1.方法: new File(path);
我们知道根据输入的路径path的不同 ,File可以根据path的不同格式,来访问文件。那么,path的形式有几种呢?
根据源码
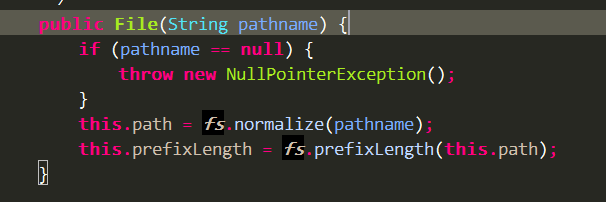

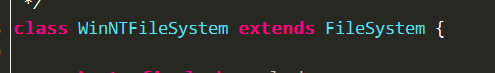
可以知道,输入的路径path其实是在类FileSystem中处理的。FileSystem是一个抽象类,所以,其实是在其实现类WinNTFileSystem中处理。
设定一个目标,我们要得到文件的绝对地址!
由如下代码
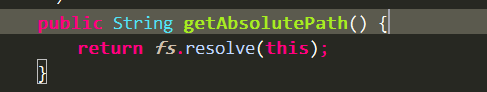
可以看出,我们是从WinNTFileSystem 的resolve得到绝对路径
@Override public String resolve(File f) { String path = f.getPath(); int pl = f.getPrefixLength(); if ((pl == 2) && (path.charAt(0) == slash)) return path; /* UNC */ if (pl == 3) return path; /* Absolute local */ if (pl == 0) return getUserPath() + slashify(path); /* Completely relative */ if (pl == 1) { /* Drive-relative */ String up = getUserPath(); String ud = getDrive(up); if (ud != null) return ud + path; return up + path; /* User dir is a UNC path */ } if (pl == 2) { /* Directory-relative */ String up = getUserPath(); String ud = getDrive(up); if ((ud != null) && path.startsWith(ud)) return up + slashify(path.substring(2)); char drive = path.charAt(0); String dir = getDriveDirectory(drive); String np; if (dir != null) { /* When resolving a directory-relative path that refers to a drive other than the current drive, insist that the caller have read permission on the result */ String p = drive + (':' + dir + slashify(path.substring(2))); SecurityManager security = System.getSecurityManager(); try { if (security != null) security.checkRead(p); } catch (SecurityException x) { /* Don't disclose the drive's directory in the exception */ throw new SecurityException("Cannot resolve path " + path); } return p; } return drive + ":" + slashify(path.substring(2)); /* fake it */ } throw new InternalError("Unresolvable path: " + path); }
我们需要两个参数,即String path = f.getPath();和int pl = f.getPrefixLength();
得到path
注意:windows 把"\"当成""处理,即 "\".length() ==1
@Override public String normalize(String path) { int n = path.length(); char slash = this.slash; char altSlash = this.altSlash; char prev = 0; for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) { char c = path.charAt(i); if (c == altSlash) // 1:包含“/” return normalize(path, n, (prev == slash) ? i - 1 : i); if ((c == slash) && (prev == slash) && (i > 1)) /:2:包含 "",并且"\",并且i>1 return normalize(path, n, i - 1); if ((c == ':') && (i > 1)) //3:包含 ":",并且i>1 return normalize(path, n, 0); prev = c; } if (prev == slash) return normalize(path, n, n - 1); return path; //4:若是绝对路径,则直接返回绝对路径
//5:"\" 或 "" 开头,直接返回 }
/* Normalize the given pathname, whose length is len, starting at the given offset; everything before this offset is already normal. */ private String normalize(String path, int len, int off) { if (len == 0) return path; if (off < 3) off = 0; /* Avoid fencepost cases with UNC pathnames */ int src; char slash = this.slash; StringBuffer sb = new StringBuffer(len); if (off == 0) { /* Complete normalization, including prefix */ src = normalizePrefix(path, len, sb); } else { /* Partial normalization */ src = off; sb.append(path.substring(0, off)); } /* Remove redundant slashes from the remainder of the path, forcing all slashes into the preferred slash */ while (src < len) { char c = path.charAt(src++); if (isSlash(c)) { while ((src < len) && isSlash(path.charAt(src))) src++; if (src == len) { /* Check for trailing separator */ int sn = sb.length(); if ((sn == 2) && (sb.charAt(1) == ':')) { /* "z:\" */ sb.append(slash); break; } if (sn == 0) { /* "\" */ sb.append(slash); break; } if ((sn == 1) && (isSlash(sb.charAt(0)))) { /* "\\" is not collapsed to "\" because "\\" marks the beginning of a UNC pathname. Even though it is not, by itself, a valid UNC pathname, we leave it as is in order to be consistent with the win32 APIs, which treat this case as an invalid UNC pathname rather than as an alias for the root directory of the current drive. */ sb.append(slash); break; } /* Path does not denote a root directory, so do not append trailing slash */ break; } else { sb.append(slash); } } else { sb.append(c); } } String rv = sb.toString(); return rv; }
路径类型的分类:
@Override public int prefixLength(String path) { char slash = this.slash; int n = path.length(); if (n == 0) return 0; char c0 = path.charAt(0); char c1 = (n > 1) ? path.charAt(1) : 0; if (c0 == slash) { if (c1 == slash) return 2; /* Absolute UNC pathname "\\foo" */ UNC的绝对路径 return 1; /* Drive-relative "\foo" */ 与驱动盘相对路径 } if (isLetter(c0) && (c1 == ':')) { if ((n > 2) && (path.charAt(2) == slash)) return 3; /* Absolute local pathname "z:\foo" */ 本地绝对路径 return 2; /* Directory-relative "z:foo" */ 目录相对路径 } return 0; /* Completely relative */ 相对路径 }
File(path)各种输入的path 及其 绝对路径
| 输入的path | /long | lo/ng | /long | long/k | long | D:JACKOK | \long(或者long) | //long |
| this.path | long | lo g | X非法输入 | longk | long | D:JACKOK | long | \long |
| this.PrefixLength | 1 | 0 | X | 0 | 0 | 3 | 1 | 2 |
| 相关类型 | 盘相关 | 项目路径相关 | 项目路径相关 | 项目路径相关 | 完全绝对路径 | 盘相关 | ||
| absolutePath | D:long | D:javaTestlong | X | D:javaTestlongk | D:javaTestlong | D:JACKOK | D:long | \long |
总结: 1:输入path 以'/' 或者 ’\‘ 开头的 ,是以项目所在的硬盘位基础路径
2:输入path 以 字母开头 的,是以项目的路径为基础路径 即: System.getProperty("user.dir")
3.输入绝对路径的,就是以该绝对路径做为路径咯