一、Producer API
1.1、消息发送流程
Kafka的Producer发送消息采用的是异步发送的方式。在消息发送的过程中,涉及到了两个线程——main线程和Sender线程,以及一个线程共享变量——RecordAccumulator。main线程将消息发送给RecordAccumulator,Sender线程不断从RecordAccumulator中拉取消息发送到Kafkabroker。
- KafkaProducer 发送消息流程
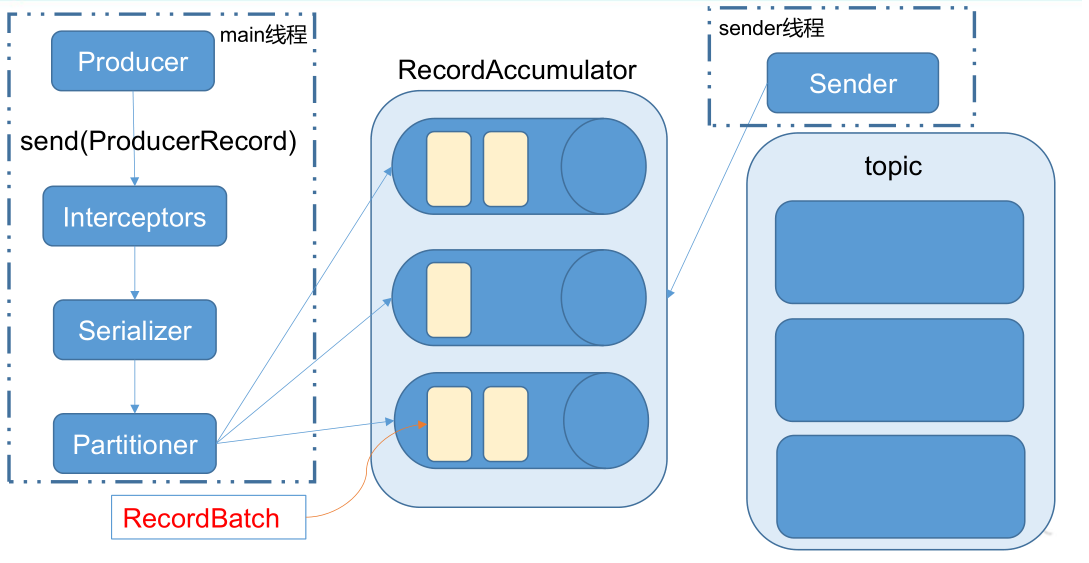
相关参数:
- batch.size :只有数据积累到 batch.size 之后,sender 才会发送数据。
- linger.ms :如果数据迟迟未达到 batch.size,sender 等待 linger.time 之后就会发送数据。
1.2、异步送发送API
- 导入依赖
<dependency> <groupId>org.apache.kafka</groupId> <artifactId>kafka-clients</artifactId> <version>0.11.0.0</version> </dependency>
需要用到的类:
-
KafkaProducer:需要创建一个生产者对象,用来发送数据
-
ProducerConfig:获取所需的一系列配置参数
-
ProducerRecord:每条数据都要封装成一个 ProducerRecord 对象
1、不带回调函数的 API
public class CustomProducer { public static void main(String[] args) { Properties props = new Properties(); //kafka 集群,broker-list props.put("bootstrap.servers", "broker2:9092"); props.put("acks", "all"); //重试次数 props.put("retries", 1); //批次大小 props.put("batch.size", 16384); //等待时间 props.put("linger.ms", 1); //RecordAccumulator 缓冲区大小 props.put("buffer.memory", 33554432); props.put("key.serializer", "org.apache.kafka.common.serialization.StringSerializer"); props.put("value.serializer", "org.apache.kafka.common.serialization.StringSerializer"); Producer<String, String> producer = new KafkaProducer<>(props); for (int i = 0; i < 100; i++) { producer.send(new ProducerRecord<String, String>("first", Integer.toString(i), Integer.toString(i))); } producer.close(); } }
2、带回调函数的 API
回调函数会在producer收到ack时调用,为异步调用,该方法有两个参数,分别是RecordMetadata和Exception,如果Exception为null,说明消息发送成功,如果Exception不为null,说明消息发送失败。
注意:消息发送失败会自动重试,不需要我们在回调函数中手动重试
public class CustomProducer_callback { public static void main(String[] args) { Properties props = new Properties(); props.put("bootstrap.servers", "broker2:9092");//kafka 集群,broker-list props.put("acks", "all"); props.put("retries", 1);//重试次数 props.put("batch.size", 16384);//批次大小 props.put("linger.ms", 1);//等待时间 props.put("buffer.memory", 33554432);//RecordAccumulator 缓冲区大小 props.put("key.serializer", "org.apache.kafka.common.serialization.StringSerializer"); props.put("value.serializer", "org.apache.kafka.common.serialization.StringSerializer"); Producer<String, String> producer = new KafkaProducer<>(props); for (int i = 0; i < 100; i++) { producer.send(new ProducerRecord<String, String>("first", Integer.toString(i), Integer.toString(i)), new Callback() { //回调函数,该方法会在 Producer 收到 ack 时调用,为异步调用 @Override public void onCompletion(RecordMetadata metadata, Exception exception) { if (exception == null) { System.out.println("success->" + metadata.offset()); } else { exception.printStackTrace(); } } }); } producer.close(); } }
1.3、同步发送 API
同步发送的意思就是,一条消息发送之后,会阻塞当前线程,直至返回ack。由于send方法返回的是一个Future对象,根据Futrue对象的特点,我们也可以实现同步发送的效果,只需在调用Future对象的get方发即可。
public class CustomProducer_Sync { public static void main(String[] args) throws ExecutionException, InterruptedException { Properties props = new Properties(); props.put("bootstrap.servers", "broker2:9092");//kafka 集群,broker-list props.put("acks", "all"); props.put("retries", 1);//重试次数 props.put("batch.size", 16384);//批次大小 props.put("linger.ms", 1);//等待时间 props.put("buffer.memory", 33554432);//RecordAccumulator 缓冲区大小 props.put("key.serializer", "org.apache.kafka.common.serialization.StringSerializer"); props.put("value.serializer", "org.apache.kafka.common.serialization.StringSerializer"); Producer<String, String> producer = new KafkaProducer<>(props); for (int i = 0; i < 100; i++) { producer.send(new ProducerRecord<String, String>("first", Integer.toString(i), Integer.toString(i))).get(); } producer.close(); } }
二、Consumer API
Consumer消费数据时的可靠性是很容易保证的,因为数据在Kafka中是持久化的,故不用担心数据丢失问题。
由于consumer在消费过程中可能会出现断电宕机等故障,consumer恢复后,需要从故障前的位置的继续消费,所以consumer需要实时记录自己消费到了哪个offset,以便故障恢复后继续消费。
所以offset的维护是Consumer消费数据是必须考虑的问题。
2.1、自动提交 offset
依赖和producer一样,需要用到的类如下:
- KafkaConsumer:需要创建一个消费者对象,用来消费数据
- ConsumerConfig:获取所需的一系列配置参数
- ConsuemrRecord:每条数据都要封装成一个 ConsumerRecord 对象
为了使我们能够专注于自己的业务逻辑,Kafka 提供了自动提交 offset 的功能。自动提交 offset 的相关参数:
- enable.auto.commit :是否开启自动提交 offset 功能
- auto.commit.interval.ms :自动提交 offset 的时间间隔
public class CustomConsumer_auto { public static void main(String[] args) { Properties props = new Properties(); props.put("bootstrap.servers", "broker2:9092"); props.put("group.id", "test"); props.put("enable.auto.commit", "true"); props.put("auto.commit.interval.ms", "1000"); props.put("key.deserializer", "org.apache.kafka.common.serialization.StringDeserializer"); props.put("value.deserializer", "org.apache.kafka.common.serialization.StringDeserializer"); KafkaConsumer<String, String> consumer = new KafkaConsumer <>(props); consumer.subscribe(Arrays.asList("first")); while (true) { ConsumerRecords<String, String> records = consumer.poll(100); for (ConsumerRecord<String, String> record : records) System.out.printf("offset = %d, key = %s, value = % s % n ", record.offset(), record.key(), record.value()); } } }
2.2、手动提交offset
虽然自动提交offset十分简介便利,但由于其是基于时间提交的,开发人员难以把握offset提交的时机。因此Kafka还提供了手动提交offset的API。
手动提交offset的方法有两种:分别是commitSync(同步提交)和commitAsync(异步提交)。两者的相同点是,都会将次本次poll的一批数据最高的偏移量提交;不同点是,commitSync阻塞当前线程,一直到提交成功,并且会自动失败重试(由不可控因素导致,也会出现提交失败);而commitAsync则没有失败重试机制,故有可能提交失败。
1、同步提交 offset
由于同步提交 offset 有失败重试机制,故更加可靠
public class CustomComsumer_Sync { public static void main(String[] args) { Properties props = new Properties(); //Kafka 集群 props.put("bootstrap.servers", "broker2:9092"); //消费者组,只要 group.id 相同,就属于同一个消费者组 props.put("group.id", "test"); props.put("enable.auto.commit", "false");//关闭自动提交 offset props.put("key.deserializer", "org.apache.kafka.common.serialization.StringDeserializer"); props.put("value.deserializer", "org.apache.kafka.common.serialization.StringDeserializer"); KafkaConsumer<String, String> consumer = new KafkaConsumer<>(props); consumer.subscribe(Arrays.asList("first"));//消费者订阅主题 while (true) { //消费者拉取数据 ConsumerRecords<String, String> records = consumer.poll(100); for (ConsumerRecord<String, String> record : records) { System.out.printf("offset = %d, key = %s, value = %s%n", record.offset(), record.key(), record.value()); } //同步提交,当前线程会阻塞直到 offset 提交成功 consumer.commitSync(); } } }
2、异步提交 offset
虽然同步提交 offset 更可靠一些,但是由于其会阻塞当前线程,直到提交成功。因此吞吐量会收到很大的影响。因此更多的情况下,会选用异步提交 offset 的方式。
ublic class CustomConsumer_Async { public static void main(String[] args) { Properties props = new Properties(); //Kafka 集群 props.put("bootstrap.servers", "broker2:9092"); //消费者组,只要 group.id 相同,就属于同一个消费者组 props.put("group.id", "test"); //关闭自动提交 offset props.put("enable.auto.commit", "false"); props.put("key.deserializer", "org.apache.kafka.common.serialization.StringDeserializer"); props.put("value.deserializer", "org.apache.kafka.common.serialization.StringDeserializer"); KafkaConsumer<String, String> consumer = new KafkaConsumer<>(props); consumer.subscribe(Arrays.asList("first"));//消费者订阅主题 while (true) { ConsumerRecords<String, String> records = consumer.poll(100);//消费者拉取数据 for (ConsumerRecord<String, String> record : records) { System.out.printf("offset = %d, key = %s, value = %s%n", record.offset(), record.key(), record.value()); } //异步提交 consumer.commitAsync(new OffsetCommitCallback() { @Override public void onComplete(Map<TopicPartition, OffsetAndMetadata> offsets, Exception exception) { if (exception != null) { System.err.println("Commit failed for" + offsets); } } }); } } }
3、数据漏消费和重复消费分析
无论是同步提交还是异步提交 offset,都有可能会造成数据的漏消费或者重复消费。先提交 offset 后消费,有可能造成数据的漏消费;而先消费后提交 offset,有可能会造成数据的重复消费。
2.3、自定义存储 offset
Kafka0.9版本之前,offset存储在zookeeper,0.9版本及之后,默认将offset存储在Kafka的一个内置的topic中。除此之外,Kafka还可以选择自定义存储offset。
offset的维护是相当繁琐的,因为需要考虑到消费者的Rebalace。
当有新的消费者加入消费者组、已有的消费者推出消费者组或者所订阅的主题的分区发生变化,就会触发到分区的重新分配,重新分配的过程叫做Rebalance。
消费者发生Rebalance之后,每个消费者消费的分区就会发生变化。因此消费者要首先获取到自己被重新分配到的分区,并且定位到每个分区最近提交的offset位置继续消费。
要实现自定义存储offset,需要借助ConsumerRebalanceListener,以下为示例代码,其中提交和获取offset的方法,需要根据所选的offset存储系统自行实现。
public class MyCustomConsumer { private static Map<TopicPartition, Long> currentOffset = new HashMap<>(); public static void main(String[] args) { //创建配置信息 Properties props = new Properties(); //Kafka 集群 props.put("bootstrap.servers", "broker2:9092"); //消费者组,只要 group.id 相同,就属于同一个消费者组 props.put("group.id", "test"); //关闭自动提交 offset props.put("enable.auto.commit", "false"); //Key 和 Value 的反序列化类 props.put("key.deserializer", "org.apache.kafka.common.serialization.StringDeserializer"); props.put("value.deserializer", "org.apache.kafka.common.serialization.StringDeserializer"); //创建一个消费者 KafkaConsumer<String, String> consumer = new KafkaConsumer<>(props); //消费者订阅主题 consumer.subscribe(Arrays.asList("first"), new ConsumerRebalanceListener() { //该方法会在 Rebalance 之前调用 @Override public void onPartitionsRevoked(Collection<TopicPartition> partitions) { commitOffset(currentOffset); } //该方法会在 Rebalance 之后调用 @Override public void onPartitionsAssigned(Collection<TopicPartition> partitions) { currentOffset.clear(); for (TopicPartition partition : partitions) { consumer.seek(partition, getOffset(partition));//定位到最近提交的 offset 位置继续消费 } } }); while (true) { ConsumerRecords<String, String> records = consumer.poll(100);//消费者拉取数据 for (ConsumerRecord<String, String> record : records) { System.out.printf("offset = %d, key = %s, value = %s%n", record.offset(), record.key(), record.value()); currentOffset.put(new TopicPartition(record.topic(), record.partition()), record.offset()); } commitOffset(currentOffset);//异步提交 } } //获取某分区的最新 offset private static long getOffset(TopicPartition partition) { return 0; } //提交该消费者所有分区的 offset private static void commitOffset(Map<TopicPartition, Long> currentOffset) { } }
三、自定义 Interceptor
3.1、拦截器原理
Producer 拦截器(interceptor)是在 Kafka 0.10 版本被引入的,主要用于实现 clients 端的定制化控制逻辑。
对于 producer 而言,interceptor 使得用户在消息发送前以及 producer 回调逻辑前有机会对消息做一些定制化需求,比如修改消息等。同时,producer 允许用户指定多个 interceptor按序作用于同一条消息从而形成一个拦截链(interceptor chain)。Intercetpor 的实现接口是
org.apache.kafka.clients.producer.ProducerInterceptor,其定义的方法包括:
- configure(configs)
获取配置信息和初始化数据时调用。 - onSend(ProducerRecord):
该方法封装进 KafkaProducer.send 方法中,即它运行在用户主线程中。Producer 确保在消息被序列化以及计算分区前调用该方法。用户可以在该方法中对消息做任何操作,但最好保证不要修改消息所属的 topic 和分区,否则会影响目标分区的计算。 - onAcknowledgement(RecordMetadata, Exception):
该方法会在消息从 RecordAccumulator 成功发送到 Kafka Broker 之后,或者在发送过程中失败时调用。并且通常都是在 producer 回调逻辑触发之前。onAcknowledgement 运行在producer 的 IO 线程中,因此不要在该方法中放入很重的逻辑,否则会拖慢 producer 的消息发送效率。 - close
关闭 interceptor,主要用于执行一些资源清理工作
如前所述,interceptor 可能被运行在多个线程中,因此在具体实现时用户需要自行确保线程安全。另外倘若指定了多个 interceptor,则 producer 将按照指定顺序调用它们,并仅仅是捕获每个 interceptor 可能抛出的异常记录到错误日志中而非在向上传递。这在使用过程中要特别留意。
3.2、拦截器案例
需求:实现一个简单的双 interceptor 组成的拦截链。第一个 interceptor 会在消息发送前将时间戳信息加到消息 value 的最前部;第二个 interceptor 会在消息发送后更新成功发送消息数或失败发送消息数。
- Kafka拦截器

1、增加时间戳拦截器
public class TimeInterceptor implements ProducerInterceptor<String, String> { @Override public ProducerRecord<String, String> onSend(ProducerRecord<String, String> record) { // 创建一个新的 record,把时间戳写入消息体的最前部 return new ProducerRecord(record.topic(), record.partition(), record.timestamp(), record.key(), System.currentTimeMillis() + "," + record.value().toString()); } @Override public void onAcknowledgement(RecordMetadata recordMetadata, Exception e) { } @Override public void close() { } @Override public void configure(Map<String, ?> map) { } }
2、统计发送消息成功和发送失败消息数,并在 producer 关闭时打印这两个计数器
public class CounterInterceptor implements ProducerInterceptor<String, String> { private int errorCounter = 0; private int successCounter = 0; @Override public ProducerRecord<String, String> onSend(ProducerRecord<String, String> producerRecord) { return null; } @Override public void onAcknowledgement(RecordMetadata recordMetadata, Exception exception) { // 统计成功和失败的次数 if (exception == null) { successCounter++; } else { errorCounter++; } } @Override public void close() { // 保存结果 System.out.println("Successful sent: " + successCounter); System.out.println("Failed sent: " + errorCounter); } @Override public void configure(Map<String, ?> map) { } }
3、producer 主程序
public class InterceptorProducer { public static void main(String[] args) { // 1 设置配置信息 Properties props = new Properties(); props.put("bootstrap.servers", "broker2:9092"); props.put("acks", "all"); props.put("retries", 3); props.put("batch.size", 16384); props.put("linger.ms", 1); props.put("buffer.memory", 33554432); props.put("key.serializer", "org.apache.kafka.common.serialization.StringSerializer"); props.put("value.serializer", "org.apache.kafka.common.serialization.StringSerializer"); // 2 构建拦截链 List<String> interceptors = new ArrayList<>(); interceptors.add("com.atguigu.kafka.interceptor.TimeInterceptor"); interceptors.add("com.atguigu.kafka.interceptor.CounterInterceptor"); props.put(ProducerConfig.INTERCEPTOR_CLASSES_CONFIG, interceptors); String topic = "first"; Producer<String, String> producer = new KafkaProducer<>(props); // 3 发送消息 for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) { ProducerRecord<String, String> record = new ProducerRecord<>(topic, "message" + i); producer.send(record); } // 4 一定要关闭 producer,这样才会调用 interceptor 的 close 方法 producer.close(); } }
4、测试
在 kafka 上启动消费者,然后运行客户端 java 程序。
bin/kafka-console-consumer.sh --bootstrap-server broker2:9092 --from-beginning --topic first 1501904047034,message0 1501904047225,message1 1501904047230,message2 1501904047234,message3 1501904047236,message4 1501904047240,message5 1501904047243,message6 1501904047246,message7 1501904047249,message8 1501904047252,message9