nodeName和nodeValue属性
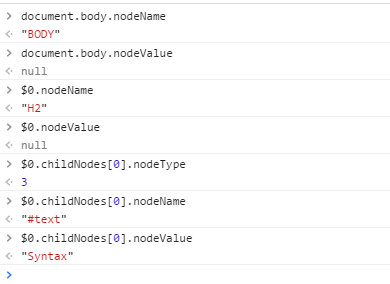
对于element节点而言,nodeName是标签名,nodeValue是null;而对于textNode节点而言,nodeName是#Text,nodeVlue是内部字符串。譬如:
node关系:
父子关系:firstChild, lastChild, parentNode
兄弟关系:nextSibling, previousSibling
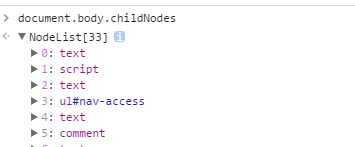
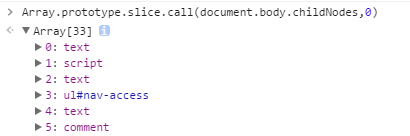
childNodes的缺陷:element.childNodes通常会把标签之间的换行或是空格当做一个TextNode节点,比如:
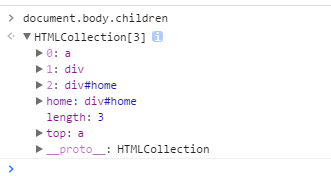
children属性
children似乎可以解决空白符解释问题,但是它只包含元素的子节点中那些也是元素的节点,换而言之,必须要有标签包含才能被识别成children。遗憾的是,Firefox却不支持children属性。
element.childNodes返回的是一个NodeList的数据,不是Array类型。虽然二者都可以使用[index]方式访问内部元素,也都拥有length属性,而且NodeList还拥有item(index)方法。Array.prototype所拥有的数组方法,对于NodeList而言并不适用。但是Array.prototype.slice()方法可以通过回调的方式把NodeList数据变为一个Array类型的数据。
以上方法之所以可以使用,而且对HTMLCollection数据类型也同样使用。MDN上是这样描述的:
slice method can also be called to convert Array-like objects / collections to a new Array.
然而,对于IE浏览器而言,以上方法并不适用,需要通过很原始的方式,逐个把NodeList的内部元素push到一个新的Array里面,然后返回整个数组即可。
function convertToArray(nodes){
var array = null;
try {
array = Array.prototype.alice.call(nodes, 0);//针对非IE浏览器
} catch (ex) {
array = new Array();
for (var i=0, len = nodes.length; i < len; i++) {
array.push(nodes[i]);
}
}
return array;
}
要注意,NodeList是一种类数组对象,它实际上是基于DOM结构动态执行查询的结果。其length属性表示的是访问NodeList的那一刻,其中包含的节点数量。
HTMLCollection与NodeList的异同