; } else { c[i][j] = c[i][j-1]; b[i][j] = LEVEL; } } } void print_lcs(int b[X_LEN+1][Y_LEN+1],char *X,int i,int j) { if(i==0 || j==0) return; if(b[i][j] == EQUAL) { print_lcs(b,X,i-1,j-1); cout<<X[i]<<" "; } else if(b[i][j] == UP) print_lcs(b,X,i-1,j); else print_lcs(b,X,i,j-1); }
结果: