为了更好地探讨Netty的内存模型,后面会用到,这里我还是决定跟大家一起看下ThreadLocal和FastThreadLocal的源码,有的时候我们在看源码的时候会一层层的遇到很多之前没有看过的内容,我觉得有的时候为了更好地理解大牛的思想,还是去跟一下源码比较好。ThreadLocal我想大家应该不陌生,这是面试的时候的必考内容,比如说ThreadLocal为什么线程安全?或者什么需要注意什么问题?为什么会出现内存泄漏?等等问题。那这里我们就一起来看下吧。也算是拓展内容了。
先贴一个模型图,方便对于源码的理解。
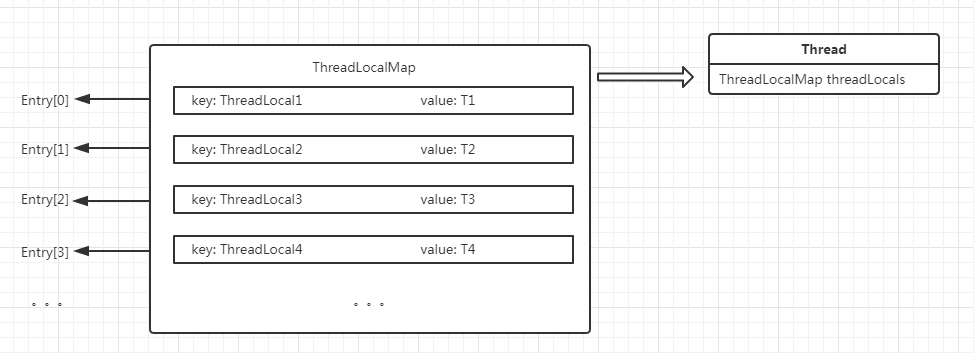
不知道画成这样大家能不能理解,大体的意思就是Thread中有一个成员变量是 ThreadLocal.ThreadLocalMap threadLocals = null ; ThreadLocalMap 是 ThreadLocal的内部类,这个Map的结构就像HashMap,是一个Entry数组,每个Entry的key是一个ThreadLocal。
简单说了一下,我们来看源码,就看下这个 ThreadLocalMap。
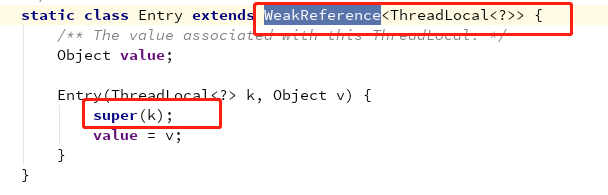
这里有一个很重要的点就是 这里,构造的这个Entry 是继承于 WeakReference , Entry的key(ThreadLocal实例)作为WeakReference的referent。
ok,说到这可能有小伙伴对WeakReference 不是很熟悉,WeakReference 就是一个弱引用。没有任何其他strong reference(强引用)指向的时候, 如果这时发生GC, 那么这个对象就会被回收,不论当前的内存空间是否足够,这个对象都会被回收。如果对GC不是很了解,可以去看我的这一篇 JVM内存模型与垃圾回收 。 如果想要更加形象的理解这个 WeakReference, 可以去看 关于Java中的WeakReference。
继续看构造函数:

注释说明这个构造函数是一个懒加载,仅仅有需要的时候才会创建。 创建一个初始化16个长度的Entry数组 。 然后计算第一个key的数组下标。 创建一个Entry对象放入table。 设置大小为 1
扩容大小门槛 设置扩容大小为 16 * 2/3 = 10 ,当有10个元素时发生扩容。
这里主要是这个下标的计算,就是用ThreadLocal哈希值 & (16-1) 得到下标,相当于 ThreadLocal哈希值 % 16, 性能更好。
那么这个哈希值怎么得来的,我们看下

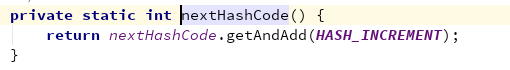
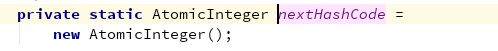
 这个东西叫 魔数:与斐波那契数列和黄金分割点有关。用于散列均匀,减少hash冲突
这个东西叫 魔数:与斐波那契数列和黄金分割点有关。用于散列均匀,减少hash冲突
那么也就是说,后面的每一个ThreadLocal的哈希值都是前一个ThreadLocal哈希值 + 0x61c88647。
我们在使用ThreadLocal最频繁的就是get方法了,我们来看下get()
public T get() { Thread t = Thread.currentThread(); // 获取当前线程 ThreadLocalMap map = getMap(t); // 获取当前线程的成员变量 threadLocals if (map != null) { ThreadLocalMap.Entry e = map.getEntry(this); // 获取当前ThreadLocal的Entry ,至于怎么获取的,我们一会再深入探讨 if (e != null) { @SuppressWarnings("unchecked") T result = (T)e.value; return result; // 取entry的value返回 } } return setInitialValue(); // 初始化map, 先说这个 }
private T setInitialValue() { T value = initialValue(); // 为子类提供重写方法 Thread t = Thread.currentThread(); ThreadLocalMap map = getMap(t); if (map != null) map.set(this, value); // 如果map不是空,那么将当前的这个ThreadLocal放入map else createMap(t, value); // 如果是空,那么创建一个map, 这个就是创建一个ThreadLocalMap,前面已经说了。 return value; }
好了,初始化说完了,除了get,常用的就是set了,我们来看下,要进入难点了
public void set(T value) { Thread t = Thread.currentThread(); ThreadLocalMap map = getMap(t); if (map != null) map.set(this, value); else createMap(t, value); }
上面这个就不说了,很简单,看下面这个
1 private void set(ThreadLocal<?> key, Object value) { 2 3 // We don't use a fast path as with get() because it is at 4 // least as common to use set() to create new entries as 5 // it is to replace existing ones, in which case, a fast 6 // path would fail more often than not. 7 8 Entry[] tab = table; // 当前Entry数组 9 int len = tab.length; // 长度 10 int i = key.threadLocalHashCode & (len-1); // 计算下标 11 // 下面就是解决hash冲突的方式,叫线性探测法。如果当前槽没有元素,直接插入元素;如果当前槽有元素,则向后寻找第一个为null的槽,放置该元素 12 for (Entry e = tab[i]; 13 e != null; 14 e = tab[i = nextIndex(i, len)]) { // 循环,等于null跳出,这个nextIndex方法就是找一个元素,也就是说,从当前ThreadLocal所在的下标开始往后循环。 15 ThreadLocal<?> k = e.get(); // 获取ThreadLocal 16 17 if (k == key) { // 如果正好循环到了与传入的ThreadLocal相等的那个实例,直接设置值,然后返回。 18 e.value = value; 19 return; 20 } 21 22 if (k == null) { // 如果遇到一个Entry的key是空的,那么将执行replaceStaleEntry(可以理解为这个位置已经无用了,可以被替换了,这里就是替换逻辑)。 为啥是空的呢?因为执行了remove()方法,remove()方法后面看。 23 replaceStaleEntry(key, value, i); 24 return; 25 } 26 } 27 28 tab[i] = new Entry(key, value); // 遇到为null的Entry,则跳出到这里,则创建一个Entry 29 int sz = ++size; // 大小 ++ 30 if (!cleanSomeSlots(i, sz) && sz >= threshold) // 查看是否需要扩容,先执行 cleanSomeSlots 清理过期数据,如果清理完成仍然达到threshold(阈值),则进行rehash扩容。 31 rehash(); 32 }
接下来就是看一下这个 replaceStaleEntry 方法,这是我觉得最难理解的部分之一,我们尽可能的去模拟一个最复杂的过程, 我简单画个图
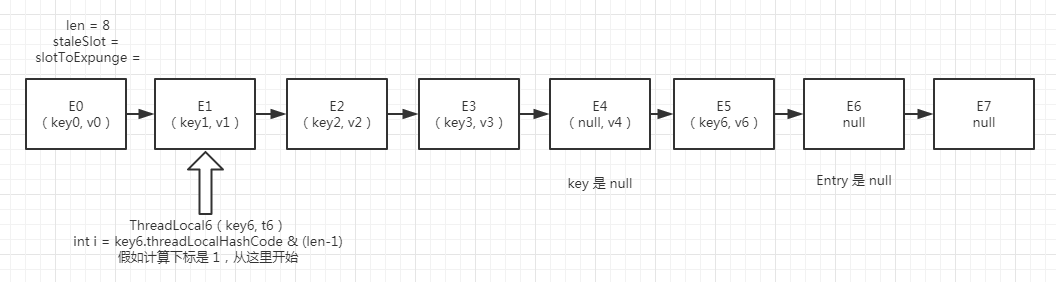
图(一)
假设上面这个是初始结构图, 我们按照上面的set方法中的线性探测法会找到E4,也就是下面这样,也就是找到了一个已经无效的Entry,就是第23行代码,然后需要进行替换 replaceStaleEntry
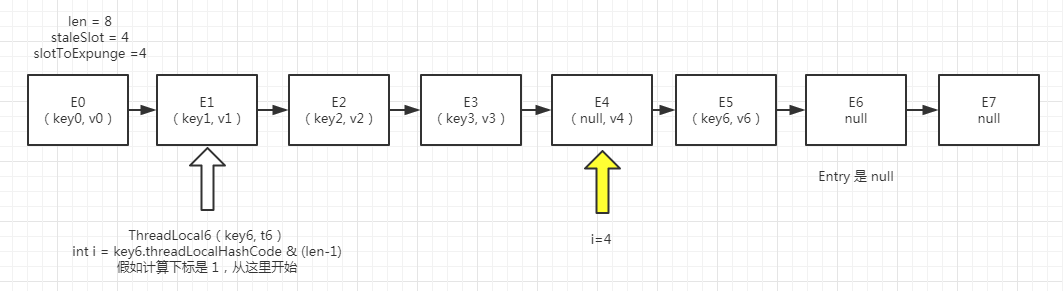
图(二)
我们继续看替换的逻辑
1 private void replaceStaleEntry(ThreadLocal<?> key, Object value, 2 int staleSlot) { 3 Entry[] tab = table; 4 int len = tab.length; // 数组长度 按照我上面的初始化图这里是8 5 Entry e; 6 7 // Back up to check for prior stale entry in current run. 8 // We clean out whole runs at a time to avoid continual 9 // incremental rehashing due to garbage collector freeing 10 // up refs in bunches (i.e., whenever the collector runs). 11 int slotToExpunge = staleSlot; // slotToExpunge = staleSlot = 4
// 往前遍历,找到第一个无效的Entry,将 slotToExpunge 设置为当前无效未被回收的索引, 走到这里,我们就假定E2已经变成无效的Entry,如图(三) 12 for (int i = prevIndex(staleSlot, len); 13 (e = tab[i]) != null; 14 i = prevIndex(i, len)) 15 if (e.get() == null) 16 slotToExpunge = i; 17 18 // Find either the key or trailing null slot of run, whichever 19 // occurs first 20 for (int i = nextIndex(staleSlot, len); // 向后遍历,找到第一个无效或者相等的位置 21 (e = tab[i]) != null; 22 i = nextIndex(i, len)) { 23 ThreadLocal<?> k = e.get(); 24 25 // If we find key, then we need to swap it 26 // with the stale entry to maintain hash table order. 27 // The newly stale slot, or any other stale slot 28 // encountered above it, can then be sent to expungeStaleEntry 29 // to remove or rehash all of the other entries in run. 30 if (k == key) { // 如果当前的k 和 传入的 key(ThreadLocal实例)是相等的 31 e.value = value; // 那么直接覆盖新值 32 33 tab[i] = tab[staleSlot]; // 然后将两个位置的Entry互换, 如图(三) 34 tab[staleSlot] = e; 35 36 // Start expunge at preceding stale entry if it exists 37 if (slotToExpunge == staleSlot) // 当前slotToExpunge = 2 staleSlot = 4 不会进入 如果待回收的槽索引就是当前的无效索引,则设置 slotToExpunge = i 38 slotToExpunge = i; 39 cleanSomeSlots(expungeStaleEntry(slotToExpunge), len); 40 return; 41 } 42 43 // If we didn't find stale entry on backward scan, the 44 // first stale entry seen while scanning for key is the 45 // first still present in the run. 46 if (k == null && slotToExpunge == staleSlot) // 如果 "k==null && 待回收的位置索引就是当前的无效索引",则设置 slotToExpunge = i, 也就是说往前遍历并未找到一个无效的Entry 47 slotToExpunge = i; 48 } 49 50 // If key not found, put new entry in stale slot 51 tab[staleSlot].value = null; // 置空当前的这个entry的value 帮助GC 52 tab[staleSlot] = new Entry(key, value); // 创建一个新的Entry放在这个位置上 53 54 // If there are any other stale entries in run, expunge them 55 if (slotToExpunge != staleSlot) // 如果不相等,那么就清理无效的entry 56 cleanSomeSlots(expungeStaleEntry(slotToExpunge), len); 57 }
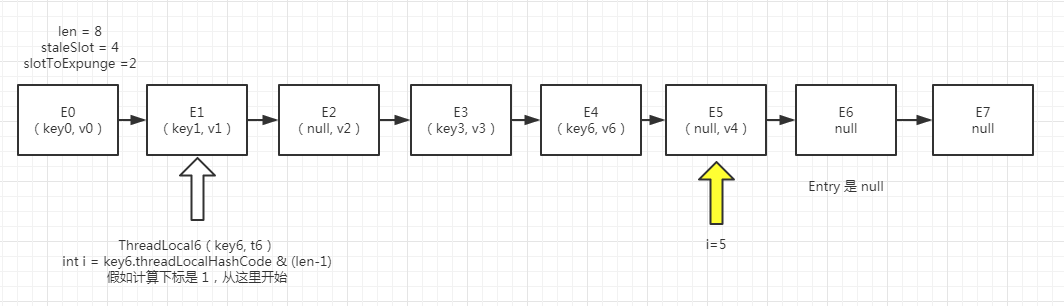
图(三)
这样,下一次查找key6根据线性探测法,就会与hash后的位置更近了一步,并且将无效的entry进行了后移
我们再假如 replaceStaleEntry 第 37 行代码是相等的,那么将进入一个 cleanSomeSlots(expungeStaleEntry(slotToExpunge), len) 这段代码
刚刚进入expungeStaleEntry应该是这样的,如图(四)
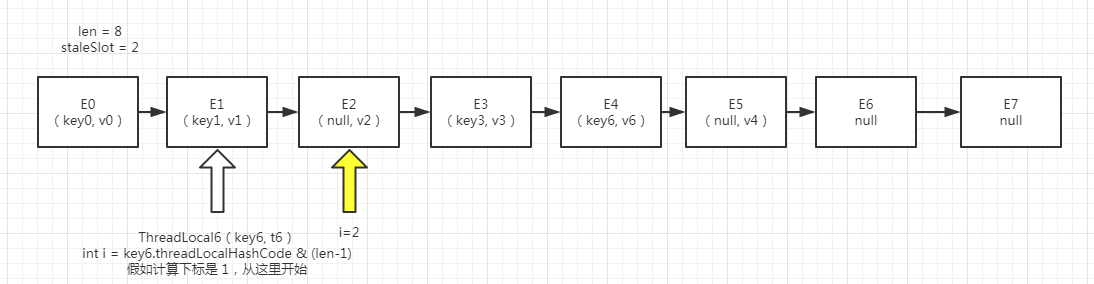
图(四)
看下代码
1 private int expungeStaleEntry(int staleSlot) { 2 Entry[] tab = table; 3 int len = tab.length; 4 5 // expunge entry at staleSlot 6 tab[staleSlot].value = null; // 将2的位置的entry的value设为null 帮助GC 7 tab[staleSlot] = null; // 将2槽位设置为null 8 size--; 9 10 // Rehash until we encounter null 11 Entry e; 12 int i; 13 for (i = nextIndex(staleSlot, len); // 从 3 开始往后遍历, 14 (e = tab[i]) != null; 15 i = nextIndex(i, len)) { 16 ThreadLocal<?> k = e.get(); 17 if (k == null) { // 找到无效的entry 设置为 null 18 e.value = null; 19 tab[i] = null; 20 size--; 21 } else { 22 int h = k.threadLocalHashCode & (len - 1); // 找到有有效的设置计算hash值,这里我们如图(四), 我们假设key3的hash 其实应该在 E2 ,之所以在E3是因为hash冲突。 23 if (h != i) { // 那么现在 h = 2 , i = 3 不相等 24 tab[i] = null; // 将 3 的entry 设置为空 25 26 // Unlike Knuth 6.4 Algorithm R, we must scan until 27 // null because multiple entries could have been stale. 28 while (tab[h] != null) // 不断遍历,直到找到一个entry = null 的位置 29 h = nextIndex(h, len); 30 tab[h] = e; // 将原本 3 位置的entry 设置到 新位置上面,运行完成后,变成如图(五) 31 } 32 } 33 } 34 return i; 35 }

图(五)
接下来进入cleanSomeSlots方法
1 private boolean cleanSomeSlots(int i, int n) { 2 boolean removed = false; 3 Entry[] tab = table; 4 int len = tab.length; 5 do { 6 i = nextIndex(i, len); 7 Entry e = tab[i]; 8 if (e != null && e.get() == null) { 9 n = len; 10 removed = true; 11 i = expungeStaleEntry(i); // 尝试回收或者rehash"i到i之后的第一个Entry为null的索引(即返回值)之间"的Entry数据, 就是执行几次上面的那个过程,进行数据整理。 12 } 13 } while ( (n >>>= 1) != 0); // 这里是重点, 因为我的n=8,不断右移 1位 ,直到成为0 , 也就是 8/2/2/2 移动三次 ,当第四次的时候 n = 0,就会结束循环 14 return removed; 15 }
说道这里,set算是说完了,我们现在看get方法就很简单了。
1 private Entry getEntry(ThreadLocal<?> key) { 2 int i = key.threadLocalHashCode & (table.length - 1); // 获取hash槽位 3 Entry e = table[i]; 4 if (e != null && e.get() == key) // 判断当前是否已经无效,如果有效并且key相等直接返回,没有发生hash冲突 5 return e; 6 else 7 return getEntryAfterMiss(key, i, e); // 无效或者发生hash冲突进入这个方法 8 }
1 private Entry getEntryAfterMiss(ThreadLocal<?> key, int i, Entry e) { 2 Entry[] tab = table; 3 int len = tab.length; 4 5 while (e != null) { 6 ThreadLocal<?> k = e.get(); 7 if (k == key) // 线性探测, 如果key相等,表示找到了,直接返回 8 return e; 9 if (k == null) // key无效, 则整理数据 10 expungeStaleEntry(i); 11 else 12 i = nextIndex(i, len); // 循环下一个 13 e = tab[i]; 14 } 15 return null; // 没找到返回null 16 }
看下remove
1 private void remove(ThreadLocal<?> key) { 2 Entry[] tab = table; 3 int len = tab.length; 4 int i = key.threadLocalHashCode & (len-1); 5 for (Entry e = tab[i]; 6 e != null; 7 e = tab[i = nextIndex(i, len)]) { 8 if (e.get() == key) { // 线性探测 找到那个相等的key对应的位置 9 e.clear(); //ThreadLocal置为null除 ,也就是entry的key = null 10 expungeStaleEntry(i); // 再次尝试整理数据 11 return; 12 } 13 } 14 }
看完之后大家有没有想过那个问题,为什么一定要调用remove方法呢?如果不调用这个方法,也就不会出现无效数据,也就不会发生回收,所以有可能会出现内存泄露。
接下来就是扩容的方式:
1 private void rehash() { 2 expungeStaleEntries(); // 回收所有无效的entry, 如果回收后达不到下面的条件,则无需扩容 3 4 // Use lower threshold for doubling to avoid hysteresis 5 if (size >= threshold - threshold / 4) // 扩容条件 len * 2/3 * 3/4 = len * 1/2 = 8 6 resize(); 7 }
1 private void resize() { 2 Entry[] oldTab = table; 3 int oldLen = oldTab.length; 4 int newLen = oldLen * 2; // 扩容到 2 倍大小 5 Entry[] newTab = new Entry[newLen]; // 新new数组 6 int count = 0; 7 8 for (int j = 0; j < oldLen; ++j) { 9 Entry e = oldTab[j]; 10 if (e != null) { 11 ThreadLocal<?> k = e.get(); 12 if (k == null) { 13 e.value = null; // Help the GC 14 } else { 15 int h = k.threadLocalHashCode & (newLen - 1); // 把老的数据重新根据新的长度进行计算下标 16 while (newTab[h] != null) 17 h = nextIndex(h, newLen); 18 newTab[h] = e; // 赋值 19 count++; 20 } 21 } 22 } 23 24 setThreshold(newLen); // 设置新的阈值 25 size = count; 26 table = newTab; 27 }
只要看懂了那个set方法,剩下的看起来都很轻松的
下一节探讨Netty重写的FastThreadLocal。